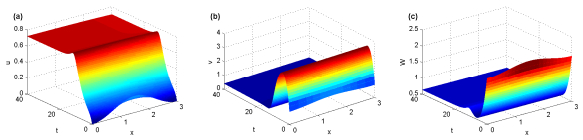
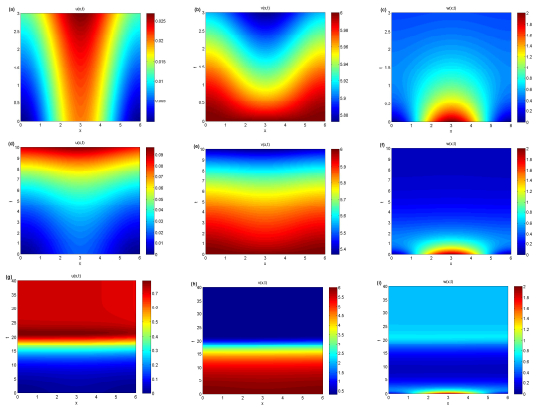
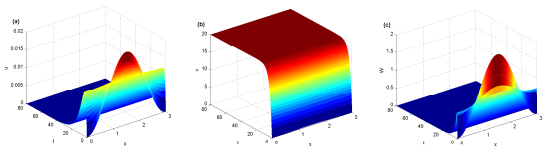
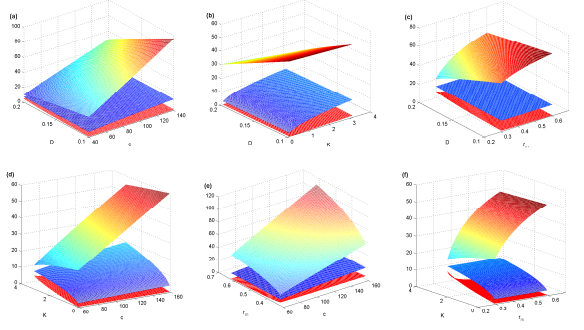
|
[1]
|
K. J. Appeldoorn, A. J. Boom, G. J. J. Kortstee, A. J. B. Zehnder, Contribution of precipitated phosphates and acid-soluble polyphosphate to enhanced biological phosphate removal, Water Res., 1992, 26(7), 937–943.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
J. F. Andrews, A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1968, 10(6), 707–723.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
F. W. Bai, L. J. Chen, W. A. Anderson, M. Moo-Young, Parameter oscillations in a very high gravity medium continuous ethanol fermentation and their attenuation on a multistage packed column bioreactor system, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2004, 88(5), 558–566.
Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
M. Balat, Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: A review, Energ. Convers. Manage., 2011, 52(2), 858–875.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
H. Biebl, Glycerol fermentation of 1, 3-propanediol by Clostridium butyricum. Measurement of product inhibition by use of a pH-auxostat, Appl. Microbiol. Biot., 1991, 35(6), 701–705.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
E. A. Buehler, A. Mesbah, Kinetic study of Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol fermentation in continuous culture, Plos One, 2016, 11(8), 1932–6203.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
A. Carruthers, Mechanisms for the facilitated diffusion of substrates across cell membranes, Biochemistry, 1991, 30(16), 3898–3906.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
D. E. Contois, Kinetics of bacterial growth: relationship between population density and specific growth rate of continuous cultures, J. Gen. Microbiol., 1959, 21(1), 40–50.
Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
E. N. Dancer, Y. H. Du, Positive solutions for a three-species competition system with diffusion-I. General existence results, Nonlinear Anal., 1995, 24(3), 337–357.
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
V. H. Edwards, R. C. Ko, S. A. Balogh, Dynamics and control of continuous microbial propagators to subject substrate inhibition, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1972, 14(6), 939–974.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
M. Esfandyari, M. A. Fanaei, R. Gheshlaghi, M. A. Mahdavi, Mathematical modeling of two-chamber batch microbial fuel cell with pure culture of Shewanella, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2017,117, 34–42.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
C. X. Gao, E. M. Feng, Z. T. Wang, Z. L. Xiu, Parameters identification problem of the nonlinear dynamical system in microbial continuous cultures, Appl. Math. Comput., 2005,169(1), 476–484.
Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
D. Henry, Geometric Theory of Semilinear Parabolic Equations, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
E. Krichen, J. Harmand, M. Torrijos, J. J. Godon, N. Bernet, A. Rapaport, High biomass density promotes density-dependent microbial growth rate, Biochem. Eng. J., 2018,130, 66–75.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
O. Levenspiel, The Monod equation: A revisit and a generalization to product inhibition situations, Biotechnol, Bioeng., 1980, 22(8), 1671–1687.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
J. H. T. Luong, Kinetics of ethanol inhibition in alcohol fermentation, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1985, 27(3), 280–285.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
C. V. Pao, Nonlinear Parabolic and Elliptic Equations, Springer Science & Business Media, New York, 1992.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
C. V. Pao, Quasisolutions and global attactor of reaction-diffusion systems, Nonlinear Anal., 1996, 26(12), 1889–1903.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
J. L. Ren and Q. G. Yuan, Bifurcations of a periodically forced microbial continuous culture model with restrained growth rate, Chaos, 2017, 27(8), 083124.
Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Y. Shen, X. Q. Zhao, X. M. Ge, F. W. Bai, Metabolic flux and cell cycle analysis indicating new mechanism underlying process oscillation in continuous ethanol fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae under VHG conditions, Biotechnol. Adv., 2009, 27(6), 1118–1123.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
P. Skupin, M. Metzger, Stability analysis of the continuous ethanol fermentation process with a delayed product inhibition, Appl. Math. Model., 2017, 49, 48–58.
Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
Z. L. Xiu, A. P. Zeng, W. D. Deckwer, Multiplicity and stability analysis of microorganisms in continuous culture: effects of metabolic overflow and growth inhibition, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1998, 57(3), 251–261.
Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
T. Yano, S. Koga, Dynamic behavior of the chemostat subject to substrate inhibition, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1969, 11(2), 139–153.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
J. X. Ye, E. M. Feng, H. S. Lian, Z. L. Xiu, Existence of equilibrium points and stability of the nonlinear dynamical system in microbial continuous cultures, Appl. Math. Comput., 2009,207(2), 307–318.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
F. Yi, J. Wei, J. Shi, Bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a homogeneous diffusive predator–prey system, J. Differ. Equations, 2009,246(5), 1944–1977.
Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
A. P. Zeng, A. Ross, H. Biebl, C. Tag, B. Gunzel, W. D. Deckwer, Multiple product inhibition and growth modeling of clostridium butyricum and klebsiella pneumoniae in glycerol fermentation, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1994, 44(8), 902–911.
Google Scholar
|





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: