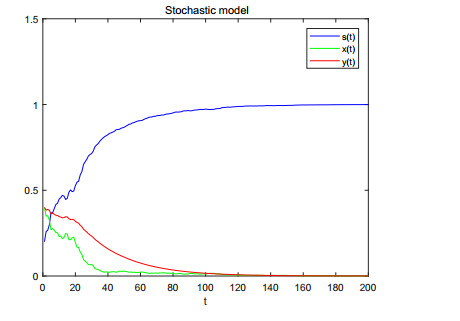
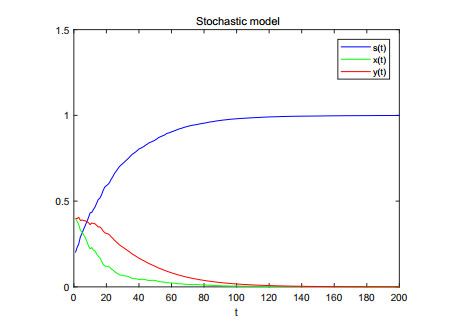
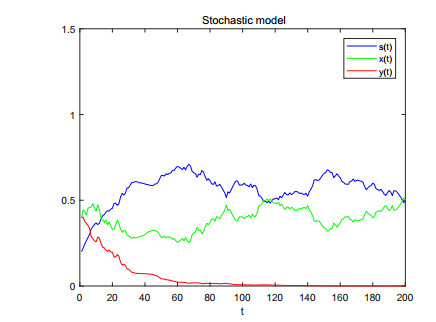
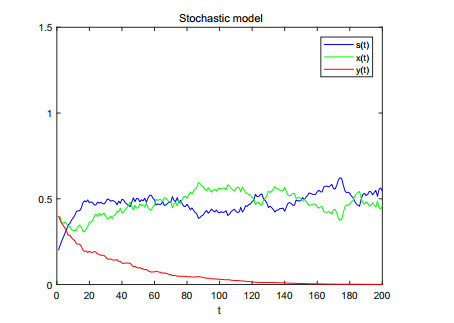
|
[1]
|
E. Ali, M. Asif and A. H. Ajbar, Study of chaotic behavior in predator-prey interactions in a chemostat, Ecol. Model., 2013, 259, 10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.02.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
L. Chen, X. Meng and J. Jiao, Biological Dynamics, Science Press, Beijing, 1993.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
M. Chi and W. Zhao, Dynamical analysis of multi-nutrient and single microorganism chemostat model in a polluted environment, Adv. Difference Equations, 2018, 2018, 120. doi: 10.1186/s13662-018-1573-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
C. Fritsch, J. Harmand and F. Campillo, A modeling approach of the chemostat, Ecol. Model., 2015, 299, 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.11.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43(3), 525-546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
L. Imhof and S. Walcher, Exclusion and persistence in deterministic and stochastic chemostat models, J. Differential Equations, 2005, 217(1), 26-53.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
C. Ji, D. Jiang and N. Shi, Multiple SIR epidemic model with stochastic perturbation, Physica A, 2011, 390, 1747-1762. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.12.042
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
Y. Kuang, Limit cycles in a chemostat-related model, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1989, 49(6), 1759-1767. doi: 10.1137/0149107
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
R. Khasminskii, Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations, Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alphen aan den Rijn, Netherlands, 1980.
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
H. Kunita, Itô's stochastic calculus: its surprising power for applications, Stochastic Process. Appl., 2010, 120(5), 622-652. doi: 10.1016/j.spa.2010.01.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
B. Li and Y. Kuang, Simple food chain in a chemostat with distinct removal rates, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2000, 242(1), 75-92.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
S. Liu, X. Wang and L. Wang, Competitive exclusion in delayed chemostat models with differential removal rates, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2014, 74(3), 634-648. doi: 10.1137/130921386
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
H. Liu, X. Li and Q. Yang, The ergodic property and positive recurrence of a multi-group Lotka-Volterra mutualistic system with regime switching, Syst. Control Lett., 2013, 62(10), 805-810. doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2013.06.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
R. May, Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems, Princeton University Press, NJ, 2001.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
X. Mao, Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications, Horwood Publishing, Chichester, 1997.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
L. Nie, Z. Teng and L. Hu, The dynamics of a chemostat model with state dependent impulsive effects, Internat. J. Bifur. Chaos, 2011, 21(5), 1311-1322. doi: 10.1142/S0218127411029173
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
H. L. Smith and P. Waltman, The Theory of the Chemostat: Dynamics of Microbial Competition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1995.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
T. Sari, Competitive exclusion for chemostat equations with variable yields, Acta Appl. Math., 2013, 123(1), 201-219. doi: 10.1007/s10440-012-9761-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
S. Sun, Y. Sun, G. Zhang and X. Liu, Dynamical behavior of a stochastic two-species Monod competition chemostat model, Appl. Math. Comput., 2017, 298, 153-170.
Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
M. Sun, Q. Dong and J. Wu, Asymptotic behavior of a Lotka-Volterra food chain stochastic model in the chemostat, Stoch. Anal. Appl., 2017, 35(4), 645-661. doi: 10.1080/07362994.2017.1299628
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
D. Voulgarelis, A. Velayudhan and F. Smith, Stochastic analysis of a full system of two competing populations in a chemostat, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2018, 175, 424-444. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2017.10.052
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
L. Wang and D. Jiang, A note on the stationary distribution of the stochastic chemostat model with general response functions, Appl. Math. Lett., 2017, 73, 22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2017.04.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
C. Xu and S. Yuan, An analogue of break-even concentration in a simple stochastic chemostat model, Appl. Math. Lett., 2015, 48, 62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2015.03.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
C. Xu and S. Yuan, Competition in the chemostat: A stochastic multi-species model and its asymptotic behavior, Math. Biosci., 2016, 280, 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2016.07.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
C. Xu, S. Yuan and T. Zhang, Sensitivity analysis and feedback control of noise-induced extinction for competition chemostat model with mutualism, Physica A, 2018, 505, 891-902. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.04.040
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
D. Zhao and S. Yuan, Critical result on the break-even concentration in a single-species stochastic chemostat model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2016, 434(2), 1336-1345. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.09.070
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
D. Zhao and S. Yuan, Sharp conditions for the existence of a stationary distribution in one classical stochastic chemostat, Appl. Math. Comput., 2018, 339, 199-205.
Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
Q. Zhang and D. Jiang, Competitive exclusion in a stochastic chemostat model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response, J. Math. Chem., 2016, 54(3), 777-791. doi: 10.1007/s10910-015-0589-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
C. Zhu and G. Yin, Asymptotic properties of hybrid diffusion systems, SIAM J. Control Optim., 2007, 46(4), 1155-1179. doi: 10.1137/060649343
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: