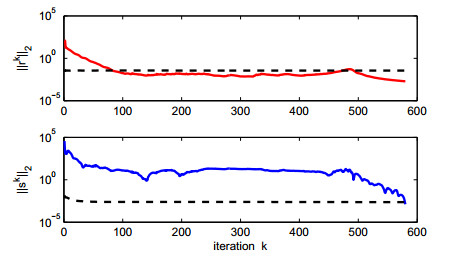
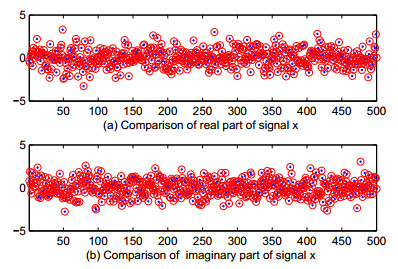
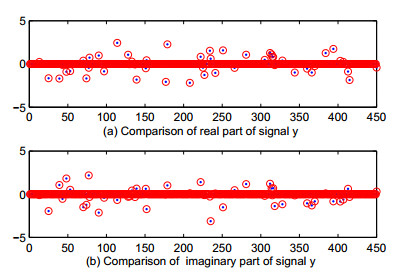
|
[1]
|
J. Annemüller T.J. Sejnowski and S. Makeig, Complex spectral domain independent component analysis of electrocephalographic data, Independent Component Anal, Workshop, Japan: Nara, 2003.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
V. D. Bos, Complex Gradient and Hessian, Vision, Image Signal Processing, IEEE Proceesing, 1994, 141(6), 380-383.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
P. Bouboulis, Wirtinger's Calculus in general Hilbert Spaces, arXiv: 1005.5170v1, 2010.
Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
S. Boyd, N. Parikh, E. Chu, B. Peleato and J. Eckstein, Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers, Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1), 1-122.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
D. H. Brandwood, A complex gradient operator and its application in adaptive array theory, Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, 1983, 130(1), 11-16.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
R. W. Cottle, F. Giannessi and J. L. Lions, Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems: Theory and Applications, Wiley, New York, 1980.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
E. J. Cands, J. Romberg and T. Tao, Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal recognition from highly incomplete frequency information, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2), 489-509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
D. Donoho, Compressed sensing, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4), 1289-1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
S. C. Dafermos, An iterative scheme for variational inequalities, Math. Programming, 1983, 26, 40-47. doi: 10.1007/BF02591891
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
F. Gaetano, Sul problema elastostatico di Signorini con ambigue condizioni al contorno, Rendiconti della Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei, Classe di Scienze Fisiche, Matematiche e Naturali, 1963, 34(2), 138-142.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
R. Glowinski, J. L. Lions and R. Tremoliérès, Numerical Analysis of Variational Inequalities, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1981.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani and J. Friedman, The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference and Prediction, Second Edition, Springer, 2009.
Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
B. S. He, L. Z. Liao, D. R. Han and H. Yang, A new inexact alternating directions method for monotone variational inequalities, Math. Progr., 2002, 92, 103-118. doi: 10.1007/s101070100280
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
B. S. He, F. Ma and X. M. Yuan, Linearized alternating direction method of multipliers via positive-indefinite proximal regularization for convex programming, http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_HTML/2016/07/5569.html.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
B. S. He and X. M. Yuan, On the O(1/n) convergence rate of the Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method, SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2012, 50(2), 700-709. doi: 10.1137/110836936
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
T. Hinamoto, A. Doiand W.-S. Lu, Realization of 3-D separable-denominator digital filters with low l2-sensitivity, IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12), 6282-6293. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2215027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
A. N. Iusem, An iterative algorithm for the variational inequality problem, Comput. Appl. Math., 1994, 13, 103-114.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
B. Jiang, S. Q. Ma and S. Z. Zhang, Alternating direction method of multipliers for real and complex polynomial optimization models, Optimization, 2014, 63(6), 883-898. doi: 10.1080/02331934.2014.895901
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
E. N. Khobotov, A modification of the extragradient method for the solution of variational inequalities and some optimization problems, USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys., 1987, 27, 1462-1473.
Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
C. N. K. Mooers, A technique for the cross spectrum analysis of pairs of complex-valued time series. with emphasis on properties of polarized components and rotational invariants, Deep-Sea Research, 1973, 20, 1129-1141.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
M. Li, D. F. Sun and K. C. Toh, A majorized ADMM with indefinite proximal terms for linearly constrained convex composite optimization, SIAM J. Optimization, 2016, 26, 922-950. doi: 10.1137/140999025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
L. Li, X. Y. Wang and G. Q. Wang, Alternating direction method of multipliers for separable convex optimization of real functions in complex variables, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2015, Article ID 104531, 14 pages, 2015.
Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
L. Li, G. Q. Wang and J. L. Zhang, On the O(1/K) Convergence Rate of Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers in Complex Domain, Australian and New Zealand Industrial and Applied Mathematics Journal, 2018.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
X. X. Li, L. L. Mo, X. M. Yuan and J. Z. Zhang, Linearized alternating direction method of multipliers for sparse group and fused LASSO models, Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2014, 79, 203-221. doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2014.05.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
J. Löfberg, YALMIP: A toolbox for modeling and optimization in MATLAB, 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2004, 284-289.
Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
W. S. Lu and T. Hinamoto, Two-dimensional digital filters with sparse coefficients, Miltimimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 22(1-3), 173-189. doi: 10.1007/s11045-010-0129-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
S. Osher, Y. Mao, B. Dong and W. Yin, Fast linearized Bregman iterations for compressed sensing and sparse denoising, Commun. Math. Sci., 2010, 8, 93-111. doi: 10.4310/CMS.2010.v8.n1.a6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
Y. y. Ouyang, Y. M. Chen, G. H. Lan and Eduardo Pasiliao JR, An Accelerated Linearized Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers, SIAM J. Imaging Sci., 2015 8(1), 644-681. doi: 10.1137/14095697X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
P. J. Schreier and L. L. Scharf, Statistical Signal Processing of Complex-Valued Data: The Theory of Improper and Noncircular Signals, Cambridge University Press, UK, 2010.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
L. Sorber, M. V. Barel and L. D. Lathauwer, Unconstrained optimization of real functions in complex variables, SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2012, 22(3), 879-898. doi: 10.1137/110832124
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
J. F. Sturm, Using SeDuMi 1.02, a Matlab toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones, Optimization Methods and Software, 1999, 11(1-4), 625-653.
Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
K. C. Toh, M. J. Todd and R. H. Tütüncü, SDPT3a MATLAB software package for semidefinite programming, version 1.3, Optimization Methods and Software, 1999, 11(1-4), 545-581. doi: 10.1080/10556789908805762
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
R. Tibshirani, Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B. 1996, 58, 267-288.
Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
G. Tauböck, Complex noise analysis of DMT. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(12), 5739-5754. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.901138
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
J. F. Yang and X. M. Yuan, Linearized Augmented Largangian and Alternating Direction Methods for Nuclear Norm Minimization, Mathematics of Computaion, 2013, 82, 301-329.
Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
Z. Z. Yang and Z. Yang, Fast linearized alternating direction method of multipliers for the augmented l1-regularized problem, Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2015, 9(7), 1601-1612. doi: 10.1007/s11760-014-0617-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
L. Zhao and S. Dafermos, General economic equilibrium and variational inequalities, Oper. Res. Lett., 1991, 10, 369-376. doi: 10.1016/0167-6377(91)90037-P
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
X. Q. Zhang, M. Burger, X. Bresson and S. Osher, Bregmanized nonlocal regularization for deconvolution and sparse reconstruction, SIAM J. Imag. Sci., 2010, 3(3), 253-276. doi: 10.1137/090746379
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
X. Q. Zhang, M. Burger and S. Osher, A unified primal-dual algorithm framework based on Bregman iteration, J. Sci. Comput., 2010, 46(1), 20-46.
Google Scholar
|




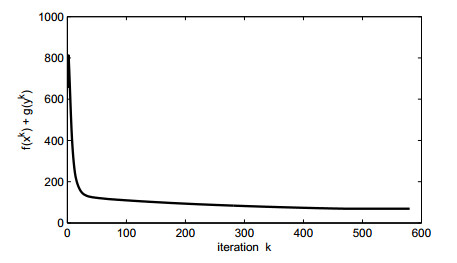

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: