| Citation: | Xinhong Zhang, Xiaoling Zou. SUFFICIENT AND NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR PERSISTENCE AND EXTINCTION OF A STOCHASTIC TWO-PREY ONE-PREDATOR SYSTEM[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(5): 1861-1884. doi: 10.11948/20210382 |
SUFFICIENT AND NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR PERSISTENCE AND EXTINCTION OF A STOCHASTIC TWO-PREY ONE-PREDATOR SYSTEM
-
Abstract
This paper applies a new approach for stochastic Kolmogorov systems generalized by Hening and Nguyen to describe the dynamics of a stochastic two independent prey one predator system perturbed by white noise. Through calculating Lyapunov exponents, we thoroughly address the stability of the ergodic invariant probability measures. Sufficient and necessary conditions under which the species persist as well as conditions under which some species go extinct are established for this three dimensional models. One of the key points is that the critical cases for Lyapunov exponents being zero are considered. Finally, some numerical simulations illustrate the analytical results.
-

-
References
[1] B. Dubey and R. Upadhyay, Persistence and extinction of one-prey and two-predators system, Nonlinear Anal: Model Control, 2004, 9, 307-329. doi: 10.15388/NA.2004.9.4.15147 [2] P. Djomegni, K. Govinder and E. Goufo, Movement, competition and pattern formation in a two prey-one predator food chain model, Comp. APPL. Math., 2018, 37, 2445-2459. doi: 10.1007/s40314-017-0459-4 [3] N. Du, D. H. Nguyen and G. Yin, Conditions for permanence and ergodicity of certain stochastic predator-prey models, J. Appl. Probab., 2016, 53, 187-202. doi: 10.1017/jpr.2015.18 [4] T. Gard and T. Hallam, Persistence in food webs. I. Lotka-Volterra food chains, Bull. Math. Biol., 1979, 41, 877-891. [5] G. Harrison, Global stability of food chains, Am. Nat., 1979, 114, 455-457. doi: 10.1086/283493 [6] R. Has'miniskii, Stochastic Stability of Differential equations, Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alphen aan den Rijn, 1980. [7] A. Hening and D. Hguyen, Coexistence and extinction for stochastic Kolmogorov systems, Ann. Appl. Probab., 2017, 28, 1893-1942. [8] A. Hening and D. Hguyen, Stochastic Lotka-Volterra food chains, J. Math. Biol., 2018, 77, 135-163. doi: 10.1007/s00285-017-1192-8 [9] A. Hening and D. Hguyen, Persistence in stochastic Lotka-Volterra food chains with intrasepcific competition, Bull. Math. Biol., 2018, 80, 2527-2560. doi: 10.1007/s11538-018-0468-5 [10] D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43, 525-546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 [11] C. Ji, D. Jiang and D. Lei, Dynamical behavior of a one predator and two independent preys system with stochastic perturbations, Physica A, 2019, 515, 649-664. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.10.006 [12] M. Liu and C. Bai, Optimal harvesting of a stochastic mutualism model with regime-switching, Appl. Math. Comut., 2020, 373, 125040. [13] J. Lliber and D. Xiao, Global dynamics of a Lotka-Volterra model with two predators competing for one prey, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2014, 74, 434-453. doi: 10.1137/130923907 [14] M. Liu and P. S. Mandal, Dynamical behavior of a one-prey two-prey model with random perturbations, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 2015, 28, 123-137. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.04.010 [15] M. Liu and K. Wang, Dynamics of a two-prey one-predator system in random environments, J. Nonlinear Sci., 2013, 23, 751-775. doi: 10.1007/s00332-013-9167-4 [16] X. Mao, G. Marion and E. Renshaw, Environmental Brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics, Stoch. Proc. Appl., 2002, 97, 95-110. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4149(01)00126-0 [17] D. Nguyen and G. Yin, Asymptotic analysis for a stochastic chemostat model in wastewater treatment, https://arxivorg/pdf/171007897pdf2017.10.24. [18] J. So, A note on the global stability and bifurcation phenomenon of a Lotka-Volterra food chain, J. Theor. Biol., 1979, 80, 185-187. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90204-2 [19] X. Zhang, Y. Li and D. Jiang, Dynamics of a stochastic Holling type Ⅱ predator-prey model with hyperboLic mortality, Nonlinear Dyn., 2017, 87, 2011-2020. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-3172-8 [20] Y. Zhao, S. Yuan and J. Ma, Survival and stationary distribution analysis of a stochastic competitive model of three species on a polluted environment, Bull. Math. Biol., 2015, 77, 1285-1326. doi: 10.1007/s11538-015-0086-4 [21] X. Zou, Y. Zhen, L. Zhang and J. Lv, Survivability and stochastic bifurcations for a stochastic Holling type Ⅱ predator-prey model, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 2020, 83, 105136. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2019.105136 [22] X. Zhang, The global dynamics of stochastic Holling type Ⅱ predator-prey models with non constant mortality rate, Filomat, 2017, 31, 5811-5825. doi: 10.2298/FIL1718811Z -
-
-
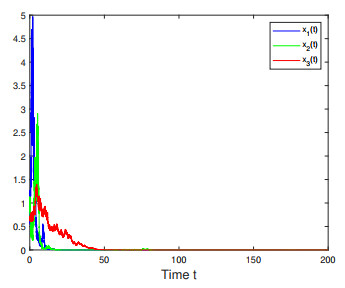
Figure 1. Numerical simulations for the solution of model (1.1) in Example 4.1 which shows that species
$ x_i(t) $ go extinct a.s.,$ i=1,2,3 $ . -
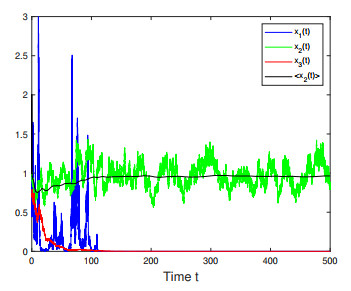
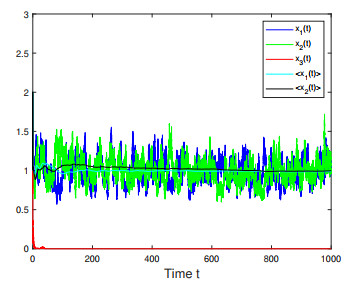
Figure 2. Numerical simulations for Case 1 in Example 4.2 which shows that only species
$ x_2(t) $ is persistent. -
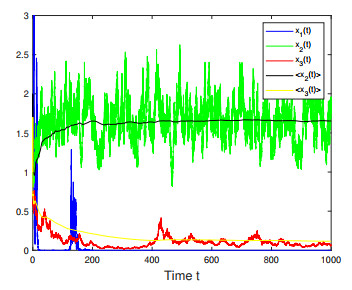
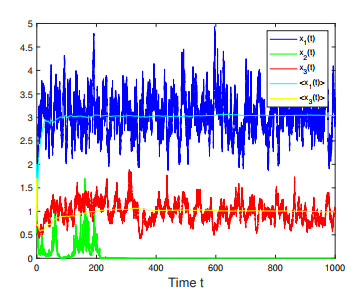
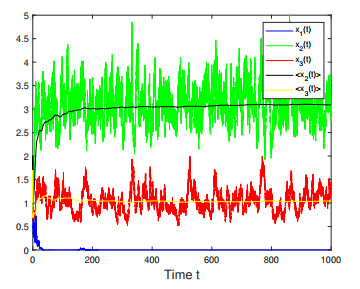
Figure 3. Numerical simulations for Case 2 in Example 4.2 which shows that species
$ x_2(t) $ and$ x_3(t) $ are persistent while$ x_1(t) $ is extinct almost surely. -
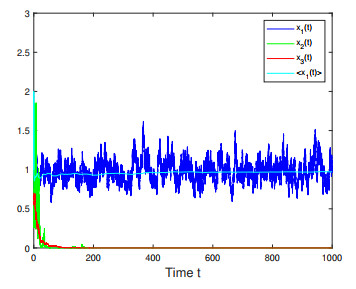
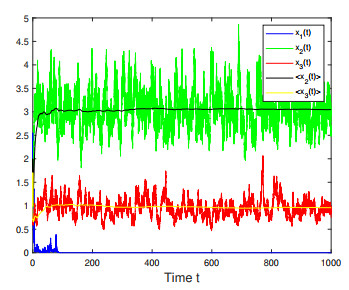
Figure 4. Numerical simulations for Case 3 in Example 4.3 which shows that only species
$ x_1(t) $ is persistent. -
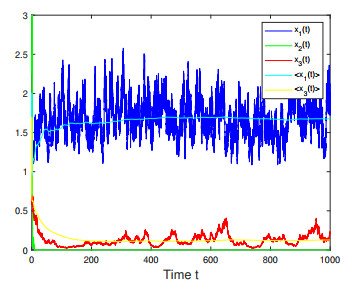
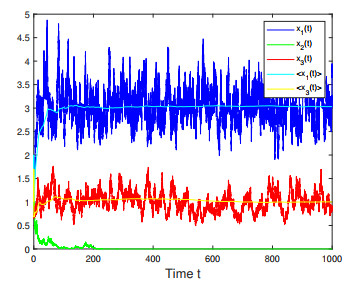
Figure 5. Numerical simulations for Case 4 in Example 4.3 which shows that species
$ x_1(t) $ and$ x_3(t) $ are persistent, and$ x_1(t) $ is extinct. -
Figure 6. Numerical simulations for Case 5 in Example 4.4 which shows that species
$ x_1(t) $ and$ x_2(t) $ are persistent, and$ x_3(t) $ is extinct. -
Figure 7. Numerical simulations for Case 6 in Example 4.4 which shows that species
$ x_1(t) $ and$ x_3(t) $ are persistent, and$ x_2(t) $ is extinct. -
Figure 8. Numerical simulations for Case 7 in Example 4.4 which shows that species
$ x_1(t) $ is extinct, and$ x_2(t) $ ,$ x_3(t) $ are persistent. -
Figure 9. Numerical simulations for Case 8 in Example 4.4 which shows that species
$ x_2(t) $ is extinct, and$ x_1(t) $ ,$ x_3(t) $ are persistent. -
Figure 10. Numerical simulations for Case 9 in Example 4.4 which shows that species
$ x_1(t) $ is extinct, and$ x_2(t) $ ,$ x_3(t) $ are persistent. -
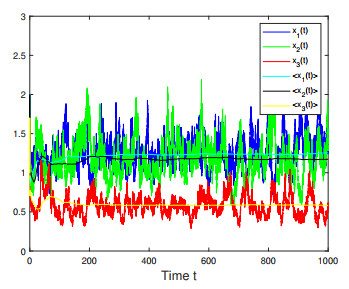
Figure 11. Numerical simulations for Case 10 in Example 4.4 which shows that species
$ x_i(t) $ ,$ i=1,2,3 $ are persistent.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: