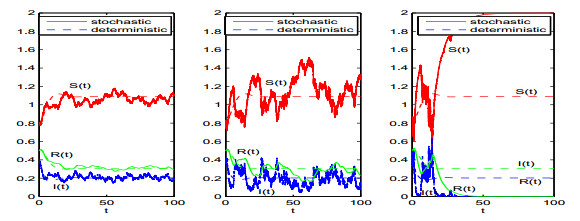
|
[1]
|
B. Berrhazi, M. Fatini, A. Lahrouz, A. Settati and R. Takia, A stochastic SIRS epidemic model with a general awareness-induced incidence, Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 512(15), 968-980.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
B. Berrhazia, M. Fatinia, A Laaribi, R. Pettersson and R. Takia, A stochastic SIRS epidemic model incorporating media coverage and driven by Lvy noise, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2017, 105, 60-68.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
G. Chowell, P. Diaz-Duen, J. Miller, A. Alcazar-Velazco, J. Hyman, P. Fenimore and C. Castillo-Chavez, Estimation of the reproduction number of dengue fever from spatial epidemic data, Math. Biosci., 2007, 208(2), 571-589. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.11.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
V. Capasso and G. Serio, A generalization of the Kermack-Mckendrick deterministic epidemic model, Math. Biosci., 1978, 42(1), 43-61.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
Y. Cai, J. Jiao, Z. Gui, Y. Liu and W. Wang, Environmental variability in a stochastic epidemic model, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2018, 329(15), 210-226.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
Y. Enatsu, Y. Nakata and Y. Muroya, Lyapunov functional techniques for the global stability analysis of a delayed SIRS epidemic model, Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2012, 13(5), 2120-2133. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2012.01.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
S. Gakkhar and K. Negi, Pulse vaccination in SIRS epidemic model with non-monotonic incidence rate, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2008, 35(3), 626-638.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
A. Gray, D. Greenhalgh, L. Hu, X. Mao and J. Pan, A stochastic differential equation SIS epidemic model, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2011, 71(3), 876-902.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
C. Ji, D. Jiang and N. Shi, The behavior of an SIR epidemic model with stochastic perturbation, Stochastic Anal. Appl., 2012, 30(5), 755-773. doi: 10.1080/07362994.2012.684319
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
C. Ji, D. Jiang and N. Shi, Multigroup SIR epidemic model with stochastic perturbation, Physica A, 2011, 390(10), 1747-1762. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.12.042
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
A. Korobeinikov and P. Maini, A Lyapunov function and global properties for SIR and SEIR epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence, Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2004, 1(1), 57-60. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2004.1.57
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
X. Li and G. Gupur, Global stability of an age-structured SIRS epidemic model with vaccination, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems Series B, 2004, 4(3), 643-652. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2004.4.643
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
M. Liu and K. Wang, Persistence and extinction in stochastic non-autonomous logistic systems, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2011, 375(2), 443-457.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
M. Liu and K. Wang, Stochastic logistic equation with infinite delay, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2012, 35(7), 812-827. doi: 10.1002/mma.1608
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
M. Liu, C. Bai and Y. Jin, Population dynamical behavior of a two-predator one-prey stochastic model with time delay, Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems-A, 2017, 37(5), 2513-2538.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
W. Liu, S. Levin and Y. Iwasa, Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 1986, 23(2), 187-204. doi: 10.1007/BF00276956
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
Y. Liu, Q. Liu and Z. Liu, Dynamical behaviors of a stochastic delay logistic system with impulsive toxicant input in a polluted environment, Journal of theoretical biology, 2013, 329, 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2013.03.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
Q. Liu, D. Jiang, N. Shi, T. Hayatce and A. Alsaedic, Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with standard incidence, Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2017, 469(1), 510-517.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
X. Mao, Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications, Horwood, Chichester, 1997.
Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Y. Muroya, Y. Enatsu and Y. Nakata, Global stability of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with a non-monotonic incidence rate, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2011, 377(1), 1-14.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
Y. Muroya, Y. Enatsu and Y. Nakata, Monotone iterative techniques to SIRS epidemic models with nonlinear incidence rates and distributed delays, Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2011, 12(4), 1897-1910. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2010.12.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
I. Moneim and D. Greenhalgh, Threshold and stability results for an SIRS epidemic model with a general periodic vaccination strategy, Journal of Biological Systems, 2005, 13(2), 131-150.
Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
C. Xia, S. Sun, Z. Liu, Z. Chen and Z. Yuan, Epidemics of SIRS model with nonuniform transmission on scale-free networks, International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2009, 23(9), 2203-2213. doi: 10.1142/S021797920905211X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
D. Xiao and S. Ruan, Global analysis of an epidemic model with nonmontone incidence rate, Math. Biosci., 2007, 208(2), 419-429. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.09.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
R. Xu and Z. Ma, Stability of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate, Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 2009, 41(5), 2319-2325. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2008.09.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
R. Xu and Z. Ma, Global stability of a SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate and time delay, Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2009, 10(5), 3175-3189. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.10.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
Q. Yang, D. Jiang, N. Shi and C. Ji, The ergodicity and extinction of stochastically perturbed SIR and SEIR epidemic models with saturated incidence, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2012, 388(1), 248-271.
Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
Y. Yang and D. Xiao, Influence of latent period and nonlinear incidence rate on the dynamics of SIRS epidemiological models, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems Series B, 2010, 13(1), 195-211.
Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
Y. Yang and Y. Xiao, Threshold dynamics for compartmental epidemicmodels with impulses, Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2012, 13(1), 224-234. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2011.07.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
X. Zhang and K. Wang, Stability analysis of a stochastic Gilpin-Ayala model driven by Lévy noise, Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2014, 19(5), 1391-1399. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2013.09.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
Y. Zhao, D. Jiang and D. O'Regan, The extinction and persistence of the stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination, Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2013, 392(20), 4916-4927. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2013.06.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
Y. Zhao and D. Jiang, The threshold of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with saturated incidence, Applied Mathematics Letters, 2014, 34, 90-93. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2013.11.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
X. Zhao and X. Zou, Threshold dynamics in a delayed SIS epidemic model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2001, 257(2), 282-291. doi: 10.1006/jmaa.2000.7319
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
T. Zhang, J. Liu and Z. Teng, Dynamic behavior for a nonautonomous SIRS epidemic model with distributed delays, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2009, 214(2), 624-631. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2009.04.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




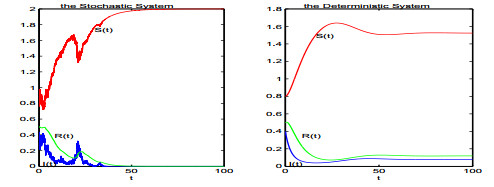

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: