| Citation: | Shuo Wang, Li Sun, Yumei Huang. A MODULUS ITERATION METHOD FOR NONNEGATIVELY CONSTRAINED PHOTOACOUSTIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(5): 3185-3206. doi: 10.11948/20240453 |
A MODULUS ITERATION METHOD FOR NONNEGATIVELY CONSTRAINED PHOTOACOUSTIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION
-
Abstract
The photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is a new biomedical imaging modality. Its assistance in early clinical diagnosis has become more and more important in the medical field. In the PAT imaging system, when a beam of short-pulsed laser irradiates the biological tissue, the photoacoustic effect results in the generation of the acoustic waves in the tissue. The initial acoustic pressure appearing in the tissue reveals the structures of the tissue. The PAT reconstruction problem aims to obtain the initial acoustic pressure in the tissue from the collected photoacoustic signal informations. In this paper, we propose a nonnegatively constrained PAT reconstruction model regularized by a hybrid Gaussian-Laplacian mixture term. The model can be reformulated as a nonnegatively constrained quadratic programming problem with a positive definite coefficient matrix and it is shown to be equivalent to a linear complementarity problem. We apply a modulus iteration method to solve the linear complementarity problem and its convergence is also demonstrated. Numerical results illustrate that the proposed method is competitive with the existing efficient methods for the PAT reconstruction problem.
-

-
References
[1] B. H. Ahn, Solution of nonsymmetric linear complementarity problems by iterative methods, J. Optim. Theory Appl., 1981, 33(2), 175-185. doi: 10.1007/BF00935545 [2] S. Antholzer, M. Haltmeier and J. Schwab, Deep learning for photoacoustic tomography from sparse data, Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng., 2019, 27(7), 987-1005. doi: 10.1080/17415977.2018.1518444 [3] S. Arridge, P. Beard and M. Betcke, Accelerated high-resolution photoacoustic tomography via compressed sensing, Phys. Med. Biol., 2016, 61(24), 8908. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/61/24/8908 [4] Z. Bai, On the convergence of the multisplitting methods for the linear complementarity problem, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 1999, 21(1), 67-78. doi: 10.1137/S0895479897324032 [5] Z. Bai, Modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods for linear complementarity problems, Numer. Linear Algebra Appl., 2010, 17(6), 917-933. doi: 10.1002/nla.680 [6] Z. Bai, A. Buccini, K. Hayami, L. Reichel, J. Yin and N. Zheng, Modulus-based iterative methods for constrained Tikhonov regularization, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2017, 319, 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2016.12.023 [7] Z. Bai and D. J. Evans, Matrix multisplitting relaxation methods for linear complementarity problems, Int. J. Comput. Math., 1997, 63(3-4), 309-326. doi: 10.1080/00207169708804569 [8] Z. Bai and D. J. Evans, Matrix multisplitting methods with applications to linear complementarity problems: Parallel asynchronous methods, Int. J. Comput. Math., 2002, 79(2), 205-232. doi: 10.1080/00207160211927 [9] Z. Bai, G. H. Golub and M. K. Ng, Hermitian and skew-Hermitian splitting methods for non-Hermitian positive definite linear systems, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 2003, 24(3), 603-626. doi: 10.1137/S0895479801395458 [10] A. G. Bell, On the production and reproduction of sound by light, Am. J. Sci., 1880, 118(3), 305-324. [11] X. L. Dean-Ben, A. Buehler and V. Ntziachristos, Accurate model-based reconstruction algorithm for three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2012, 31(10), 1922-1928. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2012.2208471 [12] X. L. Dean-Ben, V. Ntziachristos and D. Razansky, Acceleration of optoacoustic model-based reconstruction using angular image discretization, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2012, 31(5), 1154-1162. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2012.2187460 [13] W. M. G. van Bokhoven, Piecewise Linear Modeling and Analysis, Proefschrift, Eindhoven, 1981. [14] A. Buccini, M. Pasha and L. Reichel, Modulus-based iterative methods for constrained $l_p-l_q$ minimization, Inverse Probl., 2020, 36(8), 084001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6420/ab9f86 [15] R. W. Cottle, J. Pang and R. E Stone, The Linear Complementarity Problem, Academic Press, San Diego, 1992. [16] C. W. Cryer, The solution of a quadratic programming problem using systematic overrelaxation, SIAM J. Control Optim., 1971, 9(3), 385-392. doi: 10.1137/0309028 [17] L. Ding, X. L. Dean-Ben and C. Lutzweiler, Efficient non-negative constrained model-based inversion in optoacoustic tomography, Phys. Med. Biol., 2015, 60(17), 6733. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/17/6733 [18] L. Ding, X. L. Dean-Ben and D. Razansky, Real-time model-based inversion in cross-sectional optoacoustic tomography, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2016, 35(8), 1883-1891. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2536779 [19] J. Dong, J. Gao, F. Ju and J. Shen, Modulus methods for nonnegatively constrained image restoration, SIAM J. Imaging Sci., 2016, 9(3), 1226-1246. doi: 10.1137/15M1045892 [20] J. Dong and M. Jiang, A modified modulus method for symmetric positive-definite linear complementarity problems, Numer. Linear Algebra Appl., 2009, 16(2), 129-143. doi: 10.1002/nla.609 [21] Y. Dong, T. Görner and S. Kunis, An algorithm for total variation regularized photoacoustic imaging, Adv. Comput. Math., 2015, 41, 423-438. doi: 10.1007/s10444-014-9364-1 [22] Y. Gao, W. Xu, Y. Chen, W. Xie and Q. Cheng, Deep learning-based photoacoustic imaging of vascular network through thick porous media, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2022, 41(8), 2191-2204. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2022.3158474 [23] S. Gutta, S. K. Kalva, M. Pramanik and P. K. Yalavarthy, Accelerated image reconstruction using extrapolated Tikhonov filtering for photoacoustic tomography, Med. Phys., 2018, 45(8), 3749-3767. doi: 10.1002/mp.13023 [24] Y. Han, L. Ding and X. L. Dean-Ben, Three-dimensional optoacoustic reconstruction using fast sparse representation, Opt. Lett., 2017, 42(5), 979-982. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.000979 [25] Y. Hristova, P. Kuchment and L. Nguyen, Reconstruction and time reversal in thermoacoustic tomography in acoustically homogeneous and inhomogeneous media, Inverse Probl., 2008, 24(5), 055006. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/24/5/055006 [26] K. T. Hsu, S. Guan and P. V. Chitnis, Fast iterative reconstruction for photoacoustic tomography using learned physical model: Theoretical validation, Photoacoustics, 2023, 29, 100452. doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2023.100452 [27] M. J. John and I. Barhumi, Fast and efficient PAT image reconstruction algorithms: A comparative performance analysis, Signal Processing, 2022, 201, 108691. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2022.108691 [28] R. A. Kruger, P. Liu and Y. Fang, Photoacoustic ultrasound (PAUS)-reconstruction tomography, Med. Phys., 1995, 2(10), 1605-1609. [29] L. A. Kunyansky, Explicit inversion formulae for the spherical mean Radon transform, Inverse Probl., 2007, 23(1), 373. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/23/1/021 [30] X. Li, L. Qi and S. Zhang, Model-based optoacoustic tomography image reconstruction with non-local and sparsity regularizations, IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 102136-102148. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2930650 [31] Y. Lou, W. Zhou and T. P. Matthews, Generation of anatomically realistic numerical phantoms for photoacoustic and ultrasonic breast imaging, J. Biomed. Opt., 2017, 22(4), 041015. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.22.4.041015 [32] O. L. Mangasarian, Solutions of symmetric linear complementarity problems by iterative methods, J. Optim. Theory Appl., 1977, 22(4), 465-485. doi: 10.1007/BF01268170 [33] K. G. Murty and F. Yu, Linear Complementarity, Linear and Nonlinear Programming, Heldermann-Verlag, Berlin, 1988. [34] S. Na and L. V. Wang, Photoacoustic computed tomography for functional human brain imaging, Biomed. Opt. Express, 2021, 12(7), 4056-4083. doi: 10.1364/BOE.423707 [35] B. Pan, S. R. Arridge and F. Lucka, Photoacoustic reconstruction using sparsity in curvelet frame: Image versus data domain, IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging, 2021, 7, 879-893. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2021.3103606 [36] J. Prakash, S. Mandal and D. Razansky, Maximum entropy based non-negative optoacoustic tomographic image reconstruction, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 2019, 66(9), 2604-2616. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2892842 [37] R. Prakash, D. Badal, A. Paul, D. Sonker and R. K. Saha, Photoacoustic signal simulation using discrete particle approach and its application in tomography, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, 2020, 68(3), 707-717. [38] C. B. Shaw, J. Prakash and M. Pramanik, Least squares QR-based decomposition provides an efficient way of computing optimal regularization parameter in photoacoustic tomography, J. Biomed. Opt., 2013, 18(8), 080501. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.8.080501 [39] K. Sivasubramanian, V. Periyasamy and M. Pramanik, Non-invasive sentinel lymph node mapping and needle guidance using clinical handheld photoacoustic imaging system in small animal, J. Biophotonics, 2018, 11(1), e201700061. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201700061 [40] B. Stephanian, M. T. Graham and H. Hou, Additive noise models for photoacoustic spatial coherence theory, Biomed. Opt. Express, 2018, 9(11), 5566-5582. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.005566 [41] Q. Huynh-Thu and M. Ghanbari, Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment, Electron. Lett., 2008, 44(13), 800-801. doi: 10.1049/el:20080522 [42] B. E. Treeby and B. T. Cox, k-Wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields, J. Biomed. Opt., 2010, 15(2), 021314. doi: 10.1117/1.3360308 [43] P. Tseng, On linear convergence of iterative methods for the variational inequality problem, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 1995, 60(1-2), 237-252. doi: 10.1016/0377-0427(94)00094-H [44] T. Wang, M. He, K. Shen, W. Liu and C. Tian, Learned regularization for image reconstruction in sparse-view photoacoustic tomography, Biomed. Opt. Express, 2022, 13(11), 5721-5737. doi: 10.1364/BOE.469460 [45] Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh and E. P. Simoncelli, Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity, IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2004, 13(4), 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [46] Z. Wang, Z. Han and R. Hu, Noise robust face hallucination employing Gaussian-Laplacian mixture model, Neurocomputing, 2014, 133, 153-160. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.11.021 [47] Z. Wang, H. Wang and S. Ren, Research on ADMM reconstruction algorithm of photoacoustic tomography with limited sampling data, IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 113631-113641. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3104154 [48] M. Xu and L. V. Wang, Time-domain reconstruction for thermoacoustic tomography in a spherical geometry, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2002, 21(7), 814-822. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2002.801176 [49] M. Xu and L. V. Wang, Universal back-projection algorithm for photoacoustic computed tomography, Phys. Rev. E., 2005, 71(1), 016706. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.71.016706 [50] M. Xu and L. V. Wang, Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2006, 77(4), 041101. doi: 10.1063/1.2195024 [51] M. Xu, Y. Xu and L. V. Wang, Time-domain reconstruction algorithms and numerical simulations for thermoacoustic tomography in various geometries, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 2003, 50(9), 1086-1099. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2003.816081 [52] Y. Xu, D. Feng and L. V. Wang, Exact frequency-domain reconstruction for thermoacoustic tomography, I. Planar geometry, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2002, 21(7), 823-828. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2002.801172 [53] Y. Xu and L. V. Wang, Time reversal and its application to tomography with diffracting sources, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2004, 92(3), 033902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.033902 [54] Y. Xu, M. Xu and L. V. Wang, Exact frequency-domain reconstruction for thermoacoustic tomography, Ⅱ. Cylindrical geometry, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2002, 21(7), 829-833. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2002.801171 [55] P. K. Yalavarthy, S. K. Kalva and M. Pramanik, Non-local means improves total-variation constrained photoacoustic image reconstruction, J. Biophotonics, 2021, 14(1), e202000191. doi: 10.1002/jbio.202000191 [56] I. Yamaga, N. Kawaguchi Sakita and Y. Asao, Vascular branching point counts using photoacoustic imaging in the superficial layer of the breast: A potential biomarker for breast cancer, Photoacoustics, 2018, 11, 6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2018.06.002 [57] X. Yang, Y. Huang and L. Sun, A modulus iteration method for retinex problem, Numer. Linear Algebra Appl., 2018, 25(6), e2207. doi: 10.1002/nla.2207 [58] J. Zhang and X. Zhang, A modulus iteration method for non-negatively constrained TV image restoration, Comput. Math. Appl., 2023, 148, 62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2023.07.030 [59] Y. Zhang, Y. Wang and C. Zhang, Total variation based gradient descent algorithm for sparse-view photoacoustic image reconstruction, Ultrasonics, 2012, 52(8), 1046-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2012.08.012 [60] N. Zheng, K. Hayami and J. Yin, Modulus-type inner outer iterative methods for nonnegative constrained least squares problems, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 2016, 37(3), 1250-1278. doi: 10.1137/141002220 -
-
-
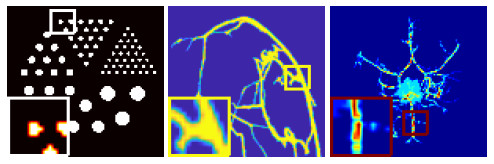
Figure 1.
The "Simulation" (left), "Breast" (middle) and "Tumor" (right) phantoms.
-
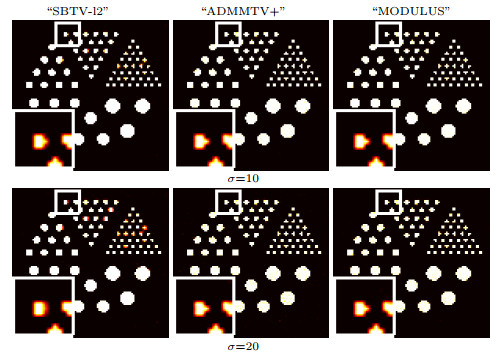
Figure 2.
Experimental results for "Simulation" image. From the first to the second line, reconstructed images for noise levels:
$ \sigma=10, 20 $ -
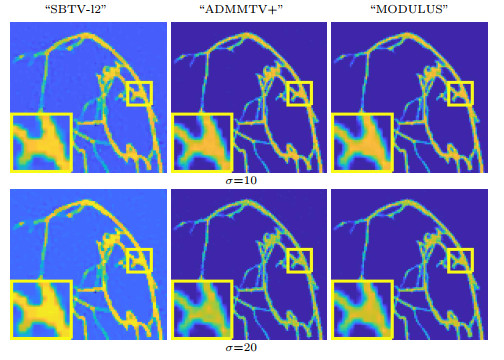
Figure 3.
Experimental results for "Breast" image. From the first to the second line, reconstructed images for noise levels:
$ \sigma=10, 20 $ -
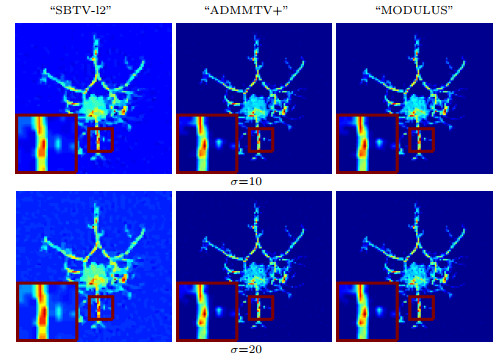
Figure 4.
Experimental results for "Tumor" image. From the first to the second line, reconstructed images for noise levels:
$ \sigma=10, 20 $ -
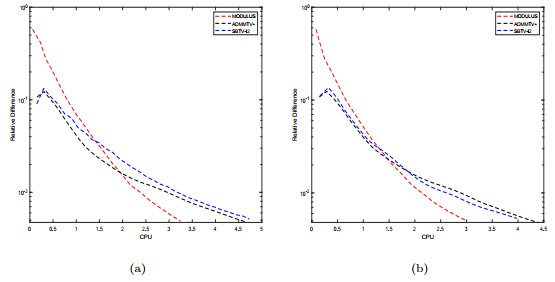
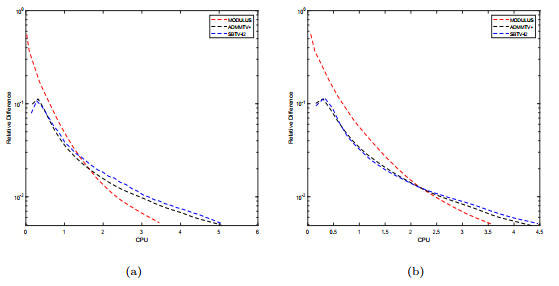
Figure 5.
"Re" versus "CPU" for "Simulation", when (a)
$ \sigma=10 $ $ \sigma=20 $ -
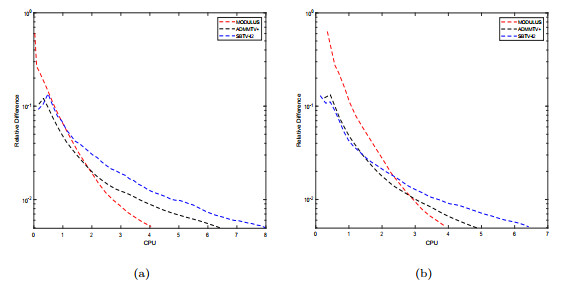
Figure 6.
"Re" versus "CPU" for "Breast", when (a) σ = 10; (b) σ = 20.
-
Figure 7.
"Re" versus "CPU" for "Tumor", when (a)
$ \sigma=10 $ $ \sigma=20 $ -
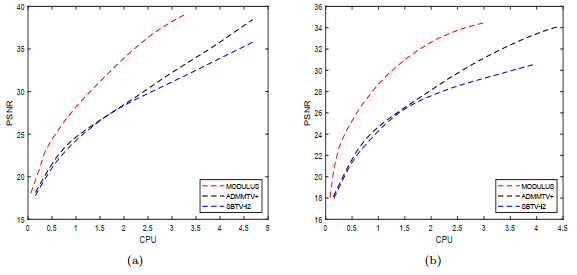
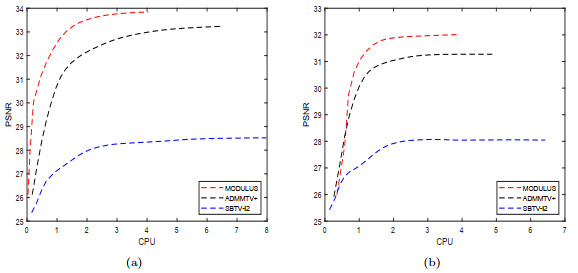
Figure 8.
"PSNR" versus "CPU" for ‘Simulation", when (a)
$ \sigma=10 $ $ \sigma=20 $ -
Figure 9.
"PSNR" versus "CPU" for "Breast", when (a) σ = 10; (b) σ = 20.
-
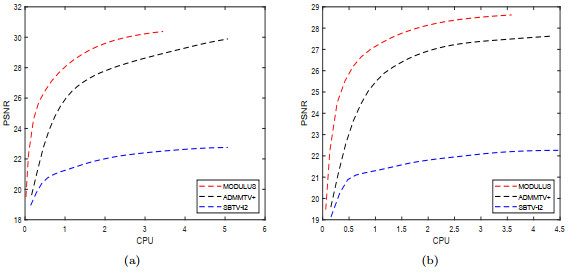
Figure 10.
"PSNR" versus "CPU" for "Tumor", when (a)
$ \sigma=10 $ $ \sigma=20 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: