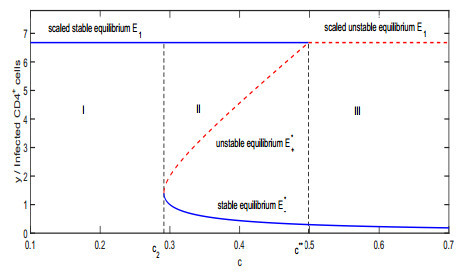
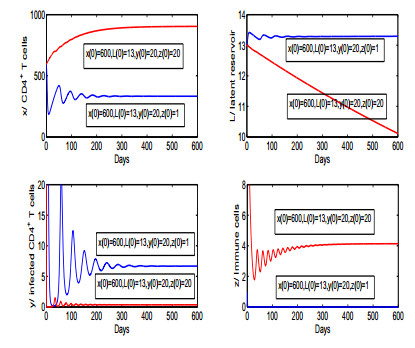
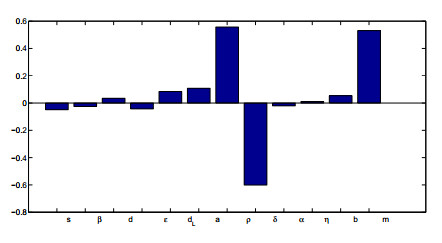
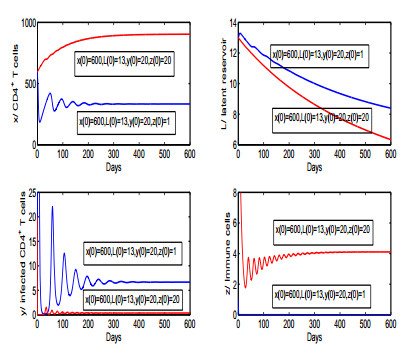
|
[1]
|
"Mississippi baby" now has detectable HIV, researchers find, National Institutes of Health News. July 10, 2014. Available at www.niaid.nih.gov/news/newsreleases/2014/pages/mississippibabyhiv.aspx.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
C. L. Althaus and R. J. De Boer, Dynamics of immune escape during HIV/SIV infection. PLoS Comput. Biol., 2008, 4. E1000103.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
E. Avila-Vales, N. Chan-Chi and G. Garcia-Almeida, Analysis of a viral infection model with immune impairment, intracellular delay and general non-linear incidence rate, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2014, 69, 1-9.
Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
C. Bartholdy, J. P. Christensen, D. Wodarz and A. R. Thomsen, Persistent virus infection despite chronic cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activation in Gamma interferon-deficient mice infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, J. Virol., 2000, 74, 1034-10311.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
S. M. Blower and H. Dowlatabadi, Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of complex models of disease transmission: an HIV model. as an example, Int. Stat. Rev., 1994, 2, 229-243.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
S. Bonhoeffer and G. M. N. D. F. Rembiszewski M, Ortiz, Risks and benefits of structured antiretroviral drug therapy interruptions in HIV-1 infection, AIDS, 2000, 14, 2313-2322.
Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
D. Burg, L. Rong, A. U. Neumann and H. Dahari, Mathematical modeling of viral kinetics under immune control during primary HIV-1 infection, J. Theor. Biol., 2009, 259, 751-759. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.04.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
R. J. De Boer and A. S. Perelson, Target cell limited and immune control models of HIV infection: A comparison., J. Theor. Biol., 1998, 190, 201-214. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1997.0548
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
S. Chen, Z. Liu and J. Shi, Nonexistence of nonconstant positive steady states of a diffusive predator-prey model with fear effect, J. Nonlinear Modeling and Analysis, 2019, 1(1), 47-56.}, ,
Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
M. J. Churchill, S. G. Deeks, D. M. Margolis et al., HIV reservoirs: what, where and how to target them, Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14, 55-60.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
K. E. Clarridge, J. Blazkova, K. Einkauf et al., Effect of analytical treatment interruption and reinitiation of antiretroviral therapy on HIV reservoirs and immunologic parameters in infected individuals, PLoS Pathog, 2018, 14. E1006792.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
J. M. Conway and A. S. Perelson, Post-treatment control of HIV infection. proc, Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015, 112, 5467-5472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419162112
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
R. V. Culshaw and S. Ruan, A delay-differential equation model of HIV infection of CD4$^{+}$ T-cells., Math. Biosci., 2000, 165, 27-39. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(00)00006-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
H. Doekes, C. Fraser and K. Lythgoe, Effect of the latent reservoir on the evolution of HIV at the within- and between-host levels., PLoS Comput Biol, 2017, 13. E1005228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005228
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
C. Gavegnano, J. H. Brehm, F. P. Dupuy et al., Novel mechanisms to inhibit HIV reservoir seeding using Jak inhibitors, PLOS Pathogens, 2017, 13. E1006740.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
J. Hale and S. M. Verduyn Lunel, Introduction to functional differential equations, Springer, New York, 1993.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
D. D. Ho, A. U. Neumann, A. S. Perelson et al., Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection, Nature, 1995, 373, 123-126.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
Z. Hu, J. Zhang, H. Wang et al., Dynamics analysis of a delayed viral infection model with logistic growth and immune impairment, Appl. Math. Model., 2014, 38, 524-534.
Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
S. Iwami, T. Miura, S. Nakaoka and Y. Takeuchi, Immune impairment in HIV infection: Existence of risky and immunodeficiency thresholds, J. Theor. Biol., 2009, 260, 490-501. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.06.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
S. Iwami, S. Nakaoka, Y. Takeuchi and T. Miura, Immune impairment thresholds in HIV infection., Immunol. Lett., 2009, 123, 149-154. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.03.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
H. Kim and A. S. Perelson, Dynamic characteristics of HIV-1 reservoirs., Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS, 2006, 1, 152-156.
Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
H. Kim and A. S. Perelson, Viral and latent reservoir persistence in HIV-1-infected patients on therapy., PLoS Comput. Biol., 2006, 2. E135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020135
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
N. N. Krasovskii, Problems of the theory of stability of motion, (Russian), (1959). English translation, Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA, 1963.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
J. P. LaSalle, Some extensions of liapunov's second method, IRE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1960, CT-7, 520-527.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
M. Li and H. Shu, Multiple stable periodic oscillations in a mathematical model of CTL response to htlv-i infection, Bull. Math. Biol., 2011, 73, 1774-1793. doi: 10.1007/s11538-010-9591-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
S. Marino, I. B. Hogue, C. J. Ray and D.E. Kirschner.A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology, Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2008, 254(1), 178-196.
Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
M. Markowitz, M. Louie, A. Hurley et al., A novel antiviral intervention results in more a urate assessment of human immunodeficiiency virus type 1 replication dynamics and T-cell decay in vivo., J. Virol, 2003, 77, 5037-5038.
Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
P. W. Nelson and A. S. Perelson, Mathematical analysis of a delay differential equation models of HIV-1 infection, Math. Biosci., 2002, 179, 73-94. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00099-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
M. A. Nowak and C. R. M. Bangham, Population dynamics of immune response to persistent viruses, Science, 1996, 272, 74-79. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5258.74
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
M. A. Nowak, R. M. May, R. E. Phillips et al., Antigenic oscillations and shifting immunodominance in HIV-1 infections, Nature, 1995, 375, 606-611.
Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
D. Persaud, H. Gay, C. Ziemniak et al., Absence of detectable HIV-1 viremia after treatment cessation in an infant, N. Engl. J. Med., 2013, 369, 1828-1835.
Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
A. Pugliese and A. Gandolfi, Asimple model of pathogen-immunedynamics including specific andnon-specific immunity, Math. Biosci., 2008, 214, 73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.04.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
R. R. Regoes, D. Wodarz and M. A. Nowak, Virus dynamics: the effect of target cell limitation and immune responses on virus evolution, J. Theor. Biol., 1998, 191, 451-462. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1997.0617
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
L. Rong and A. S. Perelson, Modeling HIV persistence, the latent reservoir, and viral blips, J. Theor. Biol., 2009, 260, 308-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.06.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
L. Rong, and A.S. Perelson, Asymmetric division of activated latently infected cells may explain the decay kinetics of the HIV-1 latent reservoir and intermittent viral blips, Math. Biosci., 2009, 217, 77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.10.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
Z. Rubinstein, A Course in Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations, Academic Press, New York, 1969.
Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
X. Song, S. Wang and X. Zhou, Stability and hopf bifurcation for a viral infection model with delayed non-lytic immune response., J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2010, 33, 251-265.
Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
B. Tang, Y. Xiao, R. A. Cheke and N. Wang, Piecewise virus-immune dynamic model with HIV-1 rna-guided therapy, J. Theor. Biol., 2015, 377, 36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.03.040
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
G. C. Treasure, E. Aga, R. J. Bosch et al., Relationship among viral load outcomes in HIV treatment interruption trials, J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr., 2016, 72, 310-313.
Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
S. Wang and L. Rong, Stochastic population switch may explain the latent reservoir stability and intermittent viral blips in HIV patients on suppressive therapy, J. Theor. Biol., 2014, 360, 137-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.06.042
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[41]
|
K. Wang, W. Wang and X. Liu, Global stability in a viral infection model with lytic and nonlytic immune response, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2007, 51, 1593-1610.
Google Scholar
|
|
[42]
|
K. Wang, W. Wang, H. Pang and X. Liu, Complex dynamic behavior in a viral model with delayed immune response, Phys. D, 2007, 226, 197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2006.12.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[43]
|
S. Wang and F. Xu, Thresholds and bistability in virus-immune dynamics, Applied Mathematics Letters, 2018, 78, 105-111. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2017.11.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[44]
|
S. Wang, F. Xu and L. Rong, bistability analysis of an hiv model with immune response, Journal of Biological Systems, 2017, 25, 677-695. doi: 10.1142/S021833901740006X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[45]
|
S. Wang, X. Song and Z. Ge, Dynamics analysis of a delayed viral infection model with immune impairment, Appl. Math. Model., 2011, 35, 4877-4885. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2011.03.043
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[46]
|
X. Wang, Y. Tao and X. Song, A delayed HIV-1 infection model with beddington-deangelis functional response, Nonlinear Dyn., 2010, 62, 67-72. doi: 10.1007/s11071-010-9699-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[47]
|
Z. Wang and X. Liu, A chronic viral infection model with immune impairment, J. Theor. Biol., 2007, 249, 532-542. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.08.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[48]
|
X. Wei, S. K. Ghosh, M. E. Taylor et al., Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection, Nature, 1995, 373, 117-122.
Google Scholar
|
|
[49]
|
D. Wodarz, J. P. Christensen and A. R. Thomsen, The importance of lytic and nonlytic immune response in viral infections, Trends Immunol, 2002, 23, 194-200. doi: 10.1016/S1471-4906(02)02189-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[50]
|
Y. Xiao, S. Tang, Y. Zhou et al., Predicting the hiv/aids epidemic and measuring the effect of mobility in mainland china, Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2013, 317, 271-285.
Google Scholar
|
|
[51]
|
W. Zhang, L. M. Wahl and P. Yu, Viral blips may not need a trigger: How transient viremia can arise in deterministic in-host models, SIAM Review, 2014, 56, 127-155. doi: 10.1137/130937421
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[52]
|
H. Zhu and X. Zou, Dynamics of a HIV-1 infection model with cell-mediated immune response and intracellular delay, Disc. Cont. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B., 2009, 12, 511-524. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2009.12.511
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: