|
[1]
|
R. Arditi and L. R. Ginzburg, Coupling in predator-prey dynamics: ratio-dependence, J. Theoret. Biol., 1989, 139, 311–326. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5193(89)80211-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
M. Bandyopadhyay and J. Chattopadyay, Ratio-dependent predator-prey model, effect of environmental fluctuation and stability, Nonlinearity, 2005, 18, 913–936. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/18/2/022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
J. R. Beddington, Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency, 1975, J. Anim. Ecol., 44, 331–340. doi: 10.2307/3866
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
H. I. Freedman, Deterministic Mathematical Models in Population Ecology, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1980.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
S. J. Gao, Y. J. Liu, J. J. Nieto and H. Andrade, Seasonality and mixed vaccination strategy in an epidemic model with vertical transmission, Math. Comput. Simul., 2011, 81, 1855–1868. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2010.10.032
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
Z. K. Guo, H. F. Huo, Q. Y. Ren and H. Xiang, Bifurcation of a modified Leslie-Gower system with discrete and distributed delays, J. Nonlinear Model. Anal., 2019, 1(1), 73–91.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43, 525–546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
Z. Y. Hu, Z. D. Teng, C. J. Jia, L. Zhang and X. Chen, Complex dynamical behaviors in a discrete eco-epidemiological model with disease in prey, Adv. Differ. Equ., 2014, 2014, 1–19. doi: 10.1186/1687-1847-2014-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
C. S. Holling, The components of predation as revealed by a study of small mammal predation of the European pine sawfly, Can. Entomol., 1959, 91, 293–320. doi: 10.4039/Ent91293-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
N. Ikeda and S. Watanabe, Stochastic Differential Equations and Diffusion Processes, North-Holland, New York, 1989.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
C. Y. Ji, D. Q. Jiang and N. Z. Shi, Analysis of a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-type Ⅱ schemes with stochastic perturbation, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2009, 359, 482–498. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2009.05.039
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
D. Q. Jiang and N. Z. Shi, A note on nonautonomous logistic equation with random perturbation, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2005, 303, 164–172. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2004.08.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
P. H. Leslie, Some further notes on the use of matrices in population mathematic, Biometrica, 1948, 35, 213–245. doi: 10.1093/biomet/35.3-4.213
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
P. H. Leslie and J. C. Gower, The properties of a stochastic model for the predator-prey type of interaction between two species, Biometrica, 1960, 47, 219–234. doi: 10.1093/biomet/47.3-4.219
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
X. Y. Li and X. R. Mao, Population dynamical behavior of nonautonomous Lotka-Volterra competitive system with random perturbation, Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst., 2009, 24, 523–545. doi: 10.3934/dcds.2009.24.523
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
Y. G. Lin, D. Q. Jiang and S. Wang, Stationary distribution of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination, Physica A, 2014, 394, 187–197. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2013.10.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
M. Liu, C. X. Du and M. L. Deng, Persistence and extinction of a modified Leslie-Gower Holling-type Ⅱ stochastic predator-prey model with impulsive toxicant input in polluted environments, Nonlinear Anal.-Hybrid Syst., 2018, 27, 177–190. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.08.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
M. Liu and K Wang, Persistence and extinction in stochastic nonautonomous logistic systems, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2011, 375, 443–457. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.09.058
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
M. Liu, K. Wang and Q. Wu, Survival analysis of stochastic competitive models in a polluted enviornment and stochastic competitive exclusion principle, Bull. Math. Biol., 2011, 73, 1969–2012. doi: 10.1007/s11538-010-9569-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
X. Q. Liu, S. M. Zhong, B. D. Tian and F. X. Zheng, Asymptotic properties of a stochastic predator-prey model with Crowley-Martin functional response, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2013, 43, 479–490.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
X. R. Mao, Stochastic Different Equations and Application, 2nd edition, Horwood, Chichester, 2008.
Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
X. R. Mao and C. G. Yuan, Stochastic differential equations with Markovian switching, Imperial College Press, London, 2006.
Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
E. C. Pielou, An Introduction to Mathematical Ecology, Wiley, New York, 1969.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
X. Y. Song and Y F Li, Dynamic behaviors of the periodic predatorCprey model with modified Leslie-Gower Holling-type Ⅱ schemes and impulsive effect, Nonlinear Anal.-Real World Appl., 2008, 9(1), 64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2006.09.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
L. Wang, Z. D. Teng and H. J. Jiang, Global attractivity of a discrete SIRS epidemic model with standard incidence rate, Math. Method. Appl. Sci., 2013, 36, 601–619. doi: 10.1002/mma.2734
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
P. J. Witbooi, Stability of an SEIR epidemic model with independent stochastic perturbations, Physica A, 2013, 392, 4928–4936. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2013.06.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
Y. Zhang, S. H. Chen and S. J. Gao, Analysis of a nonautonomous stochastic predator-prey model with Crowley-Martin functional response, Adv. Differ. Equ., 2016, 2016, 1–28. doi: 10.1186/s13662-015-0739-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




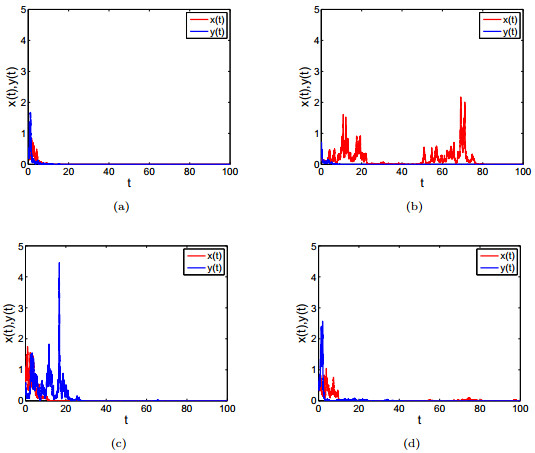

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: