| Citation: | Zhenfeng Shi, Daqing Jiang, Ningzhong Shi, Tasawar Hayat, Ahmed Alsaedi. ANALYSIS OF A MULTI-GROUP ALCOHOLISM MODEL WITH PUBLIC HEALTH EDUCATION UNDER REGIME SWITCHING[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2021, 11(5): 2279-2302. doi: 10.11948/20200370 |
ANALYSIS OF A MULTI-GROUP ALCOHOLISM MODEL WITH PUBLIC HEALTH EDUCATION UNDER REGIME SWITCHING
-
Abstract
In this paper, we study a multi-group stochastic alcoholism model with public health education, which is formulated as a piecewise deterministic Markov process. Through a rigorous analysis, we firstly show that the solution of the stochastic model is positive and global. Then we obtain sufficient conditions for the extinction of alcohol problems. In addition, sufficient conditions for the persistence in the mean of alcoholism are derived. Specifically, in the case of persistence, we prove the existence of positive recurrence of the solution to the model by employing suitable stochastic Lyapunov functions.
-
Keywords:
- Multi-group model /
- alcoholism /
- markovian switching /
- extinction /
- persistence in the mean /
- positive recurrence
-

-
References
[1] B. Benedict, Modelling alcoholism as a contagious disease: how "infected" drinking buddies spread problem drinking, SIAM News., 2007, 40(3), 1-3. [2] R. Bani, R. Hameed, S. Szymanowski, P. Greenwood, C. Kribs-Zaleta and A. Mubayi, Influence of environmental factors on college alcohol drinking patterns, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2013, 10(5), 1281-1300. [3] C. P. Bhunu and S. Mushayabasa, A theoretical analysis of smoking and alcoholism, J. Math. Model. Algor., 2012, 11(2), 387-408. [4] R. J. Bonnie and M. E. O'Connell, Reducing Underage Drinking: A Collective Responsibility, The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2004. [5] A. Berman and R. J. Plemmons, Nonnegative Matrices in the Mathematical Sciences, Academic Press, New York, 1979. [6] N. Dang, N. Du and G. Yin, Existence of stationary distributions for Kolmogorov systems of competitive type under telegraph noise, J. Diff. Eqs., 2014, 257(6), 2078-2101. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.05.029 [7] Z. Feng, W. Huang and C. Castillo-Chavez, Global behavior of a multi-group SIS epidemic model with age structure, J. Diff. Eqs., 2005, 218(2), 292-324. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2004.10.009 [8] D. M. Gorman, J. Mezic, I. Mezic and P. J. Gruenewald, Agent-based modeling of drinking behavior: a preliminary model and potential applications to theory and practice, Am. J. Public Health., 2006, 96(11), 2055-2060. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2005.063289 [9] S. Galea, C. Hall and G. A. Kaplan, Social epidemiology and complex system dynamic modelling as applied to health behaviour and drug use research, Int. J. Drug Policy., 2009, 20(3), 209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2008.08.005 [10] A. Gray, D. Greenhalgh, X. Mao and J. Pan, The SIS epidemic model with Markovian switching, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2012, 394(2), 496-516. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2012.05.029 [11] H. Guo, M. Li and Z. Shuai, Global stability of the endemic equilibrium of multigroup SIR epidemic models, Can. Appl. Math. Q., 2006, 14(3), 259-284. [12] H. Guo, M. Li and Z. Shuai, A graph-theoretic approach to the method of global Lyapunov functions, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2008, 136(8), 2793-2802. doi: 10.1090/S0002-9939-08-09341-6 [13] H. Guo, M. Li and Z. Shuai, Global dynamics of a general class of multistage models for infectious diseases, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2012, 72(1), 261-279. doi: 10.1137/110827028 [14] D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43(3), 525-546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 [15] C. Ji, D. Jiang and N. Shi, Multigroup SIR epidemic model with stochastic perturbation, Physica A, 2011, 390(10), 1747-1762. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.12.042 [16] T. Kuniya, Global Behavior of a Multi-Group SIR Epidemic Model with Age Structure and an Application to the Chlamydia Epidemic in Japan, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2019, 79(1), 321-340. doi: 10.1137/18M1205947 [17] D. Kuang, Q. Yin and J. Li, Stationary distribution and extinction of stochastic HTLV-I infection model with CTL immune response under regime switching, J. Nonl. Mod. Anal., 2020, 2, 585-600. [18] M. Li, Z. Shuai and C. Wang, Global stability of multi-group epidemic models with distributed delays, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2010, 361(1), 38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2009.09.017 [19] Q. Liu, D. Jiang and N. Shi, Threshold behavior in a stochastic SIQR epidemic model with standard incidence and regime switching, Appl. Math. Comput., 2018, 316, 310-325. [20] J. Lv, H. Liu and X. Zou, Stationary distribution and persistence of a stochastic predator-prey model with a functional response, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2019, 9(1), 1-11. [21] M. Li, Z. Jin and G. Sun, Modeling direct and indirect disease transmission using multi-group model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2017, 446(2), 1292-1309. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2016.09.043 [22] D. Li, S. Liu and J. Cui, Threshold dynamics and ergodicity of an SIRS epidemic model with Markovian switching, J. Diff. Eqs., 2017, 263(12), 8873-8915. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2017.08.066 [23] D. Li, S. Liu and J. Cui, Threshold dynamics and ergodicity of an SIRS epidemic model with semi-Markov switching, J. Diff. Eqs., 2019, 266(7), 3973-4017. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2018.09.026 [24] Q. Liu and D. Jiang, Dynamics of a multigroup SIS epidemic model with standard incidence rates and Markovian switching, Physica A, 2019, 527, 121270. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.121270 [25] Q. Luo and X. Mao, Stochastic population dynamics under regime switching, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2007, 334(1), 69-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.12.032 [26] X. Mao and C. Yuan, Stochastic Differential Equations With Markovian Switching, Imperial College Press, London, 2006. [27] X. Mao, Stability of stochastic differential equations with Markovian switching, Stoch. Process. Their Appl., 1999, 79(1), 45-67. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4149(98)00070-2 [28] J. L. Manthey, A. Y. Aidoo and K. Y. Ward, Campus drinking: an epidemiological model, J. Biol. Dyn., 2008, 2(3), 346-356. doi: 10.1080/17513750801911169 [29] G. Mulone and B. Straughan, Modeling binge drinking, Int. J. Biomath., 2012, 5(1), 1250005. doi: 10.1142/S1793524511001453 [30] A. Mubayi and P. E. Greenwood, Contextual interventions for controlling alcohol drinking, Math. Popul. Stud., 2013, 20(1), 27-53. doi: 10.1080/08898480.2013.748588 [31] S. Ma, H. Huo and H. Xiang, Threshold dynamics of a multi-group SEAR alcoholism model with public health education, Int. J. Biomath., 2019, 12(3), 1950025. doi: 10.1142/S1793524519500256 [32] X. Meng, L. Wang and T. Zhang, Global dynamics analysis of a nonlinear impulsive stochastic chemostat system in a polluted environment, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2016, 6(3), 865-875. [33] S. Nolen-Hoeksema, Gender differences in risk factors and consequences for alcohol use and problems, Clin. Psychol. Rev., 2004, 24(8), 981-1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2004.08.003 [34] H. Peng and X. Zhang, The dynamics of stochastic predator-prey models with non-constant mortality rate and general nonlinear functional response, J. Nonl. Mod. Anal., 2020, 2, 495-511. [35] H. Shu, D. Fan and J. Wei, Global stability of multi-group SEIR epidemic models with distributed delays and nonlinear transmission, Nonlinear Anal.-Real World Appl., 2012, 13(4), 1581-1592. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2011.11.016 [36] H. Song, J. Wang and W. Jiang, Global dynamics in a multi-group epidemic model for disease with latency spreading and nonlinear transmission rate, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2016, 6(1), 47-64. [37] A. Settati and A. Lahrouz, Stationary distribution of stochastic population systems under regime switching, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 244, 235-243. [38] Y. Takeuchi, N. Du, N. T. Hieu and K. Sato, Evolution of predator-prey systems described by a Lotka-Volterra equation under random environment, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2006, 323, 938-957. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.11.009 [39] M. Ventura-Cots et al., Colder weather and fewer sunlight hours increase alcohol consumption and alcoholic cirrhosis worldwide, Hepatology, 2018, 69(5), 1916-1930. [40] L. Wang and D. Jiang, Ergodic property of the chemostat: A stochastic model under regime switching and with general response function, Nonlinear Anal.-Hybrid Syst., 2018, 27, 341-352. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.10.001 [41] X. Wang, Q. Yang and H. Huo, The asymptotic behaviors of a stochastic social epidemic model with multi-perturbation, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2018, 8(1), 272-295. DOI: 10.11948/2018.272. [42] X. Wang, P. Zhang and Q. Yang, On the stochastic dynamics of a social epidemics model, Dyn. Nat. Soc., 2017, 6297074. DOI: 10.1155/2017/6297074. [43] World Health Organization, Global status report on alcohol and health, Geneva, 2018. [44] Q. Yang and X. Mao, Extinction and recurrence of multi-group SEIR epidemic models with stochastic perturbations, Nonlinear Anal.-Real World Appl., 2013, 14(3), 1434-1456. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2012.10.007 [45] X. Zhang, D. Jiang, A. Ahmed and T. Hayat, Stationary distribution of stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination under regime switching, Appl. Math. Lett., 2016, 59, 87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2016.03.010 -
-
-
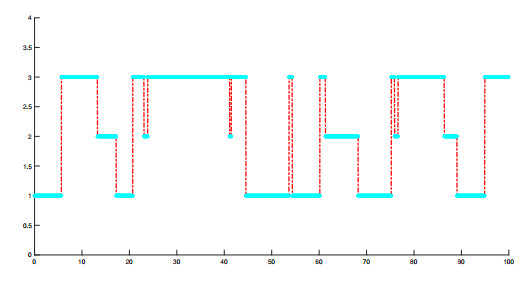
Figure 1. The Markovian chain of the extinction system with state space
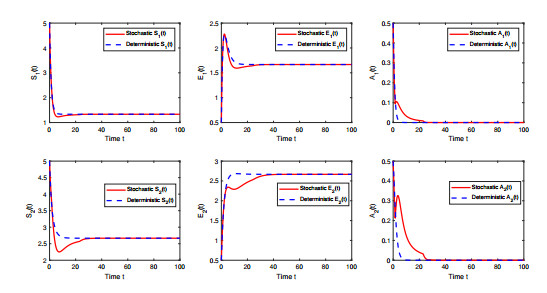
$ \mathbb{S} = \{1,2,3\} $ . - Figure 2. The diagrams track the populations size of the susceptible drinkers, educated susceptible drinkers and alcoholics of the deterministic model and the stochastic model over time, respectively.
-
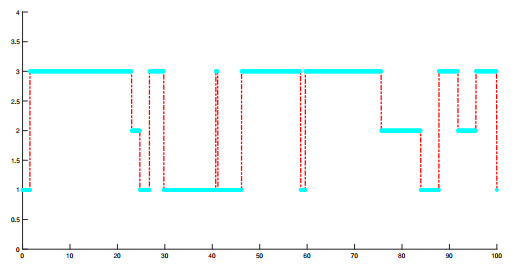
Figure 3. The Markovian chain of the persistence system with state space
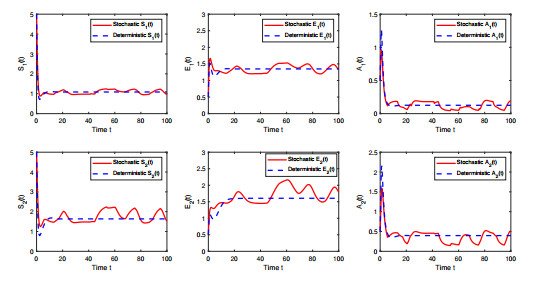
$ \mathbb{S} = \{1,2,3\} $ . - Figure 4. The diagrams track the populations size of the susceptible drinkers, educated susceptible drinkers and alcoholics of the deterministic model and the stochastic model over time, respectively.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: