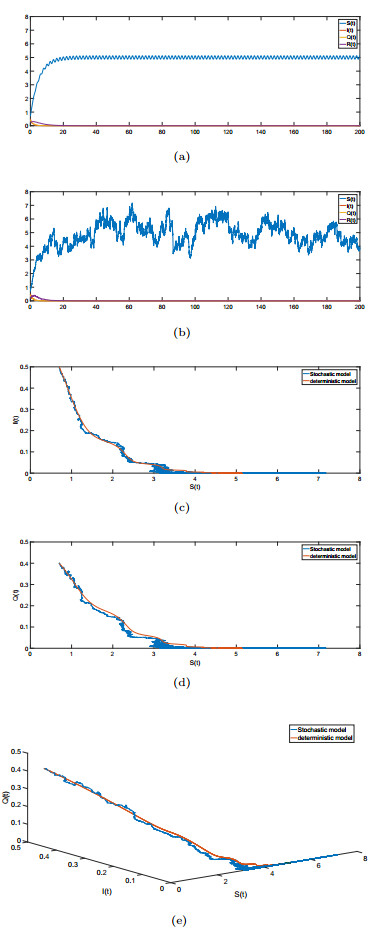
|
[1]
|
P. M. Arguin, A. W. Navin, S. F. Steele, L. H. Weld and P. E. Kozarsky, Health communication during SARS, Emerg. Infect. Dis., 2004, 10, 377-380. doi: 10.3201/eid1002.030812
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
R. Anderson and R. May, Population biology of infectious diseases: part 1., Nature, 1979, 280, 361-367. doi: 10.1038/280361a0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
F. Chen, A susceptible-infected epidemic model with voluntary vaccinations, J. Math. Biol., 2006, 53, 253-272. doi: 10.1007/s00285-006-0006-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
J. Cui, X. Tao and H. Zhu, An SIS infection model incorporating media coverage, Rocky Mountain J. Math., 2008, 38, 1323-1334. doi: 10.1216/RMJ-2008-38-5-1323
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
Y. Cai, Y. Kang, M. Banerjee and W. Wang, A stochastic epidemic model incorporating media coverage, Commun. Math. Sci., 2016, 14(4), 893-910. doi: 10.4310/CMS.2016.v14.n4.a1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
M. De la Sen, S. Alonso Quesada and A. Ibeas, On the stability of an SEIR epidemic model with distributed time-delay and a general class of feedback vaccination rules, Appl. Math. Comput., 2015, 270, 953-976.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
D. Gao and S. Ruan, An SIS path model with variable transmission coefficients, Math. Biosci., 2011, 232, 110-115. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2011.05.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
H. W. Hethcote, The mathemastics of infectious diseases, 2000, 42, 599-653.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
R. Khasminskii, Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations, Springer, Berlin, 2011.
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
T. Kuniya, Existence of a nontrivial periodic solution in an age-structured SIR epidemic model with time periodic coefficiente, Appl. Math. Lett., 2014, 27, 15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2013.08.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
J. Li and Z. Ma, Qualitative analysis of SIS epidemic model with vaccination and varying total population size, Math. Comput. Model., 2002, 35, 1235-1243. doi: 10.1016/S0895-7177(02)00082-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
J. Li and Z. Ma, Stability analysis for SIS epidemic models with vaccination and constant population size, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2004, 4, 635-642.
Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
M. Liu, X. He and J. Yu, Dynamics of a stochastic regime-switching predator-prey model with harvesting and distributed delays, Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst., 2018, 28, 87-104. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.10.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
Q. Liu and D. Jiang, The threshold of a stochastic delayed SIR epidemic model with vaccination, Phys. A, 2016, 461, 140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.05.036
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
Q. Liu, D. Jiang, H. Tasawar and A. Ahmed, Dynamics of a stochastic multigroup SIQR epidemic model with standard incidence rates, Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 365, 2960-2993.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
R. Lipster, A strong law of large numbers for local martingales, Stochastics, 1980, 3, 217-228. doi: 10.1080/17442508008833146
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
W. Liu and X. Zhang, A stochastic SIS epidemic model incorporating media coverage in a two patch setting, Appl. Math. Comput., 2015, 262, 160-168.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
X. Lv, L. Wang and X. Meng, Global analysis of a new nonlinear stochastic differential competition system with impulsive effect, Adv. Differential Equations 2017, 2017, 296.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
Y. Lin, D. Jiang and T. Liu, Nontrivial periodic solution of a stochastic epidemic model with seasonal variation, Appl. Math. Lett., 2015, 45, 103-107. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2015.01.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Z. Ma, Y. Zhou and J. Wu, Modeling and Dynamics of Infectious Diseases, Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2009, In Chinese.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
A. Misra, A. Sharma and J. Shukla, Modeling and analysis of effects of awraencess programs by media on the spread of infectious diaeases, Math. Comput. Model., 2011, 53, 1221-1228. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2010.12.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
M. Ma, S. Liu and J. Li, Does media coverage influence the spread of drug addiction? Commun. Nonlinear Sci., 2017, 50, 169-179. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.03.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
X. Mao, Stationary distribution of stochastic population systems, Systems Control Lett., 2011, 60, 398-405. doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2011.02.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
X. Mao, G. Marion and E. Renshaw, Environmental brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics, Stochastic Process. Appl., 2002, 97, 95-110. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4149(01)00126-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
X. Meng, S. Zhao, T. Feng and T. Zhang, Dynamics of a novel nonlinear stochastic SIS epidemic model with double epidemic hypothesis, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2016, 433, 227-242. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.07.056
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
X. Meng, L. Wang and T. Zhang, Global dynamics analysis of a nonlinear impulsive stochastic chemostat system in a polluted environment, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2016, 6(3), 865-875.
Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
X. Meng, L. Chen and B. Wu, A delay SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination and incubation times, Nonlinear Anal. RWA, 2010, 11, 88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.10.041
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
R. Nistal, M. De la Sen and S. Alonso Quesada, On the stability and equilibrium points of multistaged SI(n)r epidemic models, Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc., 2015, 2015, 15. Article ID: 379576.
Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
C. Sun, W. Yang, J. Arino and K. Khan, Effect of media-induced social distancing on disease transmission in a two patch setting, Math. Biosci., 2011, 230, 221-232.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
E. Shim, Z. Feng, M. Martcheva and C. C. Chavez, An age-structured epidemic model of rotavirus with vaccination, J. Math. Biol., 2006, 53, 719-746. doi: 10.1007/s00285-006-0023-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
H. C. Tuckwell and R. J. Williams, Some properties of a simple stochastic epidemic model of SIR type, Math. Biosci., 2007, 208, 76-97. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.09.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
J. M. Tchuenche, N. Dube, C. P. Bhunu, R. J. Smith and C. T. Bauch, The impact of media coverage on the transmission dynamics of human influenza, BMC Public Health 11, Article S5 2011.
Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
C. Xu, Global threshold dynamics of a stochastic differential equation SIS model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2017, 447(2), 736-757.
Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
Y. Xiao, T. Zhao and S. Tang, Dynamics of an infectious diaeases with media/psychology induced non-smooth incidence, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2013, 10, 445. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2013.10.445
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
X. Yu, Y. Sun and T. Zhang, Persistence and ergodicity of a stochastic single species model with Allee effect under regime switching, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2018, 59, 359-374. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.11.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
F. Zhang and X. Zhao, A periodic epidemic model in a patchy environment, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2007, 325(1), 496-516. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.01.085
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
J. Zhang, Z. Jin, G. Q. Sun, T. Zhou and S. Ruan, Analysis of rabies in china: transmission dynamics and control, PloS One 2011, 6: e20891.
Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
T. Zhang, T. Zhang and X. Meng, Stability analysis of a chemostat model with maintenance energy, Appl. Math. Lett., 2017, 68, 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2016.12.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
Y. Zhang, K. Fan, S. Gao, Y. Liu and S. Chen, Ergodic stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model incorporating media coverage and saturated incidence rate, Phys A, 2019, 514, 671-685. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.124
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
Y. Zhao and D. Jiang, The threshold of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 243, 718-727.
Google Scholar
|




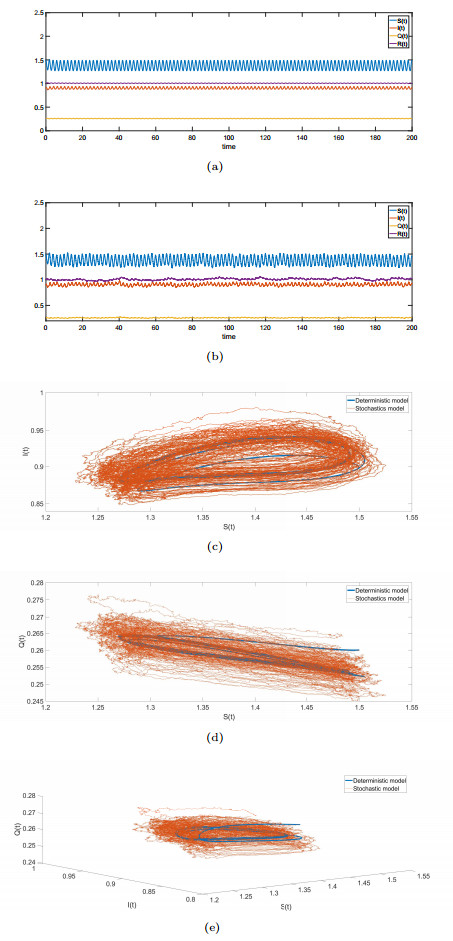

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: