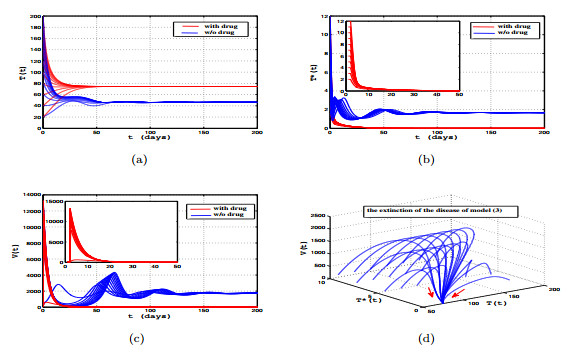
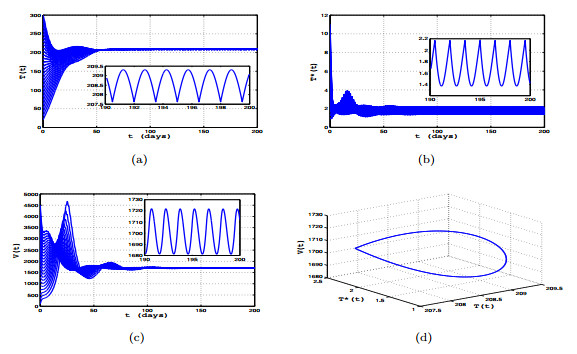
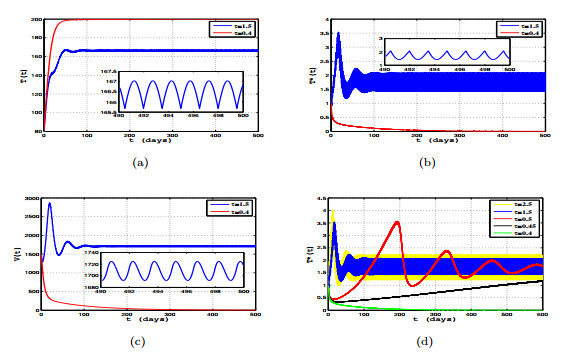
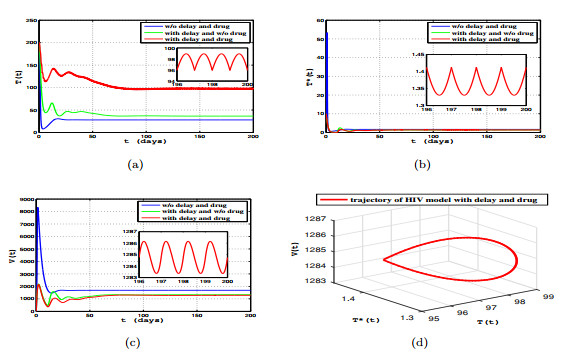
|
[1]
|
P. Aavani and L.J.S. Allen, The role of CD4 T cells in immune system activation and viral reproduction in a simple model for HIV infection,Appl. Math. Model., 2019, 75, 210-222. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.05.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
R. Arnaout, M. Nowak and D. Wodarz, HIV-1 dynamics revisited: biphasic decay by cytotoxic lymphocyte killing? Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B., 2000, 265, 1347-1354.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
D. Burg, L. Rong, A. U. Neumann and H. Dahari, Mathematical modeling of viral kinetics under immune control during primary HIV-1 infection,J. Theor. Biol., 2009, 259, 751-759. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.04.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
M. S. Ciupe, B. L. Bivort, D. M. Bortz and P.W. Nelson, Estimating kinetic parameters from HIV primary infection data through the eyes of three different mathematical models,Math. Biosci., 2006, 200, 1-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2005.12.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
J. M. Conway and A. S. Perelson, Residual viremia in treated HIV$.+$ individuals,PLoS Comput. Biol., 2016, 12(1), e1004677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004677
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
A. M. Croicu, A. M. Jarrett, N. G. Cogan and M. Y. Hussaini, Short-term antiretroviral treatment recommendations based on sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model for HIV infection of CD4(+)T cells,Bull. Math. Biol., 2017, 79(11), 2649-2671. doi: 10.1007/s11538-017-0345-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
R. V. Culshaw and S. Ruan, A delay-differential equation model of HIV infection of CD$4.+$ T-cells,Math. Biosci., 2000, 165, 27-39. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(00)00006-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
J. Danane and K. Allali, Mathematical analysis and clinical implications of an HIV Model with adaptive immunity,Comput. Math. Method Med., 2019, 2019, Article ID 7673212.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
M. Divya and M. Pitchaimani, An analysis of the delay-dependent HIV-1 protease inhibitor model,Int. J. Biomath., 2018, 11(3), Article ID 1850031.
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
A. M. Elaiw and A. D. Al Agha, Stability of a general HIV-1 reaction-diffusion model with multiple delays and immune response,Physica A, 2019, 536(15), Article ID 122593.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
K. Hattaf, N. Yousfi and A. Tridane, A delay virus dynamics model with general incidence rate,Differ. Equ. Dyn. Syst., 2014, 22, 181-190. doi: 10.1007/s12591-013-0167-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
A. V. M. Herz, S. Bonhoeffer, R. M. Anderson, R. M. May and M. A. Nowak, Viral dynamics in vivo: Limitations on estimates of intracellular delay and virus decay,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93, 7247-7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7247
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
D. D. Ho, A. U. Neumann, A. S. Perelson, W. Chen, J. M. Leonard and M. Markowitz, Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection,Nature, 1995, 373, 123-126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
P. Jacqmin, L. McFadyen and J. R. Wade, Basic PK/PD principles of drug effects in circular/proliferative systems for disease modelling,J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn., 2010, 37, 157-177. doi: 10.1007/s10928-010-9151-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
J. L. Katharine, P. G. Geoffrey and P. S. George, An estimate of the global prevalence and incidence of herpes simplex virus type 2 infection,Bull. World Health Organ., 2008, 86(10), 805-812. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.046128
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
D. E. Kirschner and G. G. Webb, Immunotherapy of HIV-1 infection,J. Biol. Syst., 1998, 6, 71-83. doi: 10.1142/S0218339098000091
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
O. Krakovska and L. M. Wahl, Optimal drug treatment regimens for HIV depend on adherence,J. Theor. Biol., 2007, 246, 499-509. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.12.038
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
V. Lakshmikantham, D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeonov, Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations,World Scientific, Singapore, 1989.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
C. Monica and M. Pitchaimani, Geometric Stability switch criteria in HIV-1 infection delay, J. Nonlinear Sci., 2019, 29(1), 163-181. doi: 10.1007/s00332-018-9481-y
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
L. F. Nie, Z. Teng and I. H. Jung, Complex dynamic behavior in a viral model with state feedback control strategies,Nonlinear Dyn., 2014, 77, 1223-1236. doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1372-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
M. A. Nowak and C. R. Bangham, Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent virues,Science, 1996, 272, 74-79. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5258.74
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
E. Numfor, Optimal treatment in a multi-strain within-host model of HIV with age structure,J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2019, 48(2), Article ID 123410.
Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
K. S. Pawelek, S. Liu, F. Pahlevani and L. Rong, A model of HIV-1 infection with two time delays: Mathematical analysis and comparison with patient data,Math. Biosci., 2012, 235, 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2011.11.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
A. S. Perelson, Modeling viral and immune system dynamics,Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2002, 2, 28-36. doi: 10.1038/nri700
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
A. S. Perelson, D. Kirschner and R. De Boer, Dynamics of HIV infection of CD4$.+$T cells,Math. Biosci., 1993, 114, 81-125. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(93)90043-A
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
A. S. Perelson and P. Nelson, Mathematical models of HIV dynamics in vivo,SIAM Review, 1999, 41, 3-44. doi: 10.1137/S0036144598335107
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
A. S. Perelson, A. Neumann, M. Markowitz, J. Leonard and D. Ho, HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span and viral generation time,Science, 1996, 271, 1582-1586. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1582
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
A. N. Phillips, Reduction of HIV concentration during acute infection: independence from a specific immune response,Science, 1996, 271, 497-499. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.497
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
L. Rong and A. S. Perelson, Asymmetric division of activated latently infected cells may explain the decay kinetics of the HIV-1 latent reservoir and intermittent viral blips,Math. Biosci., 2009, 217(1), 77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.10.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
N. Sachsenberg, A. S. Perelson, S. Yerly, G. A. Schockmel, D. Leduc, B. Hirschel and L. Perrin, Turnover of CD$4.+$ and CD$8.+$ T lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection as measured by ki-67 antigen,J. Exp. Med., 1998, 187, 1295-1303. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.8.1295
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
S. Saha, P. K. Roy and R. Smith, Modeling monocyte-derived dendritic cells as a therapeutic vaccine against HIV, J. Biol. Syst., 2018, 26(4), 579-601. doi: 10.1142/S0218339018500262
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
S. K. Sahani and Yashi, A delayed HIV infection model with apoptosis and viral loss,J. Biol. Dyn. 12(1), 2018, 1012-1034. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2018.1547427
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
E. Shamsara, Z. Afsharnezhad and S. Effati, Optimal drug control in a four-dimensional HIV infection model,Optim. Control. Appl. Meth., 2020, 41, 469-486. doi: 10.1002/oca.2555
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
R. J. Smith and L. M. Wahl, Distinct effects of protease and reverse transcriptase inhibition in an immunological model of HIV-1 infection with impulsive drug effects,Bull. Math. Biol., 2004, 66, 1259-1283. doi: 10.1016/j.bulm.2003.12.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
R. J. Smith and L. M. Wahl, Drug resistance in an immunological model of HIV-1 infection with impulsive drug effects,Bull. Math. Biol., 2005, 67, 783–813. doi: 10.1016/j.bulm.2004.10.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
Z. Teng and L. Chen, The positive periodic solutions of periodic Kolmogorov type systems with delays,Acta Math. Appl. Sci., 1999, 22, 456-464.
Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
W. Wang and X. Zhao, Threshold dynamics for compartmental epidemic models in periodic environments,J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2008, 20, 699-717. doi: 10.1007/s10884-008-9111-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, F. Brauer and J. M. Heffernan, Viral dynamics model with CTL immune response incorporating antiretroviral therapy,J. Math. Biol., 2013, 67, 901-934. doi: 10.1007/s00285-012-0580-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
D. Wodarz, Killer Cell Dynamics: Mathematical and Computational Approaches to Immunology,Springer, New York, 2007.
Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
D. Wodarz and M. Nowak, Specific therapies could lead to long-term immunological control of HIV,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1999, 96, 464-469.
Google Scholar
|
|
[41]
|
World health Organization, Global health sector strategy on HIV/AIDS 2011-2015,World Health Organization Press, Switzerland, 2011.
Google Scholar
|
|
[42]
|
World health Organization main website, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids (accessed 15 November 2019)
Google Scholar
|
|
[43]
|
Y. Yang and Y. Xiao, Threshold dynamics for an HIV model in periodic environments,J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2010, 361, 59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2009.09.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[44]
|
F. Zhang and X. Zhao, A periodic epidemic model in a patchy environmen,J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2007, 325, 496-516. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.01.085
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[45]
|
X. Zhao, Dynamical Systems in Population Biology,Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003.
Google Scholar
|
|
[46]
|
H. Zhu and X. Zou, Impact of delays in cell infection and virus production on HIV-1 dynamics,Maht. Med. Biol., 2008, 25, 99-112.
Google Scholar
|
|
[47]
|
H. Zhu and X. Zou, Dynamics of an HIV-1 infection model with cell-mediated immune response and intracellular delay,Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. B, 2009, 12, 511-524. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2009.12.511
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: