| Citation: | Yan Xu, Hexin Zhu. DIRECTED SEARCH PROCESS DRIVEN BY LÉVY MOTION WITH STOCHASTIC RESETTING[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(1): 137-159. doi: 10.11948/20230466 |
DIRECTED SEARCH PROCESS DRIVEN BY LÉVY MOTION WITH STOCHASTIC RESETTING
-
Abstract
In this paper, we demonstrate how certain active transport processes in living cells can be modeled based on a directed search process driven by Lévy motion with stochastic resetting. We focus on the motor-driven intracellular transport of vesicles to synaptic targets in the axons and dendrites of neurons, where the restart duration of the search process after reset is finite, and comprises a finite return time and a refractory period. We employ a probabilistic renewal method to calculate the splitting probabilities and conditional mean first passage times (MFPTs) for capture by a finite array of contiguous targets. We consider two different search scenarios: bounded search on the interval $ [0,L] $, where $ L $ denotes the length of the array, with a refractory boundary at $ x=0 $ and a reflecting boundary at $ x=L $ (Model A), and partially bounded search on the half-line (Model B). In the latter case, the probability that the particle cannot find a target in the absence of resetting is nonzero. We show that both models have the same splitting probability, and that increasing the resetting rate $ r $ increases the splitting probability. Furthermore, the MFPTs of Model A are monotonically increasing with respect to $ r $, whereas the MFPTs of Model B are nonmonotone with respect to $ r $, with a minimum at an optimal resetting rate.
-
Keywords:
- Stochastic resetting /
- search processes /
- renewal theory /
- Lévy motion
-

-
References
[1] F. Bartumeus and J. Catalan, Optimal Search Behaviour and Classic Foraging Theory, Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, 2009. DOI: 10.1088/1751-8113/42/43/434002. [2] O. Bénichou, M. Coppey, M. Moreau, et al., Optimal Search Strategies for Hidden Targets, Physical Review Letters, 2005. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.198101. [3] H. C. Berg, Random Walks in Biology, Princeton University Press, New York, 1993. [4] A. S. Bodrova, A. V. Chechkin and I. M. Sokolov, Nonrenewal resetting of scaled Brownian motion, Physical Review E, 2019, 100(1). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.012119. [5] A. S. Bodrova, A. V. Chechkin and I. M. Sokolov, Scaled Brownian Motion with Renewal Resetting, Physical Review E, 2019. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.012120. [6] P. C. Bressloff and H. Kim, Search-and-capture model of cytoneme-mediated morphogen gradient formation, Physical Review E, 2019, 99(5). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.99.052401. [7] M. Coppey, O. Bénichou, R. Voituriez and M. Moreau, Kinetics of target site localization of a protein on DNA: A stochastic approach, Biophysical Journal, 2004, 87(3), 1640-1649. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.045773 [8] M. R. Evans and S. N. Majumdar, Diffusion with stochastic resetting, Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106(16), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.160601. [9] M. R. Evans, S. N. Majumdar and G. Schehr, Stochastic resetting and applications, Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, 2020, 53(19). DOI: 10.1088/1751-8121/ab7cfe. [10] E. Gelenbe, Search in Unknown Random Environments, Physical Review E-Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2010. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.82.061112. [11] L. Kusmierz and E. Gudowska-Nowak, Optimal first-arrival times in Lévy flights with resetting, Physical Review E, 2015, 92(5). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.052127. [12] L. Kusmierz, S. N. Majumdar, S. Sabhapandit, et al., First order transition for the optimal search time of Lévy flights with resetting, Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(22). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.220602. [13] M. A. Lomholt, K. Tal, R. Metzler, et al., Lévy strategies in intermittent search processes are advantageous, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(32), 11055-11059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803117105 [14] S. C. Manrubia and D. H. Zanette, Stochastic multiplicative processes with reset events, Physical Review E, 1999, 59(5), 4945-4948. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.59.4945 [15] V. Méndez and D. Campos, Characterization of stationary states in random walks with stochastic resetting, Physical Review E, 2016, 93(2). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.93.022106. [16] A. Montanari and R. Zecchina, Optimizing searches via rare events, Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88(17). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.178701. [17] M. Montero and J. Villarroel, Continuous-time random walks with drift and stochastic reset events, Physical Review E-Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2013, 87(1). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.87.012116. [18] S. Reuveni, M. Urbakh and J. Klafter, Role of substrate unbinding in Michaelis-Menten enzymatic reactions, PNAS, 2014, 111(12), 4391-4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318122111 [19] T. Robin, S. Reuveni and M. Urbakh, Single-molecule theory of enzymatic inhibition, Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1), 779. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-02995-6. [20] E. Roldán, A. Lisica, D. Sánchez-Taltavull, et al., Stochastic resetting in backtrack recovery by RNA polymerases with Riemann-Liouville fractional derivative, Physical Review E, 2016, 93(6). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.93.062411. [21] T. Rotbart, S. Reuveni and M. Urbakh, Michaelis-Menten reaction scheme as a unified approach towards the optimal restart problem, Physical Review E, 2015, 92(6). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.060101. [22] V. P. Shkilev, Continuous-time random walk under time-dependent resetting, Physical Review E, 2017, 96(1). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.96.012126. [23] X. Sun and J. Duan, Fokker-Planck equations for nonlinear dynamical systems driven by non-Gaussian Lévy processes, Journal of Mathematical Physics, 2012, 53(7), 164-172. [24] H. Zhu, G. ER, I. V. Pan, et al., PDE Solution to Nonlinear Stochastic Dynamic Systems Driven by Poisson White Noise, Proceedings of the 6th National Civil Engineering Graduate Academic Forum, 2008. -
-
-
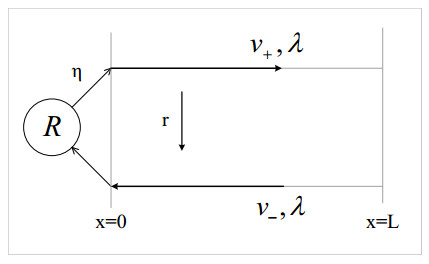
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of particle states: anterograde state with speed
$ v_+ $ $ v_- $ $ R $ $ \tau $ $ \psi(\tau)=\eta e^{-\eta\tau} $ $ r $ -
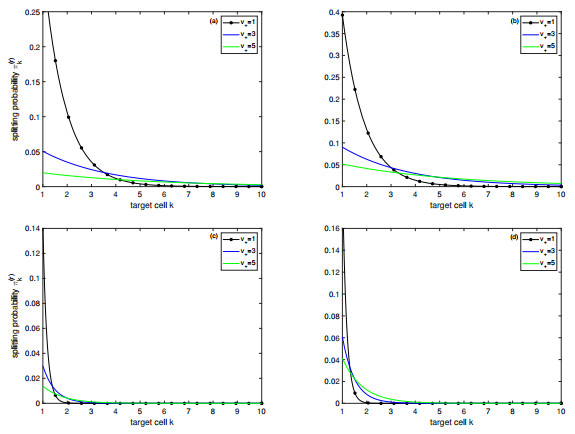
Figure 2.
Plots of the splitting probability
$ \pi_k^{(r)} $ $ k $ $ k=1,...,10 $ $ v_+ $ $ r=0.1 $ $ x=0 $ $ r=0.1 $ $ x=0.1 $ $ r=5 $ $ x=0 $ $ r=5 $ $ x=0.1 $ $ \lambda=0.1 $ -
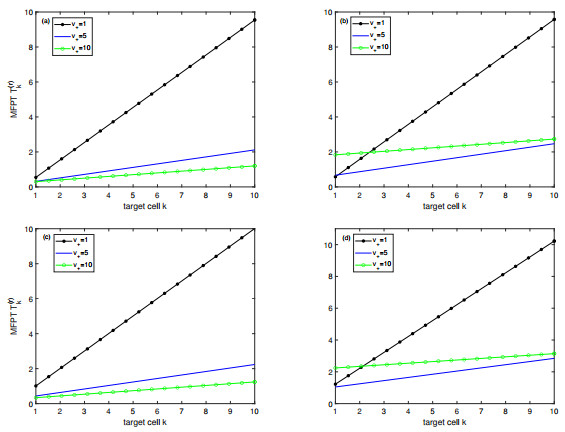
Figure 3.
Plots of conditional MFPT
$ T_k^{(r)} $ $ k $ $ k=1,...,10 $ $ v_+ $ $ r=0.1 $ $ x=0 $ $ r=0.1 $ $ x=0.1 $ $ r=1 $ $ x=0 $ $ r=1 $ $ x=0.1 $ $ v_-=1 $ $ \eta=1 $ $ \lambda=0.1 $ -
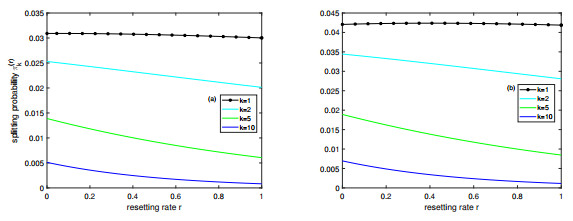
Figure 4.
Plots of the splitting probability
$ \pi_k^{(r)} $ $ r $ $ k $ $ x=0 $ $ x=0.05 $ $ v_+=5 $ $ v_-=1 $ $ \eta=1 $ $ \lambda=1 $ -
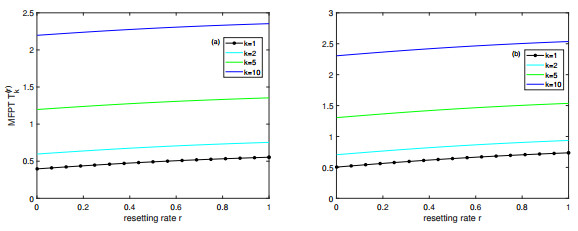
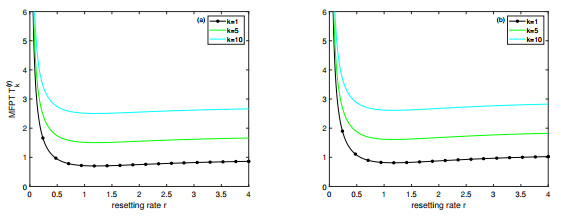
Figure 5.
Plots of conditional MFPT
$ T_k^{(r)} $ $ r $ $ x=0 $ $ x=0.05 $ $ v_+=5 $ $ v_-=1 $ $ \eta=1 $ $ \lambda=1 $ -
Figure 6.
Model B. Plots of conditional MFPT
$ T_k^{(r)} $ $ r $ $ x=0 $ $ x=0.05 $ $ v_+=5 $ $ v_-=1 $ $ \eta=1 $ $ \lambda=15 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: