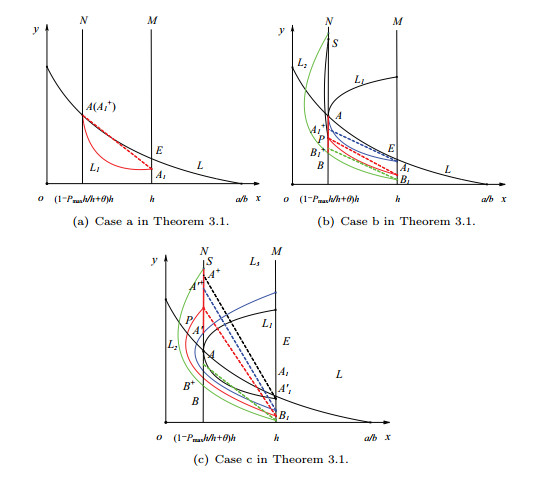
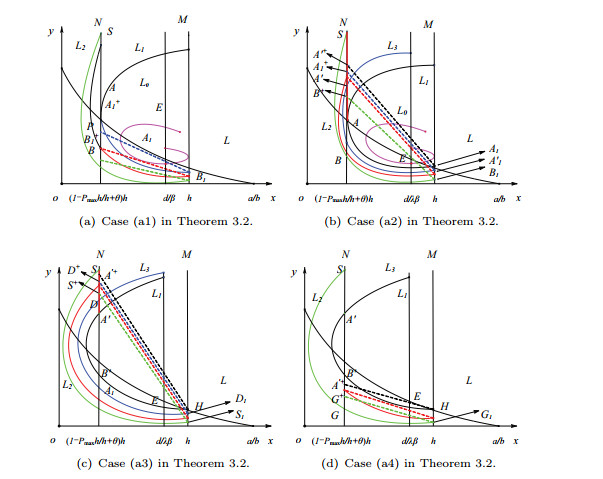
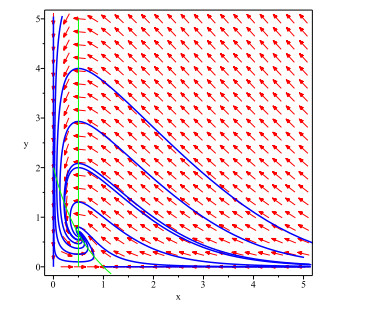
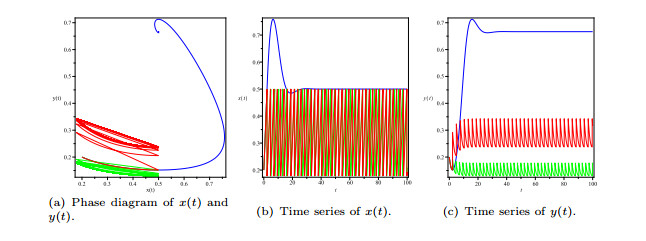
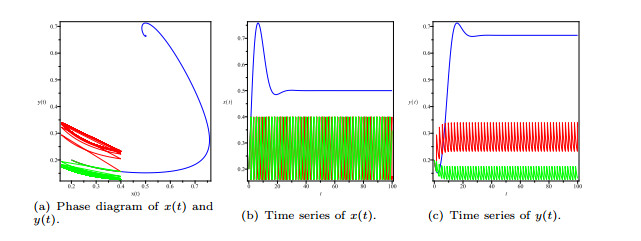
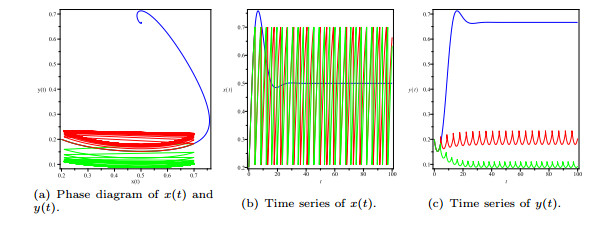
|
[1]
|
J. L. Apple and R. F. Smith (Eds), Integrated pest management, Springer, Boston, 1976.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
D. Atwood and C. Paisley-Jones, Pesticides Industry Sales and Usage 2008-2012 Market Estimates, Tech. rep., U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC., 2017.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
D. Auslander, Spatial effects on the stability of a food-limited moth population, J. Franklin Inst., 1982, 314(6), 347-365. doi: 10.1016/0016-0032(82)90021-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
J. Chen, T. Zhang, Z. Zhang et al., Stability and output feedback control for singular markovian jump delayed systems, Math. Control Relat. Fields, 2018, 8(2), 475-490. doi: 10.3934/mcrf.2018019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
L. Chen, X. Liang and Y. Pei, The periodic solutions of the impulsive state feedback dynamical system, Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci., 2018, 2018, Article ID 14.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
M. Chi and W. Zhao, Dynamical analysis of multi-nutrient and single microorganism chemostat model in a polluted environment, Adv. Difference Equ., 2018, 2018(1), 120. doi: 10.1186/s13662-018-1573-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
M. Chi and W. Zhao, Dynamical analysis of two-microorganism and single nutrient stochastic chemostat model with monod-haldane response function, Complexity, 2019, 2019, Article ID 8719067, 13 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
X. Fan, Y. Song and W. Zhao, Modeling cell-to-cell spread of HIV-1 with nonlocal infections, Complexity, 2018, 2018, Article ID 2139290, 10 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
J. Gao, B. Shen, E. Feng and Z. Xiu, Modelling and optimal control for an impulsive dynamical system in microbial fed-batch culture, Comp. Appl. Math., 2013, 32(2), 275-290. doi: 10.1007/s40314-013-0012-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
N. Gao, Y. Song, X. Wang and J. Liu, Dynamics of a stochastic sis epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rates, Adv. Difference Equ., 2019, 2019(1), 41.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
H. Guo and L. Chen, Periodic solution of a turbidostat system with impulsive state feedback control, J. Math. Chem., 2009, 46(4), 1074-1086.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
M. Hernández and A. Margalida, Pesticide abuse in europe: effects on the cinereous vulture (aegypius monachus) population in spain, Ecotoxicology, 2008, 17(4), 264-272. doi: 10.1007/s10646-008-0193-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
S. B. Hsu, Ordinary Differential Equations with Applications, World Scientific, Singapore, 1999.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
G. Jiang, Q. Lu and L. Qian, Complex dynamics of a holling type Ⅱ prey-predator system with state feedback control, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2007, 31(2), 448-461.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
Z. Jiang, X. Bi, T. Zhang and B. S. A. Pradeep, Global hopf bifurcation of a delayed phytoplankton-zooplankton system considering toxin producing effect and delay dependent coefficient, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2019, 16(5), 3807-3829. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019188
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
Z. Jiang, W. Zhang, J. Zhang and T. Zhang, Dynamical analysis of a phytoplankton-zooplankton system with harvesting term and holling iii functional response, Internat. J. Bifur. Chaos Appl. Sci. Engrg., 2018, 28(13), 1850162. doi: 10.1142/S0218127418501626
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
V. Lakshmikantham, D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeonov, Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations, World Scientific, Singapore, 1989.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
G. Li and M. Chen, Infinite horizon linear quadratic optimal control for stochastic difference time-delay systems, Adv. Difference Equ., 2015, 2015(1), 14.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
Y. Li, H. Cheng and Y. Wang, A lycaon pictus impulsive state feedback control model with allee effect and continuous time delay, Adv. Difference Equ., 2018, 2018(1), 367. doi: 10.1186/s13662-018-1820-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Y. Li, Y. Li, Y. Liu and H. Cheng, Stability analysis and control optimization of a prey-predator model with linear feedback control, Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc., 2018, 2018, Article ID 4945728, 12 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
Z. Li, L. Chen and J. Huang, Permanence and periodicity of a delayed ratio-dependent predator-prey model with holling type functional response and stage structure, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2009, 233(2), 173-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2009.07.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
J. Liang, S. Tang, R. A. Cheke and J. Wu, Adaptive release of natural enemies in a pest-natural enemy system with pesticide resistance, Bull. Math. Biol., 2013, 75(11), 2167-2195. doi: 10.1007/s11538-013-9886-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
B. Liu, Y. Zhang and L. Chen, The dynamical behaviors of a Lotka-Volterra predator-prey model concerning integrated pest management, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2005, 6(2), 227-243. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2004.08.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
F. Liu and H. Wu, A note on the endpoint regularity of the discrete maximal operator, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2019, 147(2), 583-596.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
G. Liu, Z. Chang and X. Meng, Asymptotic analysis of impulsive dispersal predator-prey systems with markov switching on finite-state space, J. Funct. Spaces, 2019, 2019, Article ID 8057153, 18 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
G. Liu, X. Wang, X. Meng and S. Gao, Extinction and persistence in mean of a novel delay impulsive stochastic infected predator-prey system with jumps, Complexity, 2017, 2017, Article ID 1950970, 15 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
H. Liu and H. Cheng, Dynamic analysis of a prey-predator model with state-dependent control strategy and square root response function, Adv. Difference Equ., 2018, 2018(1), 63.
Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
K. Liu, T. Zhang and L. Chen, State-dependent pulse vaccination and therapeutic strategy in an SI epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate, Comput. Math. Methods Med., 2019, 2019, Article ID 3859815, 10 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
X. Liu, Y. Li and W. Zhang, Stochastic linear quadratic optimal control with constraint for discrete-time systems, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 228, 264-270.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
T. Ma, X. Meng and Z. Chang, Dynamics and optimal harvesting control for a stochastic one-predator-two-prey time delay system with jumps, Complexity, 2019, 2019, Article ID 5342031, 19 pages.
Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
X. Meng and L. Zhang, Evolutionary dynamics in a Lotka-Volterra competition model with impulsive periodic disturbance, Math. Methods Appl. Sci., 2016, 39(2), 177-188. doi: 10.1002/mma.3467
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
X. Meng, S. Zhao and W. Zhang, Adaptive dynamics analysis of a predator-prey model with selective disturbance, Appl. Math. Comput., 2015, 266, 946-958.
Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
A. Miao, T. Zhang, J. Zhang and C. Wang, Dynamics of a stochastic SIR model with both horizontal and vertical transmission, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2018, 8(4), 1108-1121.
Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
G. Pang and L. Chen, Periodic solution of the system with impulsive state feedback control, Nonlinear Dynam., 2014, 78(1), 743-753.
Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
Z. Shi, J. Wang, Q. Li and H. Cheng, Control optimization and homoclinic bifurcation of a prey-predator model with ratio-dependent, Adv. Difference Equ., 2019, 2019(1), 2. doi: 10.1186/s13662-018-1933-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
F. E. Smith, Population dynamics in daphnia magna and a new model for population growth, Ecology, 1963, 44(4), 651-663. doi: 10.2307/1933011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
R. F. Smith and H. T. Reynolds, Principles, definitions and scope of integrated pest control, in Proceedings of the FAO symposium on Integrated pest control, 1965.
Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
Y. Song, A. Miao, T. Zhang et al., Extinction and persistence of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with saturated incidence rate and transfer from infectious to susceptible, Adv. Difference Equ., 2018, 2018(1), 293.
Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
K. Sun, T. Zhang and Y. Tian, Dynamics analysis and control optimization of a pest management predator-prey model with an integrated control strategy, Appl. Math. Comput., 2017, 292, 253-271.
Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
S. Tang, Y. Xiao, L. Chen and R. A. Cheke, Integrated pest management models and their dynamical behaviour, Bull. Math. Biol., 2005, 67(1), 115-135. doi: 10.1016/j.bulm.2004.06.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[41]
|
Y. Tian, K. Sun and L. Chen, Modelling and qualitative analysis of a predator-prey system with state-dependent impulsive effects, Math. Comput. Simulation, 2011, 82(2), 318-331. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2011.08.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[42]
|
G. Wang and S. Tang, Qualitative analysis of prey-predator model with nonlinear impulsive effects, Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed., 2013, 34(5), 496-505.
Google Scholar
|
|
[43]
|
J. Wang, H. Cheng, Y. Li and X. Zhang, The geometrical analysis of a predator-prey model with multi-state dependent impulsive, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2018, 8(2), 427-442.
Google Scholar
|
|
[44]
|
J. Wang, K. Liang, X. Huang et al., Dissipative fault-tolerant control for nonlinear singular perturbed systems with markov jumping parameters based on slow state feedback, Appl. Math. Comput., 2018, 328, 247-262.
Google Scholar
|
|
[45]
|
M. E. Whalon, D. Mota-Sanchez and R. M. Hollingworth, Global Pesticide Resistance in Arthropods, Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux International, Cambridge, 2008.
Google Scholar
|
|
[46]
|
C. Yin, Y. Cheng, S.-M. Zhong and Z. Bai, Fractional-order switching type control law design for adaptive sliding mode technique of 3d fractional-order nonlinear systems, Complexity, 2015, 21(6), 363-373.
Google Scholar
|
|
[47]
|
S. Yuan, P. Li and Y. Song, Delay induced oscillations in a turbidostat with feedback control, J. Math. Chem., 2011, 49(8), 1646-1666. doi: 10.1007/s10910-011-9848-x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[48]
|
J. Zhang, J. Xia, W. Sun et al., Finite-time tracking control for stochastic nonlinear systems with full state constraints, Appl. Math. Comput., 2018, 338, 207-220.
Google Scholar
|
|
[49]
|
S. Zhang, X. Meng, T. Feng and T. Zhang, Dynamics analysis and numerical simulations of a stochastic non-autonomous predator-prey system with impulsive effects, Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst., 2017, 26, 19-37. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.04.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[50]
|
T. Zhang, X. Liu, X. Meng and T. Zhang, Spatio-temporal dynamics near the steady state of a planktonic system, Comput. Math. Appl., 2018, 75(12), 4490-4504. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2018.03.044
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[51]
|
T. Zhang, W. Ma, X. Meng and T. Zhang, Periodic solution of a prey-predator model with nonlinear state feedback control, Appl. Math. Comput., 2015, 266, 95-107.
Google Scholar
|
|
[52]
|
T. Zhang, X. Meng, Y. Song and T. Zhang, A stage-structured predator-prey SI model with disease in the prey and impulsive effects, Math. Model. Anal., 2013, 18(4), 505-528. doi: 10.3846/13926292.2013.840866
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[53]
|
L. Zhao, L. Chen and Q. Zhang, The geometrical analysis of a predator-prey model with two state impulses, Math. Biosci., 2012, 238(2), 55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2012.03.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[54]
|
W. Zhao, J. Liu, M. Chi and F. Bian, Dynamics analysis of stochastic epidemic models with standard incidence, Adv. Difference Equ., 2019, 2019(1), 22. doi: 10.1186/s13662-019-1972-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[55]
|
Z. Zhao, T. Wang and L. Chen, Dynamic analysis of a turbidostat model with the feedback control, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2010, 15(4), 1028-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.05.016
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[56]
|
F. Zhu, X. Meng and T. Zhang, Optimal harvesting of a competitive n-species stochastic model with delayed diffusions, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2019, 16, 1554-1574. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019074
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[57]
|
X. Zhuo, Global attractability and permanence for a new stage-structured delay impulsive ecosystem, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2018, 8(2), 457-457.
Google Scholar
|
|
[58]
|
X.-L. Zhuo and F.-X. Zhang, Stability for a new discrete ratio-dependent predator-prey system, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2018, 17(1), 189-202. doi: 10.1007/s12346-017-0228-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




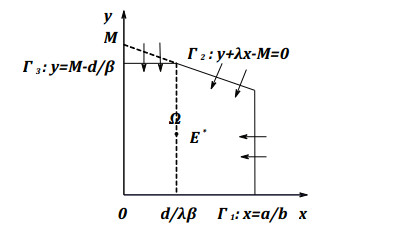

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: