| Citation: | Jian Liu, Qian Ding, Hongpeng Guo, Bo Zheng. DYNAMICS OF AN EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH RELAPSE AND DELAY[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(4): 2317-2336. doi: 10.11948/20230376 |
DYNAMICS OF AN EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH RELAPSE AND DELAY
-
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a new epidemiological model with delay and relapse phenomena. Firstly, a basic reproduction number $ R_0 $ is identified, which serves as a threshold parameter for the stability of the equilibria of the model. Then, beginning with the delay-free model, the global asymptotic stability of the equilibria is obtained through the construction of suitable Lyapunov functions. For the delay model, the stability of the positive equilibrium and the existence of the local Hopf bifurcation are discussed. Furthermore, the application of the normal form theory and center manifold theorem is used to determine the direction and stability of these Hopf bifurcations. Finally, we shed light on corresponding biological implications from a numerical perspective. It turns out that time delay affects the stability of the positive equilibrium, leading to the occurrence of periodic oscillations and disease recurrence.
-
Keywords:
- Delay /
- relapse /
- stability /
- persistence /
- hopf bifurcation
-

-
References
[1] H. Akkocaoğlu, H. Merdan and C. Çelik, Hopf bifurcation analysis of a general non-linear differential equation with delay, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2013, 237(1), 565–575. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2012.06.029 [2] C. Castillo-Garsow, G. Jordan-Salivia and A. Rodriguez-Herrera, Mathematical models for the dynamics of tobacco use, recovery, and relapse, Technical Report Series BU–1505–M, Cornell University, New York, 1997. [3] Y. M. Chen, J. Q. Li and S. F. Zou, Global dynamics of an epidemic model with relapse and nonlinear incidence, Math. Methods Appl. Sci., 2019, 42(4), 1283–1291. doi: 10.1002/mma.5439 [4] J. Chin, Control of Communicable Diseases Manual, American Public Health Association, Washington, 1999. [5] Q. Ding, Y. F. Liu, Y. M. Chen and Z. M. Guo, Dynamics of a reaction-diffusion SIRI model with relapse and free boundary, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 17(2), 1659–1676. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020087 [6] Y. Enatsu, E. Messina and Y. Muroya, Stability analysis of delayed SIR epidemic models with a class of nonlinear incidence rates, Appl. Math. Comput., 2012, 218(9), 5327–5336. [7] Y. Fan, Pattern formation of a spatial epidemic model with standard incidence rate, Indian J. Phys., 2014, 88, 413–419. doi: 10.1007/s12648-013-0431-0 [8] M. N. Frioui, T. M. Touaoula and B. Ainseba, Global dynamics of an age-structured model with relapse, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2020, 25(6), 2245–2270. [9] D. Greenhalgh, Q. J. A. Khan and F. I. Lewis, Hopf bifurcation in two SIRS density dependent epidemic models, Math. Comput. Modeling, 2004, 39(11–12), 1261–1283. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2004.06.007 [10] J. K. Hale, Oscillations in Neutral Functional Differential Equations, Non-Linear Mechanics, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2010. [11] B. D. Hassard, N. D. Kazarinoff and Y. H. Wan, Theory and Applications of Hopf Bifurcation, Cambrige University Press, New York, 1981. [12] M. W. Hirsch, S. Smale and R. L. Devaney, Differential Equations, Dynamical Systems, and an Introduction to Chaos, Academic Press, 2013. [13] W. O. Kermack and A. G. McKendrick, A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics, Pro. R. Soc. Lond. A., 1927, 115(772), 700–721. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1927.0118ticle/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202205003.htm [14] W. O. Kermack and A. G. McKendrick, Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics, II. The problem of endemicity, Pro. R. Soc. Lond. A., 1932, 138(A), 55–83. [15] Y. N. Kyrychko and K. B. Blyuss, Global properties of a delayed SIR model with temporary immunity and nonlinear incidence rate, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2005, 6(3), 495–507. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2004.10.001 [16] S. W. Martin, Livestock Disease Eradication: Evaluation of the Cooperative State-Federal Bovine Tuberculosis Eradication Program, National Academy Press, 1994. [17] H. Moreira and Y. Wang, Global stability in a $S\to I\to R\to I$ model, SIAM Rev., 1997, 39, 497–502. [18] H. L. Smith, An Introduction to Delay Differential Equations with Applications to the Life Sciences, Springer, New York, 2011. [19] B. Sounvoravong and S. J. Guo, Dynamics of a diffusive SIR epidemic model with time delay, J. Nonl. Mod. Anal., 2019, 1(3), 319–334. [20] X. H. Tian, R. Xu, N. Bai and J. Z. Lin, Bifurcation analysis of an age-structured SIRI epidemic model, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 17(6), 7130–7150. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020366 [21] D. Tudor, A deterministic model for herpes infections in human and animal populations, SIAM Rev., 1990, 32(1), 136–139. doi: 10.1137/1032003 [22] P. van den Driessche, L. Wang and X. F. Zou, Modeling diseases with latency and relapse, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2007, 4(2), 205–219. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2007.4.205 [23] P. van den Driessche and X. F. Zou, Modeling relapse in infectious diseases, Math. Biosci., 2007, 207(1), 89–103. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.09.017 [24] K. E. VanLandingham, H. B. Marsteller, G. W. Ross and F. G. Hayden, Relapse of herpes simplex encephalitis after conventional acyclovir therapy, JAMA, 1988, 259(7), 1051–1053. doi: 10.1001/jama.1988.03720070051034 [25] C. Vargas-De-León, On the global stability of infectious diseases models with relapse, Abstraction Appl., 2013, 9, 50–61. [26] J. L. Wang and H. Y. Shu, Global analysis on a class of multi-group SEIR model with latency and relapse, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2007, 13(1), 209–225. [27] L. Wang and W. Yang, Global dynamics of a two-patch SIS model with infection during transport, Appl. Math. Comput., 2011, 217(21), 8458–8467. [28] R. Xu, Global dynamics of a delayed epidemic model with latency and relapse, Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control, 2013, 18(2), 250–263. doi: 10.15388/NA.18.2.14026 [29] R. Xu, Global dynamics of an SEIRI epidemiological model with time delay, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 232(1), 436–444. [30] D. X. Yan and X. F. Zou, Dynamics of an epidemic model with relapse over a two-patch environment, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 17(5), 6098–6127. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020324 [31] Y. Yang, T. S. Abdullah, G. Huang and Y. P. Dong, Mathematical analysis of SIR epidemic model with piecewise infection rate and control strategies, J. Nonl. Mod. Anal., 2023, 5(3), 524–539. [32] Y. L. Yang, J. H. Wu, J. Q. Li and X. X. Xu, Tuberculosis with relapse: A model, Math. Popul. Stud., 2017, 24(1), 3–20. doi: 10.1080/08898480.2014.998550 [33] M. Zhao, W. T. Li and Y. Zhang, Dynamics of an epidemic model with advection and free boundaries, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 16(5), 5991–6014. -
-
-
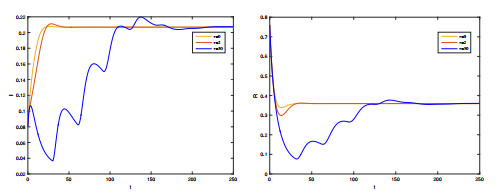
Figure 1.
With parameters given in (5.1), three curves of
$ I(t) $ $ R(t) $ $ \tau=0, 15 $ -
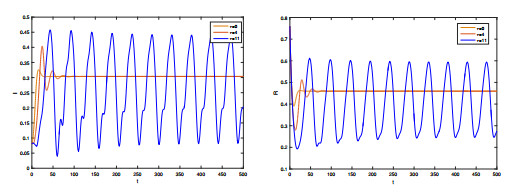
Figure 2.
In the case of
$ \tau=0, 2, 30 $ $ R_0=2.643>1 $ $ E^* $ -
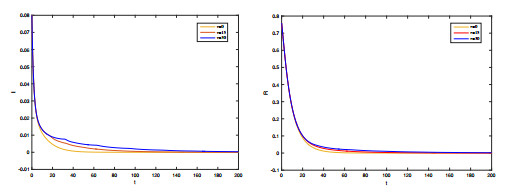
Figure 3.
When
$ \tau=0, 4, 11 $ $ E^* $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: