| Citation: | Zhihao Cao, Jiafu Wang, Lihong Huang. GLOBAL ASYMPTOTICAL STABILITY OF A PLANT DISEASE MODEL WITH AN ECONOMIC THRESHOLD[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(3): 895-906. doi: 10.11948/20210496 |
GLOBAL ASYMPTOTICAL STABILITY OF A PLANT DISEASE MODEL WITH AN ECONOMIC THRESHOLD
-
Abstract
This paper presents a plant disease model with an economic threshold, where the replanting number of susceptible plants depends on the removing number of infective plants. Making use of Lyapunov approach and Poincaré maps, we thoroughly investigate the global dynamics. We show the global asymptotical stability of endemic equilibria as well as a pseudo equilibrium. Moreover, the convergence in finite time is also examined for the infected plants. Our theoretical results indicate that the control goal could be achieved by taking appropriate removal and replanting rates.
-
Keywords:
- Filippov system /
- Poincaré map /
- economic threshold /
- stability /
- equilibrium
-

-
References
[1] A. Baciotti and F. Ceragioli, Stability and stabilization of discontinuous systems and non-smooth Lyapunov function, ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var., 1999, 4(4), 361-376. [2] C. Chen and X. Chen, Rich Sliding Motion and Dynamics in a Filippov Plant-Disease System, Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos, 2018, 28(01), 1850012. doi: 10.1142/S0218127418500128 [3] N. Chong and R. Smith, Modeling avian influenza using Filippov systems to determine culling of infected birds and quarantine, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2015, 24, 196-218. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2015.02.007 [4] M. Chan and M. Jeger, An analytical model of plant virus disease dynamics with roguing and replanting, J. Appl. Ecol., 1994, 31(3), 413-427. doi: 10.2307/2404439 [5] A. F. Filippov, Differential Equations with Discontinuous Righthand Sides, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [6] S. Fishman, R. Marcus, H. Talpaz et al., Epidemiological and economic models for the spread and control of citrus tristeza virus disease, Phytoparasitica, 1983, 11(1), 39-49. doi: 10.1007/BF02980710 [7] S. Fishman and R. Marcus, A model for spread of plant disease with periodic removes, J. Math. Biol., 1984, 21, 149-158. doi: 10.1007/BF00277667 [8] Z. Guo, L. Huang and X. Zou, Impact of discontinuous treatments on disease dynamics in an SIR epidemic model, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2013, 9(1), 97-110. [9] L. Huang, H. Ma, J. Wang, and C. Huang, Global dynamics of a Filippov plant disease model with an enconomic threshold of infected-susceptible ratio, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2020, 10(5), 2263-2277. [10] T. Iljon, J. Stirling and R. J. Smith, A mathematical model describing an outbreak of fire blight, 2012, 91-104. [11] R. Jones, Determining threshold levels for seed-borne virus infection in seed stocks, Virus Res., 2000, 71(1-2), 171-183. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1702(00)00197-0 [12] R. Jones, Using epidemiological information to develop effective integrated virus disease management strategies, Virus Res., 2004, 99(1), 5-30. [13] W. Li, L. Huang and J. Wang, Global dynamics of Filippov-type plant disease models with an interaction ratio threshold, Math. Meth. Appl. Sci., 2020, 43(11), 6995-7008. doi: 10.1002/mma.6450 [14] W. Li, L. Huang and J. Wang, Dynamic analysis of discontinuous plant disease models with a non-smooth separation line, Nonlinear Dyn., 2020, 99(1), 1675-1697. [15] W. Li, J. Ji, L. Huang and Z. Guo, Global dynamics of a controlled discontinuous diffusive SIR epidemic system, Appl. Math. Lett., 2021, 121(1), 107420. [16] W. Li, J. Ji, L. Huang and J. Wang, Bifurcations and dynamics of a plant disease system under non-smooth control strategy, Nonlinear Dyn., 2020, 99(2209), 3351-3371. [17] W. Li, L. Huang, Z. Guo and J. Ji, Global dynamic behavior of a plant disease model with ratio dependent impulsive control strategy, Math. Comput. Simul., 2020, 177, 120-139. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2020.03.009 [18] W. Li, J. Ji and L. Huang, Dynamics of a discontinuous computer worm system, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2020, 148(10), 4389-4403. doi: 10.1090/proc/15095 [19] X. Meng and Z. Li, The dynamics of plant disease models with continuous and impulsive cultural control strategies, J. Theor. Biol., 2010, 266(1), 29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.05.033 [20] R. Strange and P. Scott, Plant disease: A threat to global food security, Annu. Rev. Phytopathol, 2005, 4(1), 83-116. [21] H. Thieme and J. Heesterbeek, How to estimate the effificacy of periodic control of an infectious plant disease, Math. Biosci., 1989, 93(1), 15-29. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(89)90011-4 [22] S. Tang, Y. Xiao and R. A. Cheke, Dynamical analysis of plant disease models with cultural control strategies and economic thresholds, Math. Comput. Simul., 2010, 80(5), 894-921. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2009.10.004 [23] S. Tang, Y. Xiao and R. A. Cheke, Multiple attractors of host-parasitoid models with integrated pest management strategies: eradication, persistence and outbreak, Theor. Popul. Biol., 2008, 73(2), 181-197. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2007.12.001 [24] S. Tang and R. A. Cheke, Models for integrated pest control and their biological implications, Math. Biosci., 2008, 215(1), 115-125. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.06.008 [25] F. van den Bosch, N. McRoberts, F. van den Berg and L. V. Madden, The basic reproduction number of plant pathogens: matrix approaches to complex dynamics, Phytopathology, 2008, 98(2), 239-249. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-98-2-0239 [26] F. van den Bosch, M. J. Jeger and C. A. Gilligan, Disease control and its selection fordamaging plant virus strains in vegetatively propagated staple food crops; a heoretical assessment, Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci., 2007, 274(1606), 11-18. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3715 [27] F. van den Bosch and A. M. Roos, The dynamics of infectious diseases in orchards with roguing and replanting as control strategy, J. Math. Biol., 1996, 35(2), 129-157. doi: 10.1007/s002850050047 [28] M. Vurro, B. Bonciani and G. Vannacci, Emerging infectious diseases of crop plants in developing countries: impact on agriculture and socio-economic consequences, Food Secur., 2010, 2(2), 113-132. doi: 10.1007/s12571-010-0062-7 [29] J. Wang, X. Chen and L. Huang, The number and stability of limit cycles for planar piecewise linear systems of node-saddle type, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2019, 469(1), 405-427. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2018.09.024 [30] J. Wang, C. Huang and L. Huang, Discontinuity-induced limit cycles in a general planar piecewise linear system of saddle-focus type, Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst., 2019, 33, 162-178. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2019.03.004 [31] J. Wang, S. He and L. Huang, Limit cycles induced by threshold nonlinearity in planar piecewise linear systems of node-focus or node-center type, Internat. J. Bifur. Chaos, 2020, 30(11), 2050160. doi: 10.1142/S0218127420501606 [32] J. Wang and L. Huang, Limit cycles bifurcated from a focus-fold singularity in general piecewise smooth planar systems, J. Differ. Equ., 2021, 304, 491-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2021.10.006 [33] J. Wang, F. Zhang and L. Wang, Equilibrium, pseudoequilibrium and sliding-mode heteroclinic orbit in a Filippov-type plant disease model, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2016, 31, 308-324. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2016.01.017 [34] Y. Xiao, D. Cheng and H. Qin, Optimal impulsive control in periodic ecosystem, Syst. Control Lett., 2006, 55(7), 558-565. doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2005.12.003 [35] J. Zadoks and R. Schein, Epidemiology and Plant Disease Management, Oxford University Press, New York-Oxford, 1979. [36] T. Zhao and S. Tang, Plant disease control with economic threshold, J. Biomath., 2009, 24, 385-396. [37] T. Zhao, Y. Xiao and R. J. Smith, Non-smooth plant disease models with economic thresholds, Math. Biosci., 2013, 241(1), 34-48. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2012.09.005 -
-
-
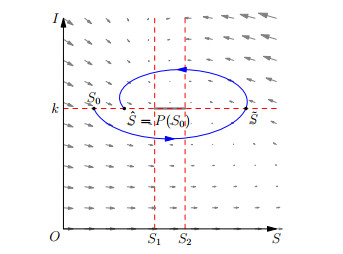
Figure 1. Illustration for the definition of the Poincaré map
$ P(\cdot) $ . -
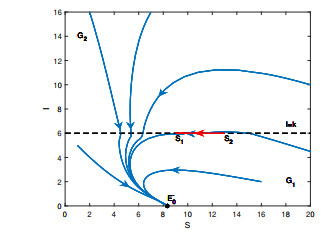
Figure 2. Global asymptotical stability of
$ E_0 $ for System (2.1) with$ A = 5 $ ,$ \beta= 0.1 $ ,$ \eta_1= 0.6 $ ,$ \eta_2 = 0.9 $ ,$ v = 0.4 $ ,$ p=0.3 $ ,$ k = 6 $ . -
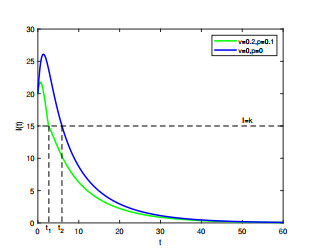
Figure 3. Time series of
$ I(t) $ by taking different$ p $ and$ v $ , where the initial condition is$ (S(0), I(0)) = (60, 20) $ and the other parameters are fixed as:$ A = 8 $ ,$ \beta = 0.04 $ ,$ \eta_1 = 0.3 $ ,$ \eta_2 = 0.8 $ ,$ k = 10 $ . -
Figure 4. Global asymptotical stability of
$ E_1 $ for System (2.1) with$ A = 8 $ ,$ \beta $ = 0.04,$ \eta_1 $ = 0.3,$ \eta_2 $ = 0.8,$ v = 0.5 $ ,$ p = 0.1 $ ,$ k = 5 $ . -
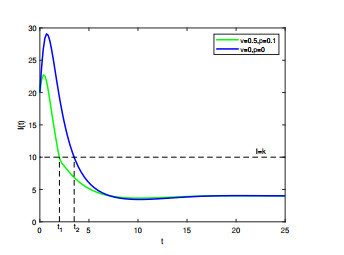
Figure 5. Time series of
$ I(t) $ by taking different$ p $ and$ v $ , where the initial condition is$ (S(0), I(0)) = (60, 20) $ and the other parameters are fixed as:$ A = 8 $ ,$ \beta = 0.04 $ ,$ \eta_1 = 0.3 $ ,$ \eta_2 = 0.8 $ ,$ k = 10 $ . -
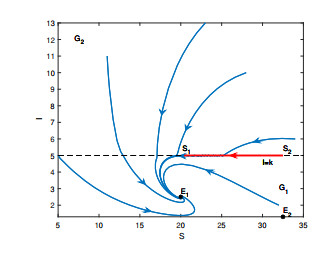
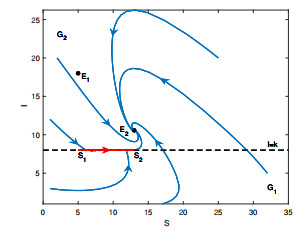
Figure 6. Global asymptotical stability of
$ E_2 $ for System (2.1), where the parameters are chosen as:$ A = 10 $ ,$ \beta=0.1 $ ,$ \eta_1=0.2 $ ,$ \eta_2 = 0.5 $ ,$ v = 0.8 $ ,$ p = 0.6 $ ,$ k = 8 $ . -
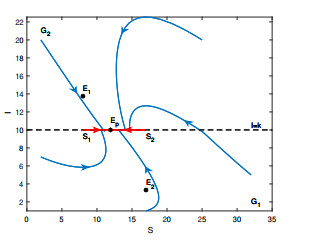
Figure 7. Global asymptotical stability of
$ E_p $ for System (2.1), where the parameters are chosen as:$ A = 15 $ ,$ \beta $ = 0.1,$ \eta_1 $ = 0.55,$ \eta_2 $ = 0.8,$ v = 0.9 $ ,$ p = 0.8 $ ,$ k = 10 $ .




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: