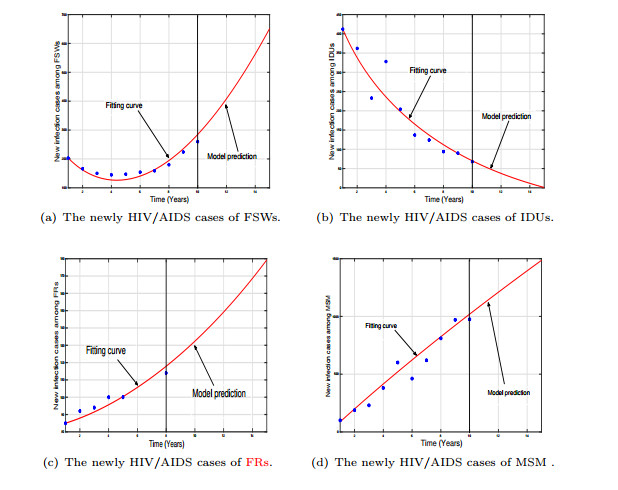
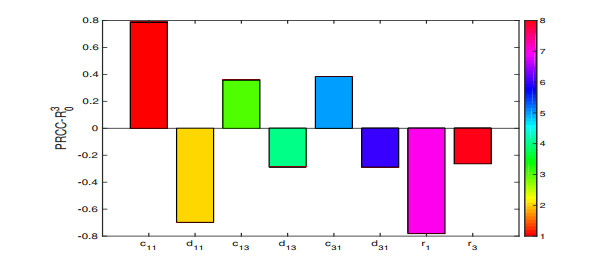
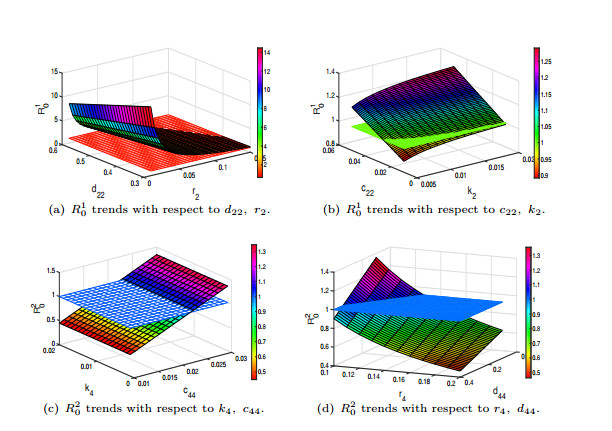
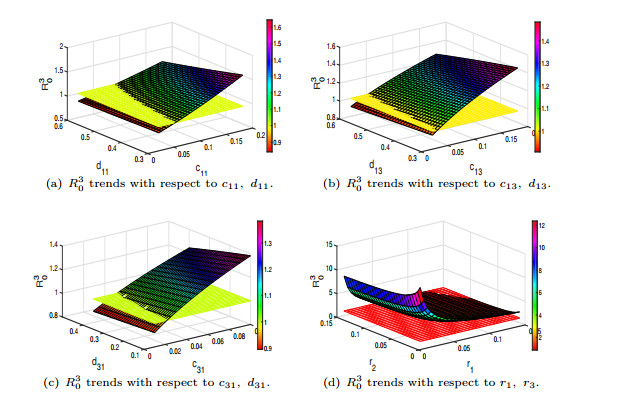
|
[1]
|
C. Cai, L. Wang, W. Guo, et al., The description of time-spatial distribution of the foreigners with HIV/AIDS in China, Chin J. AIDS. STD., 2015, 21(2), 757-761.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
Y. Cai, X. Chen, et al., Characteristics of HIV infections in adult females in Guangzhou, 2011-2017, Modern Preventive Medicine, 2019, 46(4), 2058-2061.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
W. Cheng, F. Zhong, F. Wen, et al., Investigation of HIV and syphilis infection and AIDS-related behaviors among money boys, in Guangzhou, China, Chin Prev. Med., 2010, 44(10), 1027-1031.
Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
Chinese People's Congress, Regulations of the People's Republic of China on the Entry and Exit Administration of Foreigners, 2011. Available from: http://www.npc.gov.cn.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
J. Fang, G. Lin and H. Wan, Analysis of a state-structured dengue model, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2018, 25(8), 115-128.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
Y. Fan and W. Geng, Advances in the incubation period of AIDS and its influencing factors, Chin J. Infect. Control., 2012, 11(2), 396-400.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
X. Feng, Guangzhou's AIDS status: low MSM group infection rate is high and student infection rate is 0.09%, 2016. Available from: http://gd.sina.com.cn/news/m/2016-11-28/detail-ifxyawmm3593818.shtml?from=gd_cnxh.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
Q. Feng, The large number of drug addicts in Guangzhou, only registered number over 50, 000, 2014. Available from: http://gd.people.com.cn/n/2014/1031/c123932-22777390.html.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
X. Feng, 48 percent of the total HIV/AIDS case in Guangdong province is reported from Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Dongguan city, MSM transmission increase rapidly, 2016. Available from: http://gd.sina.com.cn/dg/2016-12-01/city-dg-ifxyiayq1876894.shtml.
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
K. Gao, C. Wang, L. Chen, H. Xu and Z. Han, Analysis of the HIV/AIDS Infected Person Co-infection with Syphilis in 2011, Guangzhou, South China J. Prev. Med., 2013, 39(3), 456-459.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
Y. Guo, X. Qin, Y. Yang and Y. Zou, The analysis of epidemiological features of the HIV in Panyu, Guangzhou city from 2004 to 2013, J. Trop. Med., 2015, 15(5), 257-259.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
GD, 2004 Report on the global AIDS epidemic, 4th global report, Geneva, switzerland, 2004,
Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
Guangzhou G. C, The population of the permanence foreign residents were beyond 50000, 2016. Available from: http://guangzhou.gov.cn/special/2016/node_2927/node_2931/2016/01/05/1451965112624378.shtml.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
Guangzhou CDC, More than 40 percent of new HIV/AIDSinfection cases are due to MSM sexual transmission, 2014. Available from: http://gz.bendibao.com/news/2014122/content176016.shtml.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
Guangzhou Statistics Bureau, Guanghzou Demograhic Yearbook of 2009, 2009. Available from: http://210.72.4.52/gzStat1/chaxun/njsj.jsp.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
W. Hirsch, H. Hanisch and J. Gabril, Differential equation models of some parasitic infections: methods for the study of asymptotic behavior, Commun. Pure. Appl. Math., 1985, 38(6), 733-753. doi: 10.1002/cpa.3160380607
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
Z. Han, H. Wu, C. Liang, et al., Distribution of HIV-1 subtypes among foreign patients, in Guangzhou, between 2008 and 2010, and in 2015, Chin J. Epidemiol., 2017, 38(4), 805-809.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
H. Hethcote and J. Ark, Modeling HIV Transmission and AIDS in the United States, 2$.{nd}$ edition, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 1992.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
Z. Han, Z. Zhang, C. Liang, et al., HIV Sentinel Surveillance for drug users in Guangzhou from 1995-2008, South China J. Prev. Med., 2009, 23(9), 934-938.
Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Q. He, Y. Wang, P. Lin, Y. Liu, F. Yang, X. Fu, Y. Li, B. Sun, J. Li and X. Zhao, Potential bridges for HIV infection to men who have sex with men in Guangzhou, China, AIDS and Behavior, 2006, 10(1), 17-23.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
L. He, X. Zhu, Z. Xu and M. Deng, An investigation of HIV infection incidence and risk factors among 520 men who have sex with men in Guangzhou city, J. Diagn Ther Dermato-Venereol, 2017, 24(7), 207-211.
Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
B. Jr and W. Tan, A stochastic model of the HIV epidemic and the HIV infection distribution in a homosexual population, Math. Biosci., 1993, 113 (1), 115-143. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(93)90011-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
Y. Li, J. Cheng and J. Lou, The persistence of HIV-1 spreading in MSM population in China, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2019, 9(1), 245-260.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
X. Li, Guangzhou: the number of students with HIV/AIDS fell 8 percent in the first 10 months, Nanfang Daily China[N], 2017, 11-28.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
H. Liang, D. Ye, K. Tang, M. Huang and Y. Tan, Investigation of intervention effects on the cognition on STD/AIDS of sex workers, Modern Preventive Medicine, 2008, 35 (8), 93-95.
Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
S. Marino, I. Hogue, C. Ray, et al., A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology, J. Theoret. Biol., 2008, 254 (1), 178-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.04.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
Z. Mukandavire and W. Garira, Sex-structured HIV/AIDS model to analyze the effects of condom use with application to Zimbabwe, J. Math. Biol., 2007, 54(5), 669-699. doi: 10.1007/s00285-006-0063-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
NCAIDS, China CDC, Update on the AIDS/STD epidemic in China and main response in control and prevention in December, 2017, Chin J. AIDS. STD., 2018, 21, S3-S7.
Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
X. Sun, Y. Xiao, Z. Peng, et al., Modelling HIV/AIDS epidemic among men who have sex with men in China, BioMed Research International, 2013, 13(5), 121-134.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
X. Sun, Y. Xiao and Z. Peng, Modelling HIV superinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2016, 13(1), 171-191.
Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
C. Sun, Y. Hsieh and P. Georgescu, A model for HIV transmission with interacting high-risk groups, Nonlinear Anal: RWA, 2018, 40(8), 170-184.
Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
T. T. Yusuf and F. Benyah, Optimal strategy for controlling the spread of HIV/ AIDS disease: a case study of South Africa, J. Biol. Dyn., 2012, 6(2), 475-494. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2011.628700
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
W. Tan and D. Zhou., Effects of Ramdomness of Risk Factors on the HIV epidemic in Homosexual populations, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1995, 55(6), 1697-1723.
Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
W. Tan and Z. Xiang, A stochastic model for the HIV epidemic in homosexual population involving age and race, Math. Comput. Modelling, 1996, 24(12), 67-105. doi: 10.1016/S0895-7177(96)00179-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
W. Tan and Z. Xiang, The state space model of the HIV epidemic with variable infection in the homosexual population, J. Statist. Planning Inference, 1999, 78(3), 71-87.
Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
H. Thieme, Persistence under relaxed point dissipativity (with application to an endemic model), SIAM J. Math. Anal., 1993, 24(2), 407-435. doi: 10.1137/0524026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
J. Wen, H. Zhang, L. Wu, L. Zhu, W. Chen and J. Lu, Characteristics of HIV/AIDS epidemic in Tianhe district of Guangzhou city, 1995-2010, J. Trop. Med., 2012, 12(2012), 1148-1149.
Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
R. Wu, HIV/AIDS infected cases in Guangzhou increased by 13 percent annually, 90 percent was through sexual transmission, 2013. Available from: http://gz.bendibao.com/news/2013121/content143351.shtml.
Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
J. Wu, The newly HIV/AIDS reported case is 678 in Dongguan, the main routes of transmission is sexual transmission, 2016. Available from: http://news.sun0769.com/dg/headnews/201612/t20161201_7055430.shtml.
Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
B. Wang, Methods for estimating the population size of high risk for AIDS used in drug users in Guangzhou city, Ph.D thesis, Public Health Institute of SYSU in Zhongshan, 2010.
Google Scholar
|
|
[41]
|
C. Wang, Application of Multiplier Method and Capture mark recapture Method in Estimating the size of Male homosexual Population in Guangzhou City, Ph.D thesis, Public Health Institute of SYSU in Zhongshan, 2009.
Google Scholar
|
|
[42]
|
L. Wang, Overview of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, scientific research and government responses in China, AIDS, 2007, 21(8), S3-S7
Google Scholar
|
|
[43]
|
F. Wang, The number of resident foreigner was 118000, the primary, second rank was Japanese, SouthKorea respectively, 2014. Available from: http://new.qq.com/cmsn/20141202003749.
Google Scholar
|
|
[44]
|
World Health Organization, 10 facts about HIV/AIDS, HIV Fact sheet No. 204 Updated July 2018, 2018. Available from: http://www.who.int/news-room/facts-in-pictures/detail/hiv-aids.
Google Scholar
|
|
[45]
|
P. Xu, K. Liu, G. Zeng and F. Lv, Effect analysis of the cancellation of immigration restrictions for foreigners with HIV/AIDS in China, Chin J. Health Policy., 2011, 18(4), 60-63.
Google Scholar
|
|
[46]
|
X. Xu, Y. Xiao and N. Wang, Modeling sexual transmission of HIV/AIDS in Jiangsu province, China, Math. Meth. Appl. Sci., 2011, 36(2), 234-248.
Google Scholar
|
|
[47]
|
X. Xiao, The number of drug addicts in Guangzhou become more younger, and the under 17 years old number is growing by 8% a year, 2014. Available from: http://static.nfapp.southcn.com/content/201703/27/c339143.html.
Google Scholar
|
|
[48]
|
W. Yang, Z. Shu, L. James and C. Sun, Global dynamics of an HIV model incorporating senior male clients, Appl. Math. Comput., 2017, 311, 203-216.
Google Scholar
|
|
[49]
|
H. Yu, Z. Li and Y. Ye, Investigation on Surveilance of HIV/AIDS in Baiyun District Guangzhou, 1991-2008, J. Trop. Med., 2008, 28(8), 852-854.
Google Scholar
|
|
[50]
|
Y. Yang, H. Zhang, X. Qin, G. Huang and Z. Li, The analysis of the prevalence of HIV epidemic in Panyu district Guangzhou from 1998 to 2009, South China J. Prev. Med., 2010, 36(10), 38-40.
Google Scholar
|
|
[51]
|
M. Zindoga, C. Chiyaka, G. Magombedze and G. Musuka, Assessing the effects of homosexual and bisexuals on the intrisic dynamics of HIV/AIDS in heterosexual settings, Math. Comput. Modelling, 2009, 49(9-10), 1869-1882. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2008.12.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[52]
|
T. Zhang and Y. Zhou, Mathematical model of transmission dynamics of human immune-deficiency virus: A case study for Yunnan, China, Appl. Math. Modelling, 2016, 40(7-8), 4859-4875. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2015.12.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[53]
|
L. Zou, S. Ruan and W. Zhang, On the sexual transmission dynamics of hepatitis B virus in China, J. Theoret. Biol., 2015, 369, 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.01.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[54]
|
F. Zhong, H. Xu, F. Qin, W. Cheng, M. Wang and L. Ling, Analysis of HIV prevalence among men who have sex with men in Guangzhou from 2000 to 2010, J. Trop. Med., 2014, 14(4), 345-348.
Google Scholar
|
|
[55]
|
Y. Zhao, F. Qin, Z. Han, et al., Incidents of HIV and HIV drug resistance among foreigners in Guangzhou city, Chin J. Public Health, 2016, 32(6), 121-129.
Google Scholar
|
|
[56]
|
H. Zhang, Z. Han, K. Gao, et al., Genotypic drug resistance analysis of HIV-1 positive foreigners in Guangzhou, Chin J. AIDS. STD., 2014, 20(4), 3385-3397.
Google Scholar
|
|
[57]
|
T. Zhang and Y. Zhou, Mathematical model of transmission dynamics of human immune deficiency virus: A case study for Yunnan, China, Appl. Math. Modelling, 2016, 40(7-8), 4859-4875. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2015.12.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[58]
|
Y. Zhang, Y. Bao, C. Li, et al., Study of HIV/syphilis infection status of commercial sex workers in 15 cities of China, Chin Prev. Med., 2011, 12(1), 387-390.
Google Scholar
|
|
[59]
|
S. Zheng, Newly HIV/AIDS reported cases are 1900 in Shenzhen before ten months, 2016. Available from: http://news.eastday.com/eastday/13news/auto/news/china/20161130/u7ai6252517.html.
Google Scholar
|





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: