| Citation: | Haiyan Xu, Zhigui Lin, Carlos Alberto Santos. PERSISTENCE, EXTINCTION AND BLOWUP IN A GENERALIZED LOGISTIC MODEL WITH IMPULSES AND REGIONAL EVOLUTION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(5): 1922-1944. doi: 10.11948/20210393 |
PERSISTENCE, EXTINCTION AND BLOWUP IN A GENERALIZED LOGISTIC MODEL WITH IMPULSES AND REGIONAL EVOLUTION
-
Abstract
To explore the impacts of regional evolution and impulses on the persistence or extinction of species, a generalized logistic model with impulses in an evolving domain is proposed and researched. Firstly, the ecological reproduction index, which is regarded as a threshold value, is introduced and characterized. Secondly, in the case of monotone or non-monotone impulsive function, the asymptotic behavior of population is fully investigated and the sufficient conditions for the solution to persist, be extinct or blow up are given. Finally, numerical simulations results indicate that whatever impulse is, larger periodic evolution rates are more favorable for species. However, impulsive harvesting has a negative impact on persistence of species, while birth pulse admits a positive impact and even results in blowup.
-

-
References
[1] B. Adam, Z. Lin and A. K. Tarboush, Asymptotic profile of a mutualistic model on a periodically evolving domain, Int. J. Biomath., 2019, 12(7). [2] L. J. S. Allen, B. M. Bolker, Y. Lou et al., Asymptotic profies of the steady states for an SIS epidemic reaction-diffusion model, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., 2008, 21, 1-20. doi: 10.3934/dcds.2008.21.1 [3] Z. Bai and X. Zhao, Basic reproduction ratios for periodic and time-delayed compartmental models with impulses, J. Math. Biol., 2020, 80(4), 1095-1117. doi: 10.1007/s00285-019-01452-2 [4] R. J. H. Beverton, On the dynamics of exploited fish populations, Reviews in Fish Biology & Fisheries, 1994, 4(2), 259-260. [5] F. Brauer and C. Castillo-Chš¢vez, Mathematical models in population biology and epidemiology, Springer, New York, 2001. [6] R. S. Cantrell and C. Cosner, Spatial ecology via reaction-diffusion equations, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., New York, 2003. [7] E. J. Crampin, E. A. Gaffney and P. K. Maini, Mode-doubling and tripling in reaction-diffusion patterns on growing domains: a piecewise linear model, J. Math. Biol., 2002, 44(2), 107-128. doi: 10.1007/s002850100112 [8] Y. Du and W. Ni, Analysis of a West Nile virus model with nonlocal diffusion and free boundaries, Nonlinearity, 2020, 33(9), 4407-4448. doi: 10.1088/1361-6544/ab8bb2 [9] S. P. Ellner, E. E. Mccauley, B. E. Kendall et al., Habitat structure and population persistence in an Experimental community, Nature, 2001, 412, 538-543. [10] J. Ge, K. I. Kim, Z. Lin and H. Zhu, A SIS reaction-diffusion-advection model in a low-risk and high-risk domain, J. Differential Equations, 2015, 259(10), 5486-5509. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2015.06.035 [11] J. Ge, Z. Lin and H. Zhu, Modeling the spread of West Nile virus in a spatially heterogeneous and advective environment, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2021, 11(4), 1868-1897. [12] R. P. Gupta and P. Chandra, Dynamical properties of a prey-predator-scavenger model with quadratic harvesting, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2017, 49, 202-214. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.01.026 [13] J. Jiao and L. Chen, Dynamical analysis of a delayed predator-prey system with birth pulse and impulsive harvesting at different moments, Adv. Difference Equ., 2010. DOI: 10.1155/2010/954684. [14] D. Jiang and Z. Wang, The diffusive logistic equation on periodically evolving domains, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2018, 458(2), 93-111. [15] K. I. Kim, Z. Lin and Q. Zhang, An SIR epidemic model with free boundary, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2013, 14(5), 1992-2001. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2013.02.003 [16] Y. Kawai, Y. Yamada and M. Zhang, Multiple Spreading phenomena for a free boundary problem of a reaction-diffusion equation with a certain class of bistable nonlinearity, J. Differential Equations, 2016, 261(1), 538-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2016.03.017 [17] S. Kondo, R. Asia and P. Driessche, A reaction-diffusion wave on the skin of the marine angelfish Pomacanthus, Nature, 1995, 376(31), 765-768. [18] M. Kot, M. A. Lewis and P. Driessche, Dispersal data and the spread of invading species, Ecology, 1996, 77(7), 2027-2042. doi: 10.2307/2265698 [19] M. A. Lewis and B. Li, Spreading speed, traveling waves, and minimal domain size in impulsive reaction-diffusion models, Bull. Math. Biol., 2012, 74(10), 2383-2402. doi: 10.1007/s11538-012-9757-6 [20] Z. Liu, S. Zhong, C. Yin et al., Dynamics of impulsive reaction-diffusion predator-prey system with Holling III type functional response, Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2011, 35(12), 5564-5578. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2011.05.019 [21] Y. Lou and X. Zhao, A reaction-diffusion malaria model with incubation period in the vector population, J. Math. Biol., 2011, 62(4), 543-568. doi: 10.1007/s00285-010-0346-8 [22] D. Maity, M. Tucsnak and E. Zuazua, Controllability and positivity constraints in population dynamics with age structuring and diffusion, J. Math. Pures. Appl., 2019, 129(9), 153-179. [23] Y. Meng, Z. Lin and M. Pedersen, A model for spatial spreading and dynamics of fox rabies on a growing domain, Electron. J. Qual. Theory Differ. Equ., 2020, 20, 1-14. [24] Y. Meng, Z. Lin and M. Pedersen, Effects of impulsive harvesting and an evolving domain in a diffusive logistic model, Nonlinearity, 2021, 34(10), 7005-7029. doi: 10.1088/1361-6544/ac1f78 [25] A. Okubo and S. Levin, Diffusion and ecological problems, Springer, New York, 2001. [26] R. Peng and X. Zhao, A reaction-diffusion SIS epidemic model in a time-periodic environment, Nonlinearity, 2012, 25(5), 1451-1471. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/25/5/1451 [27] L. Pu and Z. Lin, Effects of depth and evolving rate on phytoplankton growth in a periodically evolving environment, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2021, 493(1), 124502. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2020.124502 [28] J. Shang, B. Li and M. R. Barnard, Bifurcations in a discrete time model composed of Beverton-Holt function and Ricker function, Mathematical Biosciences, 2015, 263, 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2015.02.014 [29] S. Tang and L. Chen, Modelling and analysis of integrated pest management strategy, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., 2012, 4(3), 759-768. [30] A. M. Turing, The chemical basis of morphogenesis, Bull. Math. Biol., 1952, 237(641), 37-72. [31] N. Wang, L. Zhang and Z. Teng, A reaction-diffusion model for nested within-host and between-host dynamics in an environmentally-driven infectious disease, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2021, 11(4), 1898-1926. [32] W. Wang and X. Zhao, Basic reproduction numbers for reaction-diffusion epidemic models, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2012, 11(4), 1652-1673. doi: 10.1137/120872942 [33] R. Wu and X. Zhao, Spatial invasion of a birth pulse population with nonlocal dispersal, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2019, 79(3), 1075-1097. doi: 10.1137/18M1209805 [34] H. Xu, J. Ge and Z. Lin, The Diffusive Characteristics of the Generalized Logistic Model on an Evolving Domain, Journal of jiangxi Normal University, 2020, 44(4), 19-23. [35] M. Zhang and Z. Lin, A reaction-diffusion-advection model for Aedes aegypti mosquitoes in a time-periodic environment, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2019, 46, 219-237. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2018.09.014 [36] X. Zhao, Dynamical systems in population biology, Second edition, CMS Books in Mathematics, Springer, Cham, 2017. -
-
-
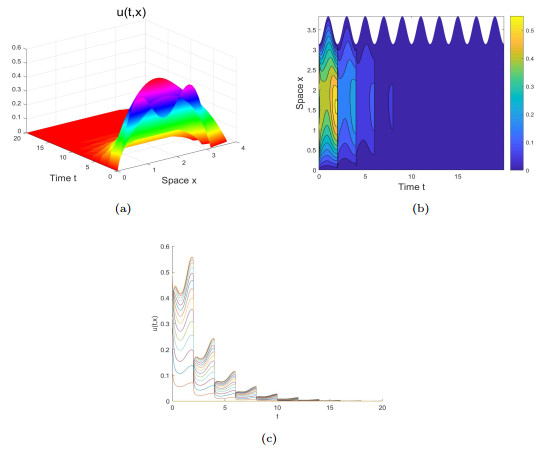
Figure 1. For a smaller evolution rate
$ \rho_1(t)=e^{-0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ , we obtain$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{0.993}<1 $ . Graphs (a)-(c) show that$ u(t, x) $ gradually tends to zero with time$ t $ . It can be seen from Graph (c) that the impulse occurs at each time$ T=2 $ . -
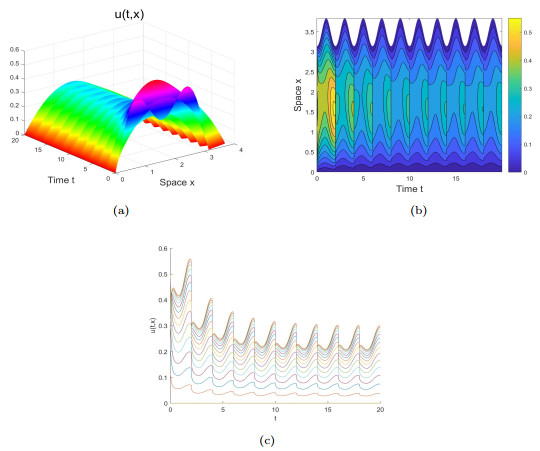
Figure 2. For bigger evolution rate
$ \rho_2(t)=e^{-0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ , we obtain$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{1.496}>1 $ . is calculated. Graphs (a)-(c) characterize the population density stabilizes to a equilibrium state in a periodic evolving domain. -
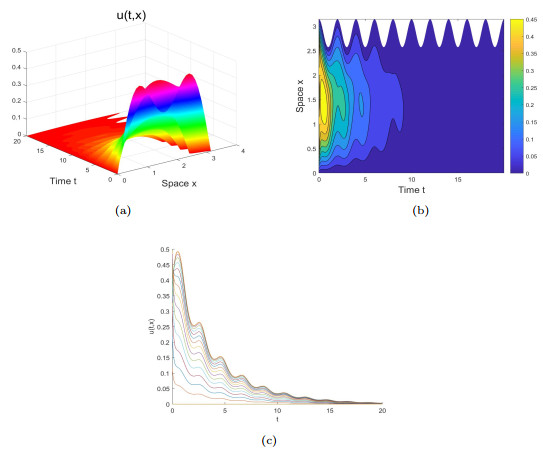
Figure 3. A numerical simulation to the graph of
$ u(t, x) $ without impulses by choosing$ \rho_1(t)=e^{-0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ .$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{0.973} <1 $ , Graphs (a)-(c) depict that the species finally tends to vanish. -
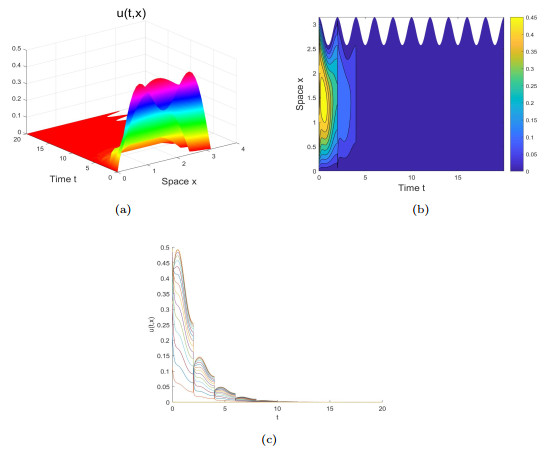
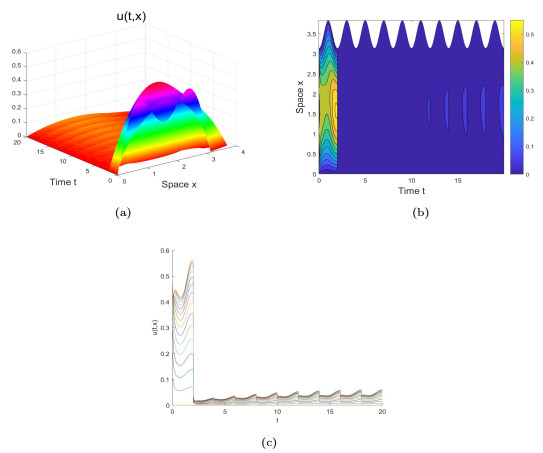
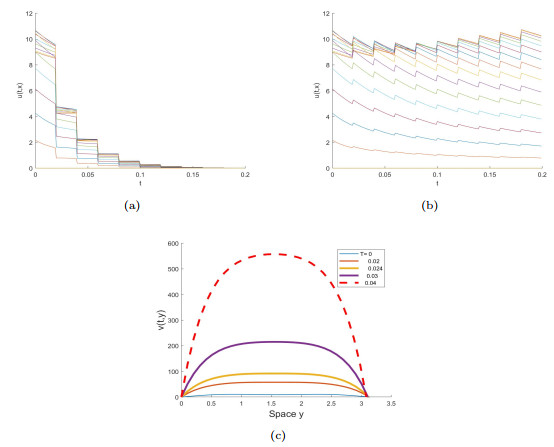
Figure 4. For the smaller evolution rate, Beverton-Holt impulse with
$ m=8, a=10 $ , we acquire$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{0.892}<1 $ .Graphs (a)-(c) describe that the population density decays to zero. It can be seen from Graph (c) that the impulse arises at each time$ T=2 $ . -
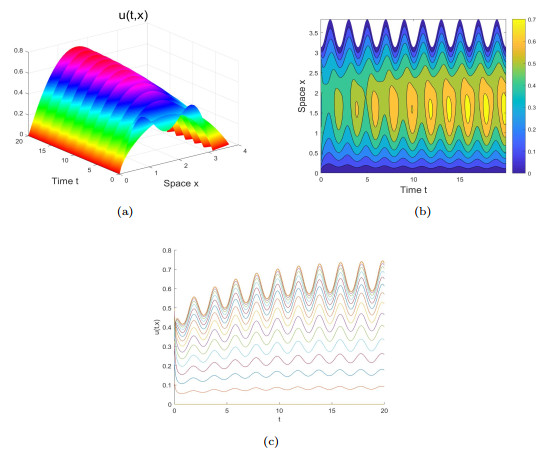
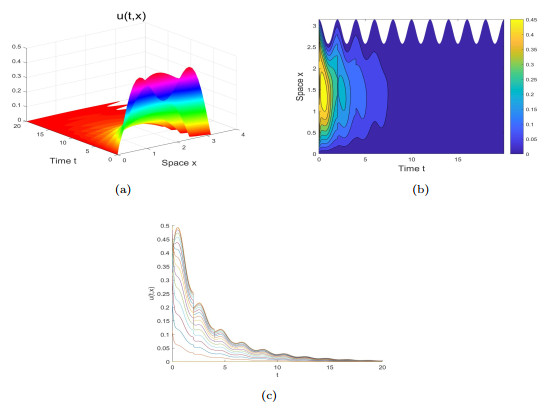
Figure 5. Without impulses, a numerical approximation to the graph of
$ u(t, x) $ . By choosing$ \rho_2(t)=e^{0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ ,$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{1.451}>1 $ . Graphs (a)-(c) show that the population gradually tends to a steady state. -
Figure 6.
$ \rho_2(t)=e^{0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ and Beverton-Holt function with$ m=4, a=10 $ are given, such that$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{0.934}<1 $ . Graphs (a)-(c) portray that population density$ u(t, x) $ decays ultimately to zero. -
Figure 7.
$ \rho_2(t)=e^{0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ , Ricker function with parameter values$ r=0.05 $ and$ b=8 $ are given such that$ {\mathcal{R}}_0\approx{1.496}>1 $ . Graphs (a)-(c) characterize that the population stabilizes to a smaller positive steady state. -
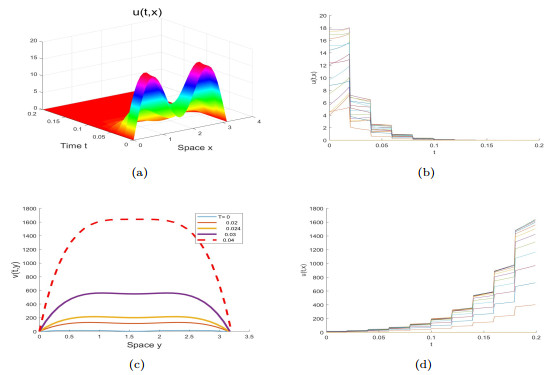
Figure 8.
$ \rho_2(t)=e^{0.1(1-\cos{\pi{t}})} $ and big initial value$ v_0(y)=14\sin{x}+10\sin{3x} $ . Graphs (a) and (b) with$ c=0.4(<1) $ characterizes the solution tends to zero, while$ c=1.5(>1) $ in Graphs (c) and (d) means$ u(t, x) $ still blow up. -
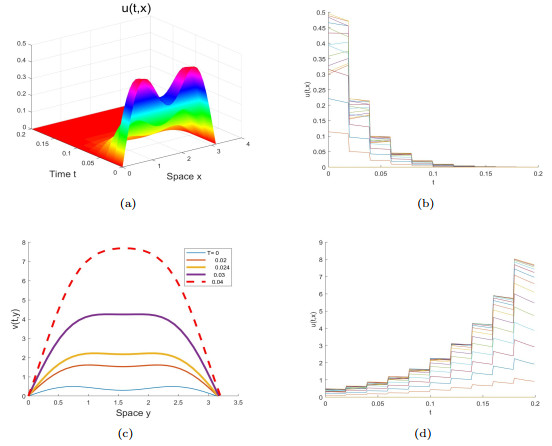
Figure 9. Graphs (a) and (b) means the population will be extinct with
$ c=0.47(<1) $ , while Graphs (c)-(d) indicate the solution will blow up with$ c=1.4(>1) $ . -
Figure 10. Graph (a) means
$ u(t, x) $ decays to zero with$ c=0.5(c<1) $ , Graph (b) characterizes the population stabilizes to a steady state with$ c=1.07(>1) $ , and Graph (c) indicates that the solution will blow up when$ c=1.4(>1) $ .




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: