| Citation: | Xinhong Zhang, Zhenfeng Shi, Hao Peng. TRANSMISSION DYNAMICS OF STOCHASTIC SVIR INFLUENZA MODELS WITH MEDIA COVERAGE[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2021, 11(6): 2792-2814. doi: 10.11948/20200444 |
TRANSMISSION DYNAMICS OF STOCHASTIC SVIR INFLUENZA MODELS WITH MEDIA COVERAGE
-
Abstract
This paper focuses on the dynamical behaviors of two stochastic SVIR models with media coverage. The first system is based on system perturbation. It is shown that the transmission dynamics can be classified by a critical value $ R_0^s $. If $ R_0^s<1 $, the disease will die out. $ R_0^s>1 $ implies that the disease will persist. Furthermore, the system has an ergodic stationary distribution if $ R_0^s>1 $. The second system is based on transmission parameter perturbation. Sufficient conditions for persistence and extinction are derived. Finally, theoretical results and numerical simulations show the effect of media coverage and environmental white noise.
-

-
References
[1] M. E. Alexander, C. Bowman, S. M. Moghadas, R. Summers, A. B. Gumel and B. M. Sahai, A vaccination model for transmission dynamics of influenza, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2004, 3(4), 503-524. doi: 10.1137/030600370 [2] Y. Cai, Y. Kang, M. Banerjee and W. Wang, A stochastic epidemic model incorporating media coverage, Commun. Math. Sci., 2015, 14(4), 893-910. [3] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Underlying Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released in 2020. Data are from the Multiple Cause of Death Files, 1999-2019, as compiled from data provided by the 57 vital statistics jurisdictions through the Vital Statistics Cooperative Program. Accessed at http://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html on Jul 14, 2021 7: 05: 18 AM. [4] K. Church and X. Liu, Analysis of a SIR model with pulse vaccination and temporary immunity: Stability, bifurcation and a cylindrical attractor, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2019, 50, 240-266. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2019.04.015 [5] N. H. Du and N. N. Nhu, Permanence and extinction for the stochastic SIR epidemic model, J. Differ. Equations, 2020, 269(11), 9619-9652. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2020.06.049 [6] S. Gao, H. Ouyang and J. Nieto, Mixed vaccination strategy in SIRS epidemic model with seasonal variability on infection, Int. J. Biomath., 2011, 4(4), 473-491. doi: 10.1142/S1793524511001337 [7] W. Guo, Q. Zhang, X. Li and W. Wang, Dynamic behavior of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with media coverage, Math. Meth. Appl. Sci., 2018, 41(24), 5506-5525. [8] D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43(3), 525-546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 [9] L. Imhof and S. Walcher, Exclusion and persistence in deterministic and stochastic chemostat models, J. Differ. Equations, 2005, 217(1), 26-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2005.06.017 [10] R. Khasminskii, Stochastic Stability of Differential equations, Sijthoff and Noordhoff press, Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 1980. [11] A. Lahrouz and L. Omari, Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with non-linear incidence, Stat. Probab. Lett., 2013, 83(4), 960-968. doi: 10.1016/j.spl.2012.12.021 [12] R. Lipster, A strong law of large numbers for local martingales, Stochastics, 1980, 3(1-4), 217-228. doi: 10.1080/17442508008833146 [13] M. Liu, C. Bai and Y. Jin, Population dynamical behavior of a two-predator one-prey stochastic model with time delay, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., 2017, 37(5), 2513-2538. doi: 10.3934/dcds.2017108 [14] M. Liu and M. Fan, Permanence of stochastic Lotka-Volterra systems, J. Nonlinear Sci., 2017, 27(2), 425-452. doi: 10.1007/s00332-016-9337-2 [15] X. Liu, Y. Takeuchi and S. Iwami, SVIR epidemic models with vaccination strategies, J. Theor. Biol., 2008, 253(1), 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.10.014 [16] R. Liu, J. Wu and H. Zhu, Media/psychological impact on multiple outbreaks of emerging infectious disease, Comput. Math. Meth. Med., 2007, 8(3), 153-164. doi: 10.1080/17486700701425870 [17] D. H. Nguyen, G. Yin and C. Zhu, Long-term analysis of a stochastic SIRS model with general incidence rates, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2020, 80(2), 814-838. doi: 10.1137/19M1246973 [18] M. Nuño, G. Chowell and A. B Gumel, Assessing the role of basic control measures, antivirals and vaccine in curtailing pandemic influenza: Scenarios for the US, UK and the Netherlands, J. R. Soc. Interface., 2006, 4(14), 505-521. [19] S. M. Salman, Memory and media coverage effect on an HIV/AIDS epidemic model with treatment, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2021, 385, 113203. [20] Z. Shi, X. Zhang and D. Jiang, Dynamics of an avian influenza model with half-saturated incidence, Appl. Math. Comput., 2019, 355, 399-416. [21] J. M. Tchuenche, N. Dube, C. P Bhunu, R. J. Smith and C. T. Bauch, The impact of media coverage on the transmission dynamics of human influenza, BMC Public Health, 2011, 11(S1), S5. [22] Y. Zhao, D. Jiang and D. O'Regan, The extinction and persistence of the stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination, Physica A, 2013, 392(20), 4916-4927. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2013.06.009 [23] Y. Zhao and D. Jiang, The threshold of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 243, 718-727. -
-
-
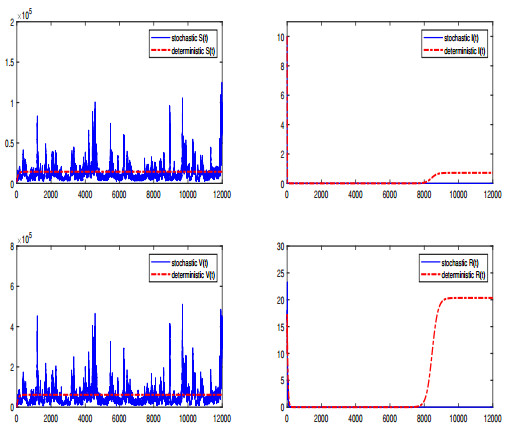
Figure 1. Simulations of solution
$ (S(t), I(t), V(t), R(t)) $ for deterministic model (1.1) and stochastic model (1.2) with white noise$ \delta_k = 0.16 $ ,$ (k = 1, 2, 3, 4) $ . -
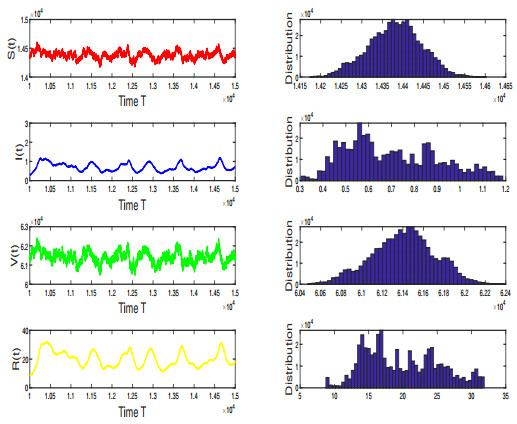
Figure 2. Left panels: Simulations of solution
$ (S(t), I(t), V(t), R(t)) $ for stochastic model (1.2). Right panels: Histogram stochastic system (1.2) with white noise$ \delta_k = 0.001 $ ,$ (k = 1, 2, 3, 4) $ . -
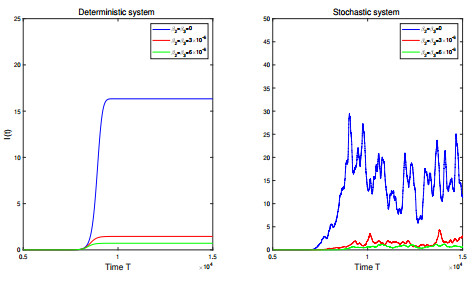
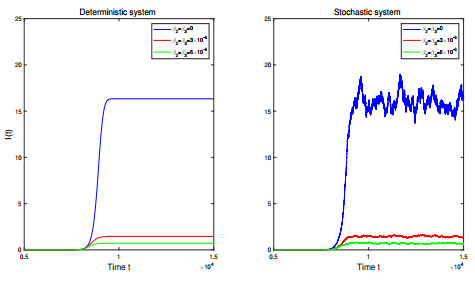
Figure 3. Simulations of
$ I(t) $ of deterministic model (1.1) and stochastic model (1.2) with different$ \beta_2 $ and$ \beta_3 $ values. -
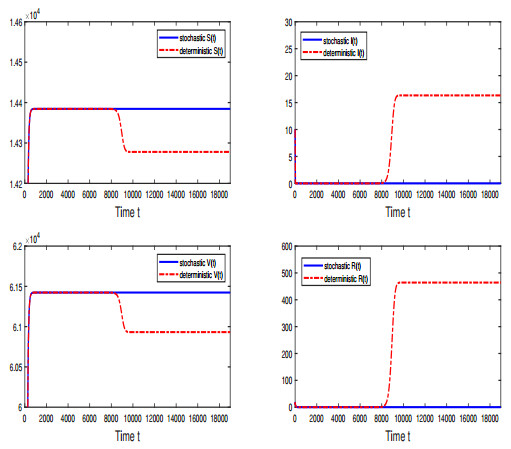
Figure 4. Simulations of solution
$ (S(t), I(t), V(t), R(t)) $ for deterministic model (1.1) and stochastic model (1.3) with white noise$ \delta = 0.05 $ . -
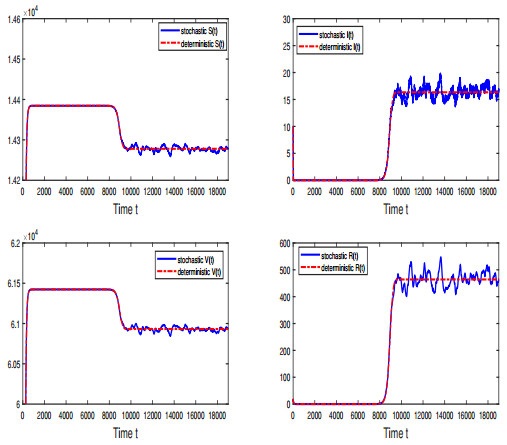
Figure 5. Simulations of solution
$ (S(t), I(t), V(t), R(t)) $ for deterministic model (1.1) and stochastic model (1.3) with white noise$ \delta = 0.008 $ . -
Figure 6. Simulations of
$ I(t) $ of deterministic model (1.1) and stochastic model (1.3) with different$ \beta_2 $ and$ \beta_3 $ values.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: