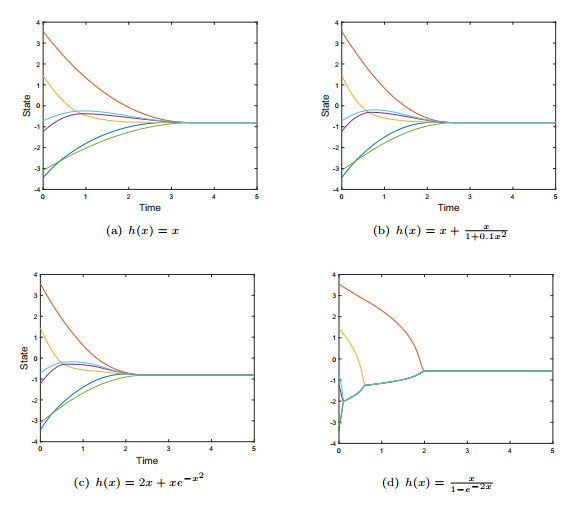
|
[1]
|
G. Albi, D. Balagué, J. A. Carrillo and J. V. Brecht, Stability analysis of flock and mill rings for second order models in swarming, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2014, 74(3), 794–818.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
F. M. Atay, The consensus problem in networks with transmission delays, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 2013, 371(1999), 20120460. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2012.0460
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
D. Bauso and M. Cannon, Consensus in opinion dynamics as a repeated game, Automatica, 2018, 90, 204–211. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.12.062
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
S. P. Bhat and D. S. Bernstein, Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems, SIAM J. Control Optim., 2000, 38(3), 751–766.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
Y. Cheng, X. Wang and B. Shi, Consensus of a two-agent opinion dynamical system with processing delay, Int. J. Biomath., 2018, 11(6), 1850081. doi: 10.1142/S179352451850081X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
L. Cheng, Z. G. Hou and M. Tan, A mean square consensus protocol for linear multi-agent systems with communication noises and fixed topologies, IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2014, 59(1), 261–267. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2270873
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
T. Chu, L. Wang, T. Chen and S. Mu, Complex emergent dynamics of anisotropic swarms: Convergence vs oscillation, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2006, 30(4), 875–885.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
J. Cortés, Finite-time convergent gradient flows with applications to network consensus, Automatica, 2006, 42(11), 1993–2000. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.06.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
F. Cucker and S. Smale, Emergent behavior in flocks, IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2007, 52(5), 852–862. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.895842
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
H. Geng, Z. Chen, C. Zhang, Z. Liu and Q. Zhang, Consensus of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with linear and nonlinear dynamics, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2016, 6(1), 1–11.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
E. Girejko and A. B. Malinowska, Leader-following consensus for networks with single-and double-integrator dynamics, Nonlinear Anal.-Hybrid Syst., 2019, 31, 302–316. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2018.10.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
C. Hua, X. Sun, X. You and X. Guan, Finite-time consensus control for second-order multi-agent systems without velocity measurements, Int. J. Syst. Sci., 2017, 48(2), 337–346. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2016.1181224
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
G. H. Hardy, J. E. Littlewood and G. Pólya, Inequalities, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1934.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
R. A. Horn and C. R. Johnson, Matrix Analysis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
Y. Kim and M. Mesbahi, On maximizing the second smallest eigenvalue of a state-dependent graph laplacian, IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2006, 51(1), 116–120. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.861710
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
M. G. Medina-Guevara and A. Gallegos, On $S^{1}$ as an alternative continuous opinion space in a three-party regime, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2017, 318(C), 230–241.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
J. Ni, L. Liu, C. Liu, X. Hu and S. Li, Further improvement of fixed-time protocol for average consensus of multi-agent systems, IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2017, 50(1), 2523–2529. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.064
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
K. Ogiwara, T. Fukami and N. Takahashi, Maximizing algebraic connectivity in the space of graphs with fixed number of vertices and edges, IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst., 2017, 4(2), 359–368. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2015.2503561
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
R. Olfati-Saber and R. M. Murray, Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays, IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2004, 49(9), 1520–1533. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
C. Pignotti and I. Reche Vallejo, Flocking estimates for the Cucker–Smale model with time lag and hierarchical leadership, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2018, 464(2), 1313–1332.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
V. D. Silva and R. Ghrist, Converage in sensor networks via persistent homology, Algebr. Geom. Topol., 2007, 7(1), 339–358. doi: 10.2140/agt.2007.7.339
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
T. Vicsek, A. Czirók, E. Ben-Jacob, I. Cohen and O. Shochet, Novel type of phase transition in a system of self-driven particles, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1995, 75(6), 1226–1229. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.1226
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
F. Xiao and L. Wang, State consensus for multi-agent systems with switching topologies and time-varying delays, Int. J. Control, 2006, 79(10), 1227–1284.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
W. Yu, W. Ren, W. X. Zheng, G. Chen and J. Lü, Distributed control gains design for consensus in multi-agent systems, Automatica, 2013, 49(7), 2107–2115. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.03.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
B. Zhu, L. Xie, D. Han, X. Meng and R. Teo, A survey on recent progress in control of swarm systems, Sci. China-Inf. Sci., 2017, 60(7), 070201. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-9088-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
X. Zhang, L. Liu and G. Feng, Leader-follower consensus of time-varying nonlinear multi-agent systems, Automatica, 2015, 52, 8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.127
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
Z. Zuo and L. Tie, A new class of finite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems, Int. J. Control, 2014, 87(2), 363–370. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2013.834484
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




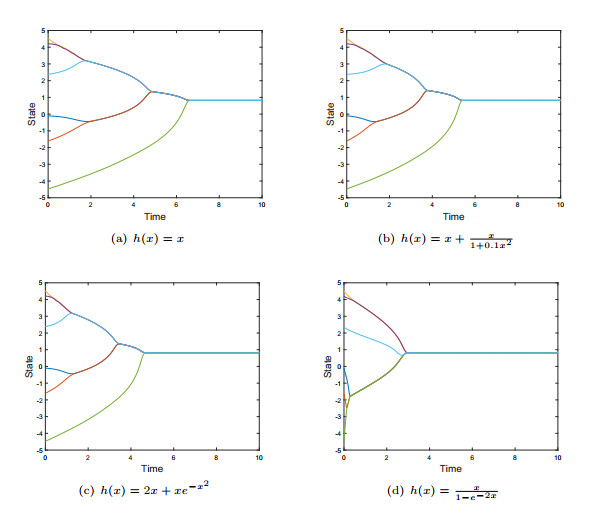

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: