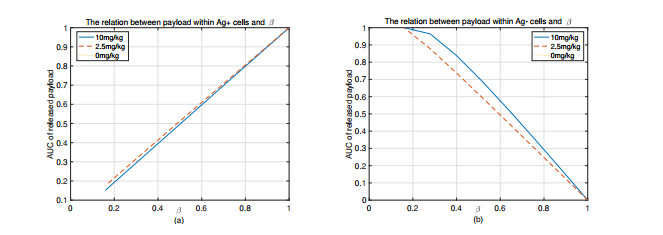
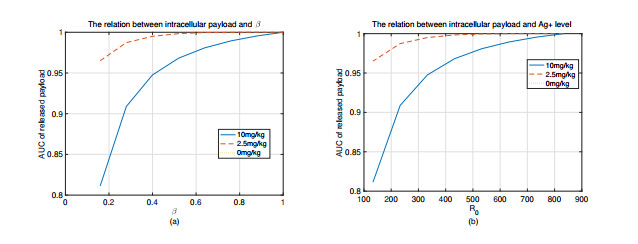
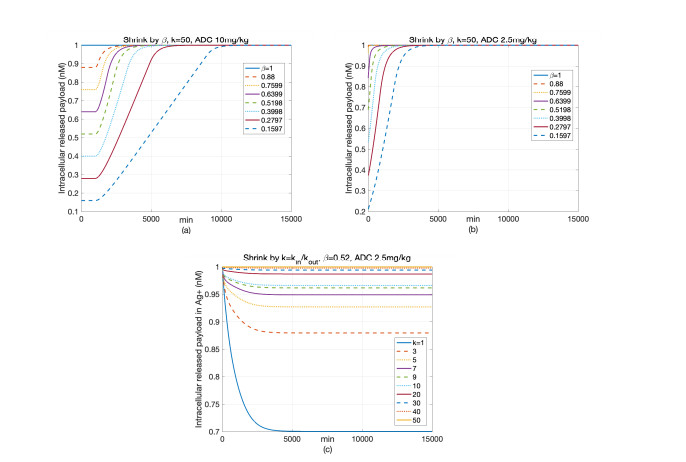
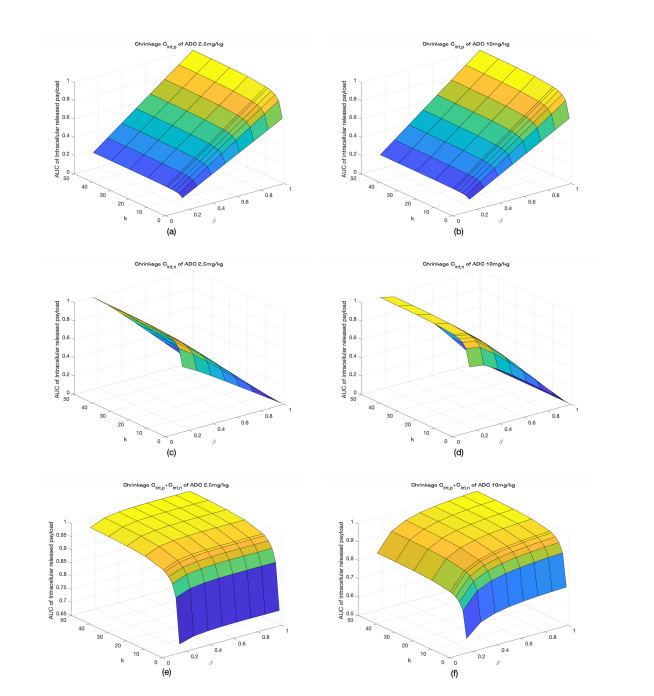
|
[1]
|
P. J. Aston, G. Derks, B. M. Agoram and P. H. van der Graaf, A mathematical analysis of rebound in a target-mediated drug disposition model: I. without feedback, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2014, 68(6), 1453-1478. doi: 10.1007/s00285-013-0675-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
A. Beck, L. Goetsch, C. Dumontet and N. Corvaïa, Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2017, 16(5), 315-337.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
A. Beck, T. Wurch, C. Bailly and N. Corvaia, Strategies and challenges for the next generation of therapeutic antibodies, Nature Reviews. Immunology, 2010, 10(5), 345. doi: 10.1038/nri2747
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
E. R. Boghaert, K. Khandke, L. Sridharan et al., Tumoricidal effect of calicheamicin immuno-conjugates using a passive targeting strategy, International Journal of Oncology, 2006, 28(3), 675-684.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
C. A. Boswell, D. B. Yadav, E. E. Mundo et al., Biodistribution and efficacy of an anti-tenb2 antibody-drug conjugate in a patient-derived model of prostate cancer, Oncotarget, 2019, 10(58), 6234. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27263
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
J. H. Byun and I. H. Jung, Modeling to capture bystander-killing effect by released payload in target positive tumor cells, BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1), 194. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5336-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
R. V. Chari, Targeted cancer therapy: conferring specificity to cytotoxic drugs, Accounts of Chemical Research, 2007, 41(1), 98-107.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
R. Deng, C. Zhou, D. Li et al., Preclinical and translational pharmacokinetics of a novel thiomabTM antibody-antibiotic conjugate against staphylococcus aureus, in mAbs, Taylor & Francis, 2019, 1-13.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
H. P. Gerber, F. E. Koehn and R. T. Abraham, The antibody-drug conjugate: an enabling modality for natural product-based cancer therapeutics, Natural Product Reports, 2013, 30(5), 625-639. doi: 10.1039/c3np20113a
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
L. Gibiansky and E. Gibiansky, Target-mediated drug disposition model and its approximations for antibody-drug conjugates, Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, 2014, 41(1), 35-47.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
C. P. Graff and K. D. Wittrup, Theoretical analysis of antibody targeting of tumor spheroids: importance of dosage for penetration, and affinity for retention, Cancer Research, 2003, 63(6), 1288-1296.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
K. J. Hamblett, P. D. Senter, D. F. Chace et al., Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate, Clinical Cancer Research, 2004, 10(20), 7063-7070. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0789
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
N. Jain, S. W. Smith, S. Ghone and B. Tomczuk, Current adc linker chemistry, Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 32(11), 3526-3540. doi: 10.1007/s11095-015-1657-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
M. C. Janin-Bussat, M. Dillenbourg, N. Corvaia et al., Characterization of antibody drug conjugate positional isomers at cysteine residues by peptide mapping lc-ms analysis, Journal of Chromatography B, 2015, 981, 9-13.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
J. Jin, G. Park, J. B. Park et al., An anti-egfr $\times$ cotinine bispecific antibody complexed with cotinine-conjugated duocarmycin inhibits growth of egfr-positive cancer cells with kras mutations, Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 2018, 50(5), 67.
$\times$ cotinine bispecific antibody complexed with cotinine-conjugated duocarmycin inhibits growth of egfr-positive cancer cells with kras mutations" target="_blank">Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
E. Khera, C. Cilliers, S. Bhatnagar and G. M. Thurber, Computational transport analysis of antibody-drug conjugate bystander effects and payload tumoral distribution: implications for therapy, Molecular Systems Design & Engineering, 2018, 3(1), 73-88.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
Y. V. Kovtun, C. A. Audette, Y. Ye et al., Antibody-drug conjugates designed to eradicate tumors with homogeneous and heterogeneous expression of the target antigen, Cancer Research, 2006, 66(6), 3214-3221. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3973
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
A. Krol, J. Maresca, M. W. Dewhirst and F. Yuan, Available volume fraction of macromolecules in the extravascular space of a fibrosarcoma: implications for drug delivery, Cancer Research, 1999, 59(16), 4136-4141.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
F. Li, K. K. Emmerton, M. Jonas et al., Intracellular Released Payload Influences Potency and Bystander-Killing Effects of Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Preclinical Models, Cancer Research, 2016, 76(9), 2710-2719. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1795
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Q. Li, A. Barrett, B. Vijayakrishnan et al., Improved inhibition of tumor growth by diabody-drug conjugates via half-life extension, Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2019, 30(4), 1232-1243. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00170
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
D. E. Mager and W. J. Jusko, General pharmacokinetic model for drugs exhibiting target-mediated drug disposition, Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, 2001, 28(6), 507-532. doi: 10.1023/A:1014414520282
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
D. E. Mager and W. Krzyzanski, Quasi-equilibrium pharmacokinetic model for drugs exhibiting target-mediated drug disposition, Pharmaceutical Research, 2005, 22(10), 1589-1596. doi: 10.1007/s11095-005-6650-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
R. K. Mittapalli, S. Stodtmann, A. Friedel et al., An integrated population pharmacokinetic model versus individual models of depatuxizumab mafodotin, an anti-egfr antibody drug conjugate, in patients with solid tumors likely to overexpress egfr, The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2019.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
A. Mullard, Maturing antibody-drug conjugate pipeline hits 30, 2013.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
N. M. Okeley, J. B. Miyamoto, X. Zhang et al., Intracellular activation of sgn-35, a potent anti-cd30 antibody-drug conjugate, Clinical Cancer Research, 2010, 16(3), 888-897. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2069
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
H. L. Perez, P. M. Cardarelli, S. Deshpande et al., Antibody-drug conjugates: current status and future directions, Drug Discovery Today, 2014, 19(7), 869-881. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.11.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
G. D. L. Phillips, G. Li, D. L. Dugger et al., Targeting her2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-dm1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate, Cancer Research, 2008, 68(22), 9280-9290. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1776
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
L. Schwartz and I. de mathématique (Strasbourg), Théorie des distributions, 2, Hermann Paris, 1957.
Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
A. P. Singh, L. Guo, A. Verma et al., A cell-level systems pk-pd model to characterize in vivo efficacy of adcs, Pharmaceutics, 2019, 11(2), 98. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11020098
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
A. P. Singh and D. K. Shah, A "dual" cell-level systems pk-pd model to characterize the bystander effect of adc, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2019, 108(7), 2465-2475. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2019.01.034
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
A. P. Singh, S. Sharma and D. K. Shah, Quantitative characterization of in vitro bystander effect of antibody-drug conjugates, Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, 2016, 43(6), 567-582. doi: 10.1007/s10928-016-9495-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
A. H. Staudacher and M. P. Brown, Antibody drug conjugates and bystander killing: is antigen-dependent internalisation required?, British Journal of Cancer, 2017, 117(12), 1736. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.367
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
P. A. Trail, Antibody drug conjugates as cancer therapeutics, Antibodies, 2013, 2(1), 113-129.
Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
C. Vasalou, G. Helmlinger and B. Gomes, A mechanistic tumor penetration model to guide antibody drug conjugate design, Plos One, 2015, 10(3), e0118977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118977
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
J. Wang, W. Shen and J. L. Zaro, Antibody-Drug Conjugates: The 21st Century Magic Bullets for Cancer, 17, Springer, 2015.
Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
Wikipedia contributors, Brentuximab vedotin - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 2018.
Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
H. Yao, L. Feng, S. R. Suthe et al., Therapeutic efficacy, pharmacokinetic profiles, and toxicological activities of humanized antibody-drug conjugate zt/g4-mmae targeting ron receptor tyrosine kinase for cancer therapy, Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer, 2019, 7(1), 75. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0525-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: