| Citation: | Yantao Luo, Yunqiang Yuan, Zhidong Teng. ANALYSIS OF A DEGENERATED DIFFUSION SVEQIRV EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH GENERAL INCIDENCE IN A SPACE HETEROGENEOUS ENVIRONMENT[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(5): 2704-2732. doi: 10.11948/20230346 |
ANALYSIS OF A DEGENERATED DIFFUSION SVEQIRV EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH GENERAL INCIDENCE IN A SPACE HETEROGENEOUS ENVIRONMENT
-
Abstract
Considering the comprehensive impact of vaccination, quarantine and spatial heterogeneity on diseases dynamics, we formulates an SVEQIRV model with degenerate diffusion. Firstly, we discuss the well-posedness of the model solution. Then, we analyze the dynamic properties of model by using the semigroup theory and the global exponential attractor theory. We use the threshold feature $\lambda^{*}$ which is the principal eigenvalue of the eigenvalue problem associated with the linearized system at the disease free equilibrium, to describe the transmission dynamics of epidemics. The results show that the disease-free equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable when $\lambda^{*}<0$ and the system is uniformly persistent when $\lambda^{*}>0$. Finally, some numerical simulations and the sensitivity analysis are conducted to visualize the theoretical results and the effect of vaccination rate on disease dynamics.
-

-
References
[1] A. Alshehri and M. El. Hajji, Mathematical study for Zika virus transmission with general incidence rate, AIMS Math., 7(4), 7117–7142. doi: 10.3934/math.2022397 [2] X. An and X. Song, A spatial SIS model in heterogeneous environments with vary advective rate, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2021, 18(5), 5449–5477. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021276 [3] S. Annas, M. I. Pratama, M. Rifandi, et al., Stability analysis and numerical simulation of SEIR model for pandemic COVID-19 spread in Indonesia, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2020, 139, 110072. [4] E. Avila-Vales and Á. G. C. Pérez, Dynamics of a reaction–diffusion SIRS model with general incidence rate in a heterogeneous environment, Z. Angew. Math. Phys., 2022, 73(1), 9. doi: 10.1007/s00033-021-01645-0 [5] Y. Cai, X. Lian, Z. Peng, et al., Spatiotemporal transmission dynamics for influenza disease in a heterogenous environment, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2019, 46, 178–194. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2018.09.006 [6] A. d'Onofrio, Globally stable vaccine-induced eradication of horizontally and vertically transmitted infectious diseases with periodic contact rates and disease-dependent demographic factors in the population, Appl. Math. Comput., 2003, 140(2–3), 537–547. [7] Z. Du and R. Peng, A priori $L^{\infty}$ estimates for solutions of a class of reaction-diffusion systems, J. Math. Biol, 2016, 72(6), 1429–1439. doi: 10.1007/s00285-015-0914-z CrossRef $L^{\infty}$ estimates for solutions of a class of reaction-diffusion systems" target="_blank">Google Scholar
[8] L. Duan, L. Huang and C. Huang, Spatial dynamics of a diffusive SIRI model with distinct dispersal rates and heterogeneous environment, Commun. Pure Appl. Anal., 2021, 20(10), 3539, 3560. [9] M. El. Hajji and A. H. Albargi, A mathematical investigation of an "SVEIR" epidemic model for the measles transmission, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2022, 19, 2853–2875. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022131 [10] H. F. Huo, K. D. Cao and H. Xiang, Modelling the effects of the vaccination on seasonal influenza in Gansu, China, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2022, 12(1), 407–435. [11] Q. Ji, R. Wu and Z. Feng, Dynamics of the nonlocal diffusive vector-disease model with delay and spatial heterogeneity, Z. Angew. Math. Phys., 2023, 74(5), 183. doi: 10.1007/s00033-023-02077-8 [12] J. Jiao, Z. Liu and S. Cai, Dynamics of an SEIR model with infectivity in incubation period and homestead-isolation on the susceptible, Appl. Math. Lett., 2020, 107, 106442. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2020.106442 [13] S. Kejriwal, S. Sheth and P. S. Silpa, Attaining herd immunity to a new infectious disease through multi-stage policies incentivising voluntary vaccination, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2022, 154, 111710. [14] W. O. Kermack and A. G. McKendrick, A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics, Proc. Roy. Soc. London Ser. A, 1927, 115(772), 700–721. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1927.0118 [15] A. Kumar and P. K. Srivastava, Vaccination and treatment as control interventions in an infectious disease model with their cost optimization, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2017, 44, 334–343. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2016.08.005 [16] A. Kumar, P. K. Srivastava and R. P. Gupta, Nonlinear dynamics of infectious diseases via information-induced vaccination and saturated treatment, Math. Comput. Simu., 2019, 157, 77–99. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2018.09.024 [17] Q. Li, M. C. Li, L. Lv, et al., A new prediction model of infectious diseases with vaccination strategies based on evolutionary game theory, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2017, 104, 51–60. [18] Y. Li, H. Zhao and K. Wang, Dynamics of an impulsive reaction-diffusion mosquitoes model with multiple control measures, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2023, 20(1), 775–806. [19] Y. Luo, L. Zhang, Z. Teng, et al., Analysis of a general multi-group reaction-diffusion epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and temporary acquired immunity, Math. Comput. Simu., 2021, 182, 428–455. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2020.11.002 [20] A. J. May and E. J. A. Vales, Global dynamics of a two-strain flu model with a single vaccination and general incidence rate, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 17(6), 7862–7891. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020400 [21] F. Ndaïrou, M. Khalighi and L. Lahti, Ebola epidemic model with dynamic population and memory, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2023, 170, 113361. [22] R. D. Nussbaum, Eigenvectors of nonlinear positive operators and the linear Krein-Rutman theorem, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006, 309–330. [23] A. Ouakka, A. El. Azzouzi and Z. Hammouch, Global dynamic behavior of a vaccination–age SVIR model with treatment and general nonlinear incidence rate, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2023, 422, 114848. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2022.114848 [24] C. V. Pao, Nonlinear Parabolic and Elliptic Equations, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. [25] R. Potluri, A. Kumar, V. Oriol-Mathieu, et al., Model-based evaluation of the impact of prophylactic vaccination applied to Ebola epidemics in Sierra Leone and Democratic Republic of Congo, BMC Infect. Dis., 2022, 22(1), 769. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07723-6 [26] M. H. Protter, H. F. Weinberger, Maximum Principles in Differential Equations, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. [27] Y. Shan, X. Wu and J. Gao, Analysis of a degenerate reaction-diffusion host-pathogen model with general incidence rate, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2021, 502(2), 125256. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2021.125256 [28] Y. Sheng, J. A. Cui and S. Guo, The modeling and analysis of the COVID-19 pandemic with vaccination and isolation: A case study of Italy, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2023, 20(3), 5966–5992. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023258 [29] H. L. Smith, Monotone Dynamical Systems: An Introduction to the Theory of Competitive and Cooperative Systems, American Mathematical Soc., 1995. [30] P. Song, Y. Lou and Y. Xiao, A spatial SEIRS reaction-diffusion model in heterogeneous environment, J. Diff. Eqs., 2019, 267(9), 5084–5114. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2019.05.022 [31] C. Tadmon, B. Tsanou and A. F. Feukouo. Avian–human influenza epidemic model with diffusion, nonlocal delay and spatial homogeneous environment, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2022, 67, 103615. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2022.103615 [32] H. R. Thieme, Convergence results and a Poincaré-Bendixson trichotomy for asymptotically autonomous differential equations, J. Math. Biol., 1992, 30(7), 755–763. [33] A. Viguerie, A. Veneziani, G. Lorenzo, et al., Diffusion–reaction compartmental models formulated in a continuum mechanics framework: Application to COVID-19, mathematical analysis, and numerical study, Comput. Mech., 2020, 66, 1131–1152. doi: 10.1007/s00466-020-01888-0 [34] I. I. Vrabie, Co-Semigroups and Applications, Elsevier, 2003. [35] J. Wang and B. Dai, Qualitative analysis on a reaction-diffusion host-pathogen model with incubation period and nonlinear incidence rate, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2022, 514(2), 126322. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2022.126322 [36] J. Wang and H. Lu, Dynamics and profiles of a degenerated reaction–diffusion host-pathogen model with apparent and inapparent infection period, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2023, 107318. [37] J. Wang, W. Wu and T. Kuniya, Analysis of a degenerated reaction–diffusion cholera model with spatial heterogeneity and stabilized total humans, Math. Comput. Simulation, 2022, 198, 151–171. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2022.02.026 [38] J. Wang, F. Xie and T. Kuniya, Analysis of a reaction-diffusion cholera epidemic model in a spatially heterogeneous environment, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2020, 80, 104951. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2019.104951 [39] S. Wang, Introduction to Sobolev Spaces and Partial Differential Equations, Beijing: Science Press, 2009. [40] R. Wu and X. Q. Zhao, A reaction–diffusion model of vector-borne disease with periodic delays, J. Nonlinear Sci., 2019, 29, 29–64. doi: 10.1007/s00332-018-9475-9 [41] Y. Zha and W. Jiang, Global dynamics and asymptotic profiles for a degenerate Dengue fever model in heterogeneous environment, J. Diff. Eqs., 2023, 348, 278–319. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2022.12.012 [42] F. Zhang, W. Cui, Y. Dai, et al., Bifurcations of an SIRS epidemic model with a general saturated incidence rate, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2022, 19(11), 10710–10730. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022501 [43] J. Zhang, P. E. Kloeden, M. Yang, et al., Global exponential $\kappa-$dissipative semigroups and exponential attraction, Discrete Contin. Dynam. Systems, 2017, 37, 3487–3502. $\kappa-$dissipative semigroups and exponential attraction" target="_blank">Google Scholar
[44] T. Zheng, L. Nie, H. Zhu, et al., Role of seasonality and spatial heterogeneous in the transmission dynamics of avian influenza, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2022, 67, 103567. [45] C. C. Zhu and J. Zhu, Dynamic analysis of a delayed COVID-19 epidemic with home quarantine in temporal-spatial heterogeneous via global exponential attractor method, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2021, 143, 110546. [46] C. C. Zhu, J. Zhu and X. L. Liu, Influence of spatial heterogeneous environment on long-term dynamics of a reaction-diffusion SVIR epidemic model with relapse, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2019, 16, 5897–5922. -
-
-
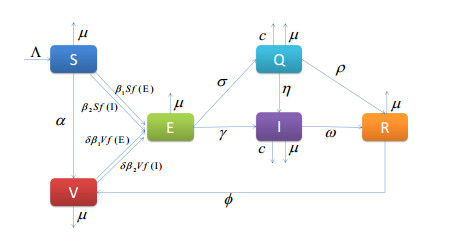
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram for the disease transmission
-
Figure 2.
The time evolution of the extinction of the system (2.1) with the constant coefficient.
-
Figure 3.
The time evolution of the uniform persistence of the system (2.1) with the constant coefficient.
-
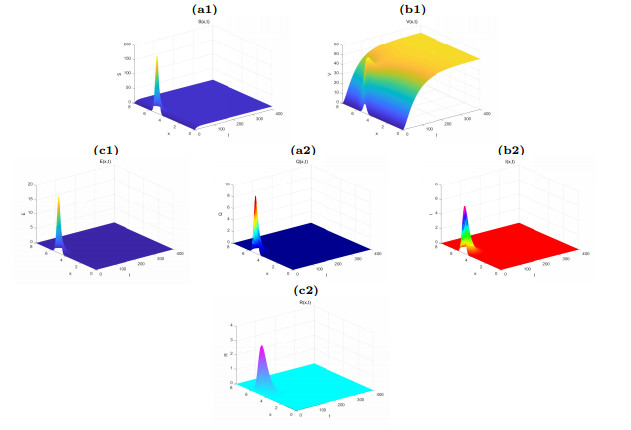
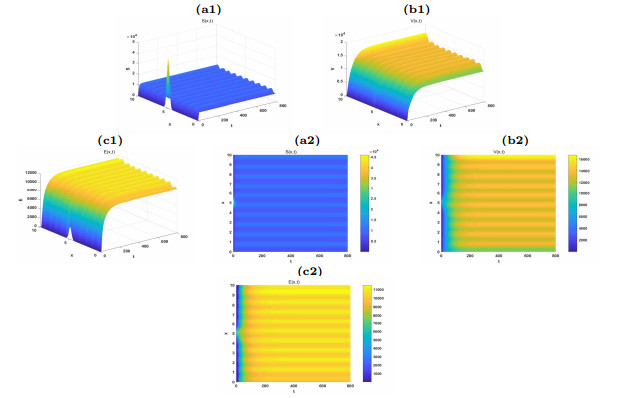
Figure 4.
The time evolution of the extinction of the system (2.1).
-
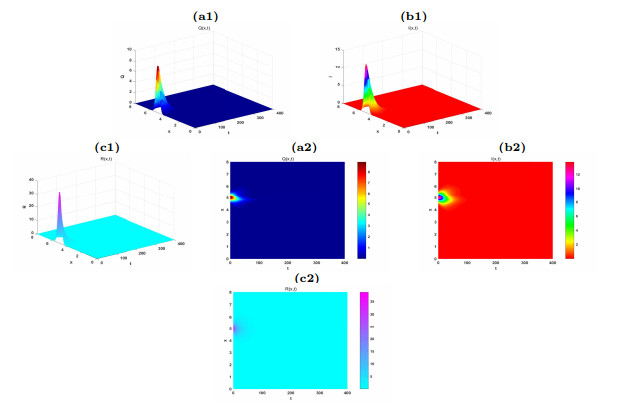
Figure 5.
The time evolution of the extinction of the system (2.1).
-
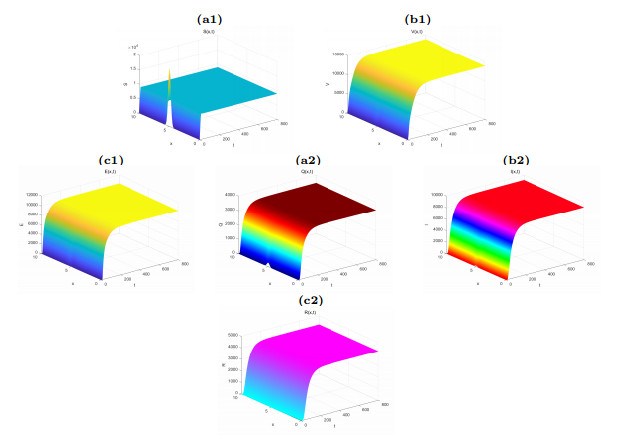
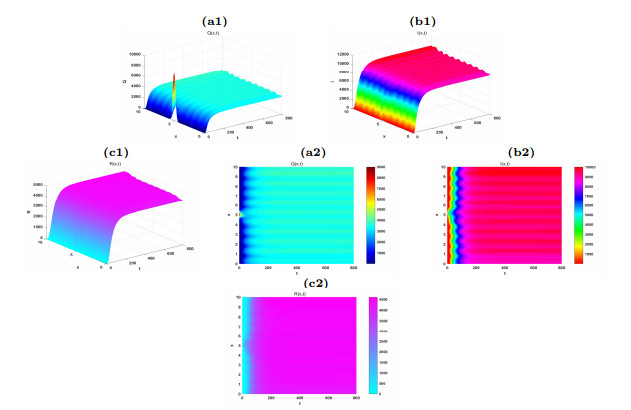
Figure 6.
The time evolution of the uniform persistence of the system (2.1).
-
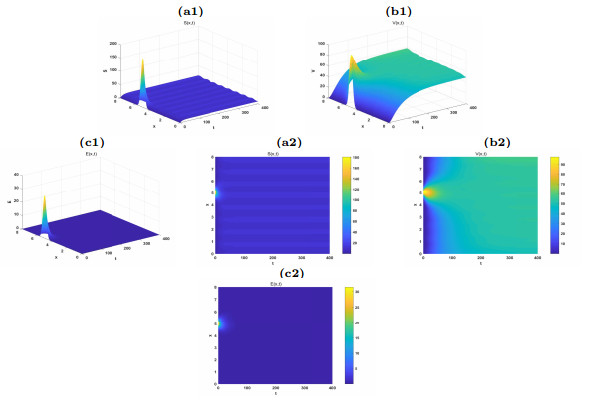
Figure 7.
The time evolution of the uniform persistence of the system (2.1).
-
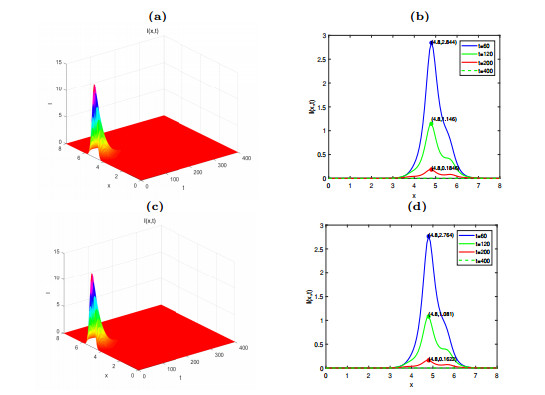
Figure 8.
The effect of different levels of vaccination rates on the number of
$ I(x, t) $ -
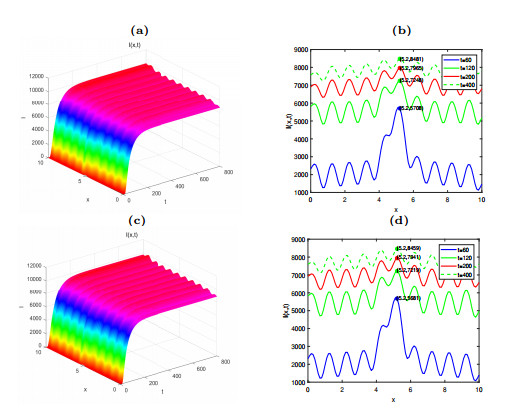
Figure 9.
The effect of different levels of vaccination rates on the number of
$ I(x, t) $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: