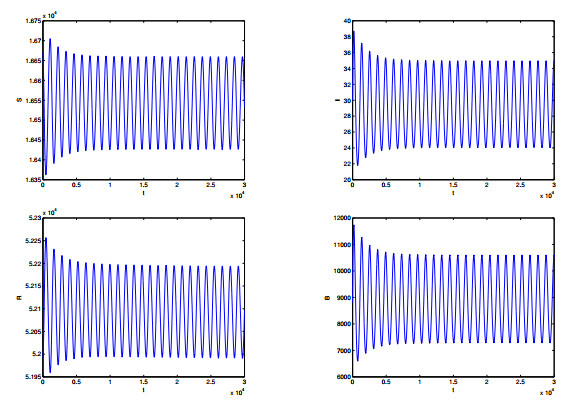
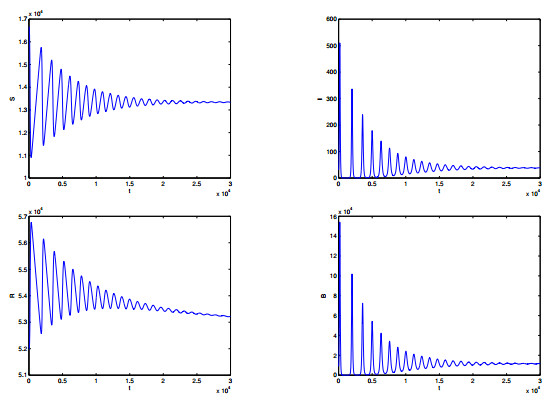
|
[1]
|
A. S. Azman, K. E. Rudolph, D. A. T. Cummings and J. Lessler, The incubation period of cholera: A systematic review, Journal of Infection, 2013, 66(5), 432-438. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2012.11.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
N. Bacaër and E. Ait Dads, On the biological interpretation of a definition for the parameter R0 in periodic population models, J. Math. Biol, 2012, 65, 601-621. doi: 10.1007/s00285-011-0479-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
E. Beretta and Y. Kuang, Geometric stability switch criteria in delay differential systems with delay dependent parameters, SIAM J. Math. Anal., 2002, 33, 1144-1165. doi: 10.1137/S0036141000376086
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
F. Brauer, Z. Shuai and P. van den Driessche, Dynamics of an age-of-infection cholera model, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2013, 10, 1335-1349. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2013.10.1335
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
V. Capasso and S. L. Paveri-Fontana, A mathematical model for the 1973 cholera epidemic in the European Mediterranean region, Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique, 1979, 27, 121-132.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
C. T. Codeço, Endemic and epidemic dynamics of cholera: the role of the aquatic reservoir, BMC Infect. Dis., 2001, 1-1.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
P. van den Driessche and J. Watmough, Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission, Math. Biosci, 2002, 180, 29-48. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00108-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
S. Gao, Z. Teng and D. Xie, Analysis of a delayed SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2009, 40(2), 1004-1011.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
M. Gatto, L. Mari, E Bertuzzo., R. Casagrandi, L. Righetto and I. Rodriguez-Iturbe, A. Rinaldo, Generalized reproduction numbers and the prediction of patterns in waterborne disease, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 48, 19703-19708.
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
M. Gatto, L. Mari, E Bertuzzo., R. Casagrandi, L. Righetto, I. Rodriguez-Iturbe and A. Rinaldo, Spatially explicit conditions for waterborne pathogen invasionz, The American Naturalist, 2013, 182, 328-346. doi: 10.1086/671258
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
M. Giaquinta and G. Modica, Mathematical Analysis. An Introduction to Functions of Several Variables, Birkhauser Boston, Inc., Boston, MA, 2009.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
D. M. Hartley, J. Glenn Morris Jr and D. L. Smith, Hyperinfectivity: a critical element in the ability of V. cholerae to cause epidemic? PLoS Medicine, 2006, 3(1), e7.
Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
T. R. Hendrix, The pathophysiology of cholera, Bull. NY Acad. Med., 1971, 47, 1169-1180.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
H. W. Hethcote and D. W. Tudor, Integral equation models for endemic infectious diseases, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 1980, 9(1), 37. doi: 10.1007/BF00276034
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
D. L. Heymann (Ed.), Control of Communicable Diseases Manual, nineteenth ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, 2008.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
M. S. Islam, M. A. Miah, M. K. Hasan, R. B. Sack and M. J. Albert. Detection of non-culturable Vibrio cholerae O1 associated with a cyanobacterium from an aquatic environment in Bangladesh, T. Roy. Soc. Trop. Med. H., 1994, 88, 298-299. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(94)90085-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
J. B. Kaper, J. G. Morrisa and M. M. Levine Cholera, Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 1995, 8, 48-86. doi: 10.1128/CMR.8.1.48
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
J. Lin, R. Xu and X. Tian, Global dynamics of an age-structured cholera model with both human-to-human and environment-to-human transmissions and saturation incidence, Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2018, 63, 688-708. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2018.07.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
I. M. Longini Jr, A. Nizam, M. Ali, M. Yunus, N. Shenvi and J.D. Clemens, Controlling endemic cholera with oral vaccines, PLoS Med, 2007, 4(11), e336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040336
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
R. L. Miller Neilan, E. Schaefer, H. Gaff, K. R. Fister and S. Lenhart, Modeling optimal intervention strategies for cholera, Bull. Math. Biol, 2010, 72, 2004-2018. doi: 10.1007/s11538-010-9521-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
Z. Mukandavire and W. Garira, Sex-structured HIV/AIDS model to analyse the effects of condom use with application to Zimbabwe, J. Math. Bio, 2007, 54, 669-699. doi: 10.1007/s00285-006-0063-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
E. J. Nelson, J. B. Harris, J. G. Morris, S. B. Calderwood and A. Camilli, Cholera transmission: the host, pathogen and bacteriophage dynamics, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2009, 7, 693-702. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2204
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
M. Pascual, M. J. Bouma and A. P. Dobson, Cholera and climate: revisiting the quantitative evidence, Microbes Infect., 2002, 4, 237-245. doi: 10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01533-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
A. Rinaldo, E. Bertuzzo, L. Mari, L. Righetto, M. Blokesch and M. Gatto, Reassessment of the 2010-2011 Haiti cholera outbreak and rainfall-driven multiseason projections, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(17), 6602-6607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203333109
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
L. Righetto, R. Casagrandi, E. Bertuzzo, L. Mari, M. Gatto, I. Rodriguez-Iturbe and A. Rinaldo, The role of aquatic reservoir fluctuations in long-term cholera patterns, Epidemics, 2013, 4, 33-42.
Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
S. Ruan and J. Wei, On the zeros of a third degree exponential polynomial with applications to a delayed model for the control of testosterone secretion, IMA J. Mathematics Applied in Medicine and Biology, 2001, 18, 41-52. doi: 10.1093/imammb/18.1.41
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
Z. Shuai, J. H. Tien and P. van den Driessche, Cholera models with hyperinfectivity and temporary immunity, Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2012, 74(10), 2423-2445. doi: 10.1007/s11538-012-9759-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
J.P. Tian and J. Wang, Global stability for cholera epidemic models, Mathematical Biosciences, 2011, 232, 31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2011.04.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
V. Tudor, I. Strati and Smallpox, Cholera, Abacus Press, Tunbridge Wells, 1977.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
World Health Organization web page: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs107/en/
Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
R. Xu and Y. Du, A delayed SIR epidemic model with saturation incidence and constant infectious period, J. Appl. Math. Comp., 2010, 35, 229-250.
Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
X. Zhou and J. Cui, Modelling and stability analysis for a cholera model with vaccination, Math. Method. Appl. Sci, 2011, 34(14), 1711-1724.
Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
X. Zhou, X. Shi and J. Cui, Stability and backward bifurcation on a cholera epidemic model with saturated recovery rate, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2017, 40(4), 1288-1306. doi: 10.1002/mma.4053
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




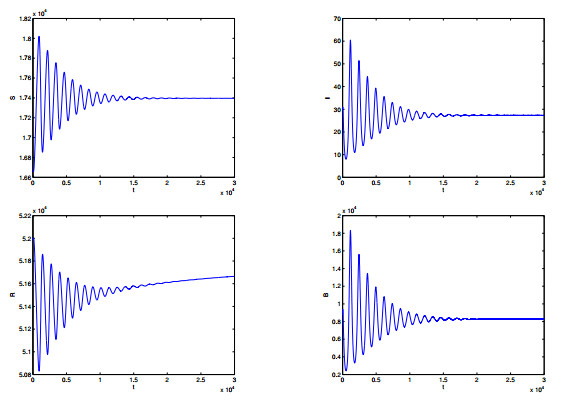

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: