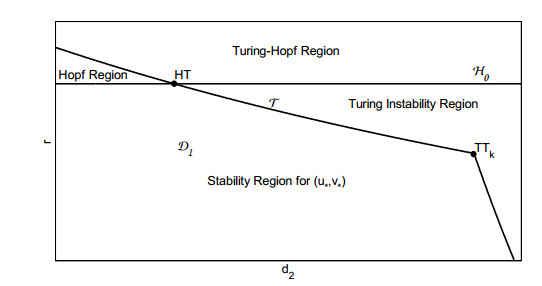
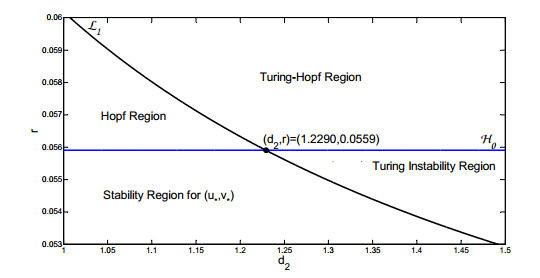
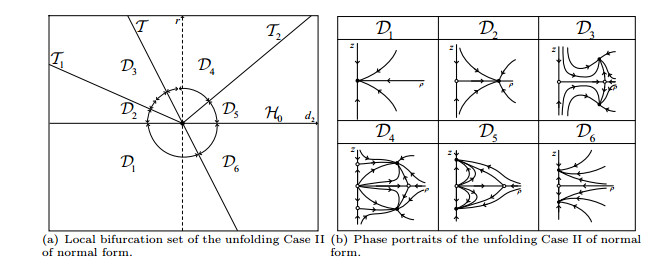
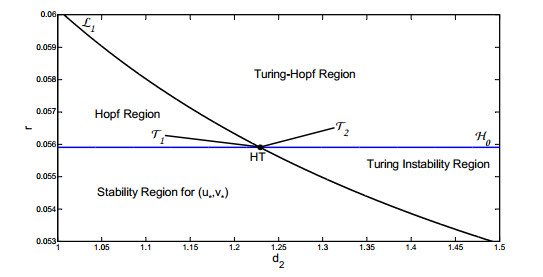
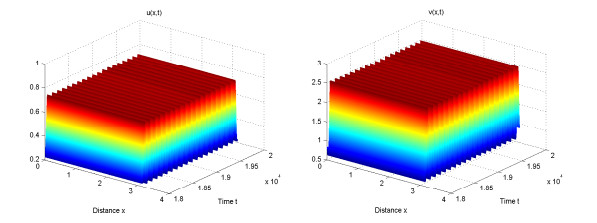
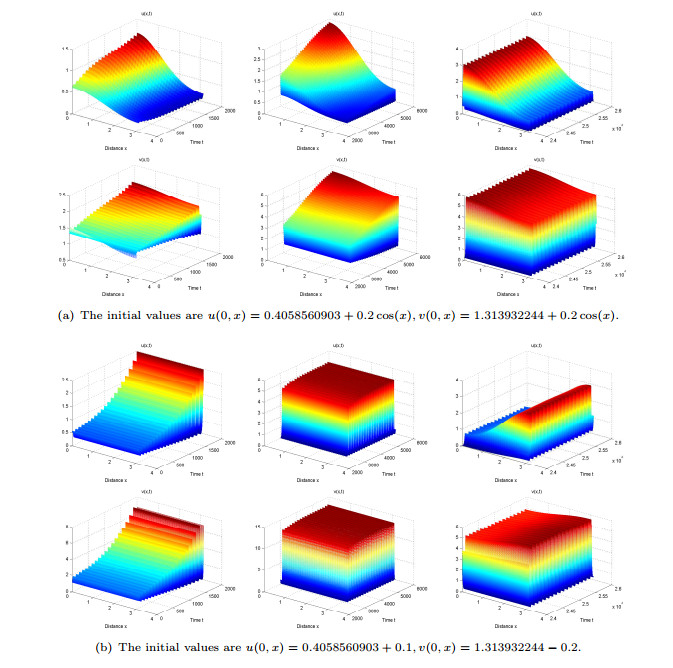
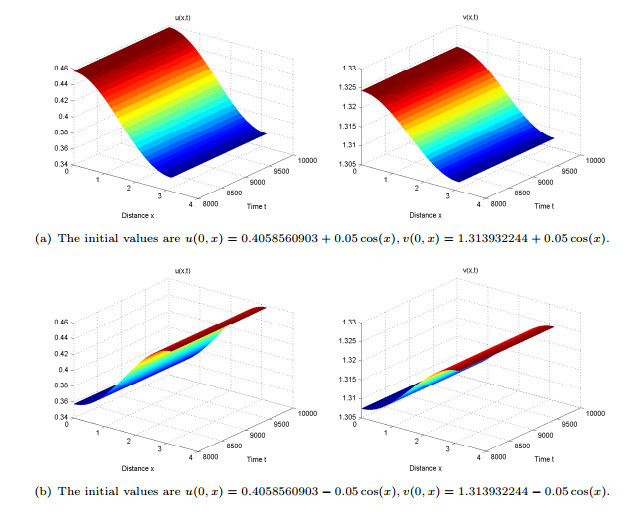
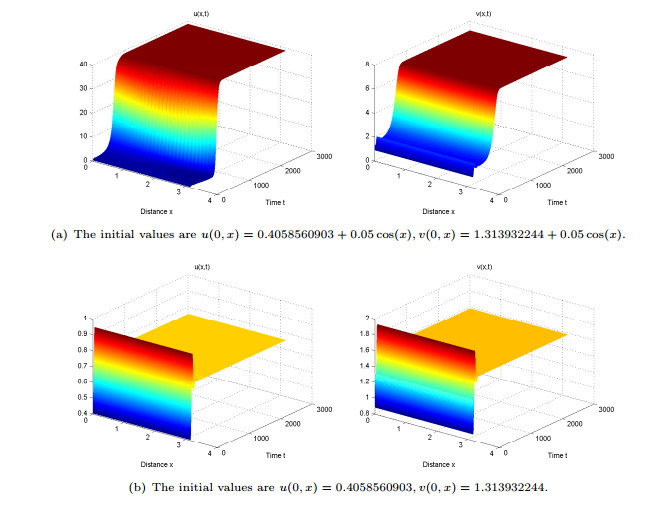
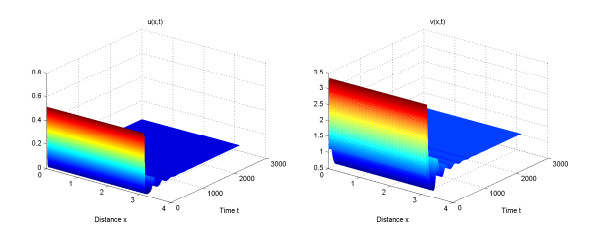
|
[1]
|
M. Baurmann, T. Gross and U. Feudel, Instabilities in spatially extended predator-prey systems: Spatio-temporal patterns in the neighborhood of Turing-Hopf bifurcations, J. Theoret. Biol., 2007, 245(2), 220-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.09.036
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
A. D. Bazykin, A. I. Khibnik and B. Krauskopf, Nonlinear Dynamics of Interacting Populations, World Scientific, 1998.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
B. I. Camara, M. Hague and H. Mokrani, Patterns formations in a diffusive ratio-dependent predator-prey model of interacting populations, Phys. A, 2016, 461, 374-383. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.05.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
S. Chakraborty, P. K. Tiwari, S. K. Sasmal et al., Interactive effects of prey refuge and additional food for predator in a diffusive predator-prey system, Appl. Math. Model., 2017, 47, 128-140. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2017.03.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
S. Chen, J. Shi and J. Wei, Bifurcation analysis of the Gierer-Meinhardt system with a saturation in the activator production, Appl. Anal., 2013, 93(6), 1115-1134.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
H. Ddumba, J. Y. T. Mugisha, J. W. Gonsalves and G. I. H. Kerley, Periodicity and limit cycle perturbation analysis of a predator-prey model with interspecific species' interference, predator additional food and dispersal, Appl. Math. Comput., 2013, 219(15), 8338-8357.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
A. Diouf, H. Mokrani, D. Ngom et al., Detection and computation of high codimension bifurcations in diffuse predator-prey systems, Phys. A, 2019, 516, 402-411. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.10.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
T. Faria, Normal forms and hopf bifurcation for partial differential equations with delays, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc., 2000, 352(5), 2217-2238. doi: 10.1090/S0002-9947-00-02280-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
T. Faria, W. Huang and J. Wu, Smoothness of center manifolds for maps and formal adjoints for semilinear fdes in general Banach spaces, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2002, 34(1), 173-203. doi: 10.1137/S0036141001384971
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
S. Gakkhar and A. Singh, Control of chaos due to additional predator in the hastings-powell food chain model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2012, 385(1), 423-438. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2011.06.047
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
S. Ghorai and S. Poria, Pattern formation and control of spatiotemporal chaos in a reaction diffusion prey-predator system supplying additional food, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2016, 85, 57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2016.01.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
J. Guckenheimer and P. Holmes, Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcations of Vector Fields, Springer, New York, 1983.
Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
L. N. Guin and P. K. Mandal, Spatiotemporal dynamics of reaction-diffusion models of interacting populations, Appl. Math. Model., 2014, 38(17-18), 4417-4427. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2014.02.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
S. Guo and J. Man, Center manifolds theorem for parameterized delay differential equations with applications to zero singularities, Nonlinear Anal., 2011, 74(13), 4418-4432. doi: 10.1016/j.na.2011.04.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
J. K. Hale, Theory of Functional Differential Equations, Springer-Verlag, 1977.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
M. Haque, A detailed study of the Beddington-Deangelis predator-prey model, Math. Biosci., 2011, 234(1), 1-16.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
C. S. Holling, The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation, Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 1965, 97(45), 1-60.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
W. Jiang, Q. An and J. Shi, Formulation of the normal forms of Turing-Hopf bifurcation in reaction-diffusion systems with time delay, submitted, 2018, arXiv: 1802.10286.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
W. Jiang and Y. Yuan, Bogdanov-Takens singularity in van der pol's oscillator with delayed feedback, Phys. D, 2007, 227(2), 149-161. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2007.01.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
D. Kumar and S. P. Chakrabarty, A comparative study of bioeconomic ratio-dependent predator-prey model with and without additional food to predators, Nonlinear Dynam., 2015, 80(1-2), 23-38. doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1848-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
X. Li, W. Jiang and J. Shi, Hopf bifurcation and turing instability in the reaction-diffusion Holling-Tanner predator-prey model, IMA J. Appl. Math., 2011, 78(2), 287-306.
Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
S. Ma and Z. Feng, Fold-hopf bifurcations of the Rose-Hindmarsh model with time delay, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos, 2011, 21(2), 437-452. doi: 10.1142/S0218127411028490
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
P. J. Pal, P. K. Mandal and K. K. Lahiri, A delayed ratio-dependent predator-prey model of interacting populations with Holling type iii functional response, Nonlinear Dynam., 2014, 76(1), 201-220. doi: 10.1007/s11071-013-1121-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
B. Sahoo and S. Poria, Effects of additional food on an ecoepidemic model with time delay on infection, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 245, 17-35.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
B. Sahoo and S. Poria, Effects of additional food in a delayed predator-prey model, Math. Biosci., 2015, 261, 62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2014.12.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
S. Samanta, R. Dhar, I. M. Elmojtaba and J. Chattopadhyay, The role of additional food in a predator-prey model with a prey refuge, J. Biol. Systems, 2016, 24(2-3), 345-365.
Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
S. Sarwardi, M. Haque and P. K. Mandal, Persistence and global stability of bazykin predator-prey model with Beddington-Deangelis response function, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2014, 19(1), 189-209. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2013.05.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
S. K. Sasmal, Y. Kang and J. Chattopadhyay, Intra-specific competition in predator can promote the coexistence of an eco-epidemiological model with strong allee effects in prey, Biosystems, 2015, 137, 34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2015.09.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
M. Sen, P. D. N. Srinivasu and M. Banerjee, Global dynamics of an additional food provided predator-prey system with constant harvest in predators, Appl. Math. Comput., 2015, 250, 193-211.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
Y. Song, T. Zhang and Y. Peng, Turing-Hopf bifurcation in the reaction-diffusion equations and its applications, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2016, 33, 229-258. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.10.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
Y. Song and X. Zou, Bifurcation analysis of a diffusive ratio-dependent predator-prey model, Nonlinear Dynam., 2014, 78(1), 49-70. doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1421-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
P. D. N. Srinivasu and B. S. R. V. Prasad, Time optimal control of an additional food provided predator-prey system with applications to pest management and biological conservation, J. Math. Biol., 2010, 60(4), 591-613. doi: 10.1007/s00285-009-0279-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
Y. Su and X. Zou, Transient oscillatory patterns in the diffusive non-local blowfly equation with delay under the zero-flux boundary condition, Nonlinearity, 2014, 27(1), 87-104. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/27/1/87
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
C. Wang, R. Liu, J. Shi and C. M. Del Rio, Spatiotemporal mutualistic model of mistletoes and birds, J. Math. Biol., 2014, 68(6), 1479-1520. doi: 10.1007/s00285-013-0664-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
J. Wang and W. Jiang, Hopf-zero bifurcation of a delayed predator-prey model with dormancy of predators, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2017, 7(3), 1051-1069.
Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
J. Wang, J. Wei and J. Shi, Global bifurcation analysis and pattern formation in homogeneous diffusive predator-prey systems, J. Differential Equations, 2016, 260(4), 3495-3523. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2015.10.036
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
S. Wiggins, Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos, Springer Science & Business Media, 2003.
Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
J. Wu, Theory and Applications of Partial Functional Differential Equations, Springer, 1996.
Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
X. Xu and J. Wei, Turing-Hopf bifurcation of a class of modified Leslie-Gower model with diffusion, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2018, 23(2), 765-783.
Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
L. Yang, M. Dolnik, A. M. Zhabotinsky and I. R. Epstein, Spatial resonances and superposition patterns in a reaction-diffusion model with interacting turing modes, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2002, 88(20).
Google Scholar
|
|
[41]
|
R. Yang and Y. Song, Spatial resonance and turing-hopf bifurcations in the Gierer-Meinhardt model, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2016, 31, 356-387. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2016.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[42]
|
R. Z. Yang, M. Liu and C. R. Zhang, A delayed-diffusive predator-prey model with a ratio-dependent functional response, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2017, 53, 94-110. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.04.034
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[43]
|
F. Yi, J. Wei and J. Shi, Bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a homogeneous diffusive predator-prey system, J. Differential Equations, 2009, 246(5), 1944-1977. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2008.10.024
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[44]
|
R. Yuan, W. Jiang and Y. Wang, Saddle-node-hopf bifurcation in a modified leslie-gower predator-prey model with time-delay and prey harvesting, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2015, 422(2), 1072-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2014.09.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[45]
|
T. Zhang, X. Liu, X. Meng and T. Zhang, Spatio-temporal dynamics near the steady state of a planktonic system, Comput. Math. Appl., 2018, 75(12), 4490-4504. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2018.03.044
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




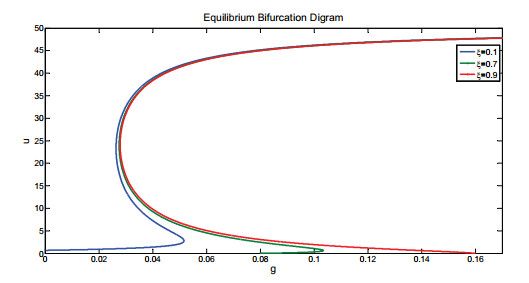

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: