| Citation: | Yanyu Bao, Jianing Chen, Lijun Zhang, Mingji Zhang. HIGHER ORDER EXPANSIONS IN FINITE ION SIZE VIA POISSON-NERNST-PLANCK SYSTEMS WITH BIKERMAN'S LOCAL HARD-SPHERE POTENTIAL[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(3): 907-931. doi: 10.11948/20220001 |
HIGHER ORDER EXPANSIONS IN FINITE ION SIZE VIA POISSON-NERNST-PLANCK SYSTEMS WITH BIKERMAN'S LOCAL HARD-SPHERE POTENTIAL
-
Abstract
Finite ion sizes play significant roles in characterizing ionic flow properties of interest, such as the selectivity of ion channels. As an extension of the work done in [Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 21 (2016), 1775-1802], we further investigate the higher order (in the volume of the cation), mainly the second order, contributions from finite ion sizes to ionic flows in terms of both the total flow rate of charges and the individual fluxes. This is particularly important since the first-order terms approach zero as the left boundary concentration is close to the right one for the same ion species. The interaction between the first-order terms and the second-order terms is characterized in detail. Moreover, several critical potentials are identified, and they play critical roles in examining the qualitative properties of ionic flows. Some can be estimated experimentally. The analysis in this work could provide complementary information and better understanding of the mechanism of ionic flows through ion channels. Numerical simulations are performed to provide intuitive illustration of our analytical results.
-
Keywords:
- I-V relations /
- individual fluxes /
- critical potentials /
- finite ion sizes
-

-
References
[1] N. Abaid, R. S. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Asymptotic expansions of I-V relations via a Poisson-Nernst-Planck system. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2008, 7, 1507–1526. doi: 10.1137/070691322 [2] R. Aitbayev, P. W. Bates, H. Lu, L. Zhang and M. Zhang, Mathematical studies of Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: dynamics of ionic flows without electroneutrality conditions. J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2019, 362, 510–527. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2018.10.037 [3] V. Barcilon, Ion flow through narrow membrane channels: Part I. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1992, 52, 1391–1404. doi: 10.1137/0152080 [4] V. Barcilon, D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Ion flow through narrow membrane channels: Part Ⅱ. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1992, 52, 1405–1425. doi: 10.1137/0152081 [5] V. Barcilon, D. Chen, R. S. Eisenberg and J. W. Jerome, Qualitative properties of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: Perturbation and simulation study. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1997, 57, 631–648. doi: 10.1137/S0036139995312149 [6] P. W. Bates, J. Chen and M. Zhang, Dynamics of ionic flows via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with local hard-sphere potentials: Competition between cations. Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 17, 3736–3766. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020210 [7] P. W. Bates, W. Liu, H. Lu and M. Zhang, Ion size and valence effects on ionic flows via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems. Commun. Math. Sci., 2017, 15, 881–901. doi: 10.4310/CMS.2017.v15.n4.a1 [8] P. W. Bates, Z. Wen and M. Zhang, Small permanent charge effects on individual fluxes via via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with multiple cations. J. Nonlinear Sci., 2021, 31, 1–62. doi: 10.1007/s00332-020-09667-0 [9] J. J. Bikerman, Structure and capacity of the electrical double layer. Philos. Mag., 1942, 33, 384. doi: 10.1080/14786444208520813 [10] M. Burger, R. S. Eisenberg and H. W. Engl, Inverse problems related to ion channel selectivity. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2007, 67, 960–989. doi: 10.1137/060664689 [11] A. E. Cardenas, R. D. Coalson and M. G. Kurnikova, Three-Dimensional Poisson-Nernst-Planck Theory Studies: Influence of Membrane Electrostatics on Gramicidin A Channel Conductance. Biophys. J., 2000, 79, 80–93. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76275-8 [12] D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Charges, currents and potentials in ionic channels of one conformation. Biophys. J., 1993, 64, 1405–1421. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81507-8 [13] J. Chen, Y. Wang, L. Zhang and M. Zhang, Mathematical analysis of Poisson-Nernst-Planck models with permanent charges and boundary layers: Studies on individual fluxes. Nonlinearity, 2021, 34, 3879–3906. doi: 10.1088/1361-6544/abf33a [14] R. D. Coalson, Poisson-Nernst-Planck theory approach to the calculation of current through biological ion channels. IEEE Trans. Nanobioscience, 2005, 4, 81–93. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2004.842495 [15] R. Coalson and M. Kurnikova, Poisson-Nernst-Planck theory approach to the calculation of current through biological ion channels. IEEE Transaction on NanoBioscience, 2005, 4, 81–93. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2004.842495 [16] B. Eisenberg, Proteins, Channels, and Crowded Ions. Biophys. Chem., 2003, 100, 507–517. [17] R. S. Eisenberg, Channels as enzymes. J. Memb. Biol., 1990, 115, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869101 [18] R. S. Eisenberg, Atomic Biology, Electrostatics and Ionic Channels. In New Developments and Theoretical Studies of Proteins, R. Elber, Editor, World Scientific, Philadelphia, 1996, 269–357. [19] R. S. Eisenberg, From Structure to Function in Open Ionic Channels. J. Memb. Biol., 1999, 171, 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s002329900554 [20] B. Eisenberg, Y. Hyon and C. Liu, Energy variational analysis of ions in water and channels: Field theory for primitive models of complex ionic fluids. J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 133, 104104(1–23). doi: 10.1063/1.3476262 [21] B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion channels with permanent charges. SIAM J. Math. Anal., 2007, 38, 1932–1966. doi: 10.1137/060657480 [22] A. Ern, R. Joubaud and T. Leliévre, Mathematical study of non-ideal electrostatic correlations in equilibrium electrolytes. Nonlinearity, 2012, 25, 1635–1652. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/25/6/1635 [23] D. Gillespie, A singular perturbation analysis of the Poisson-Nernst-Planck system: Applications to Ionic Channels. Ph. D Dissertation, Rush University at Chicago, 1999. [24] D. Gillespie, L. Xu, Y. Wang and G. Meissner, (De)constructing the Ryanodine Receptor: Modeling Ion Permeation and Selectivity of the Calcium Release Channel. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 15598–15610. doi: 10.1021/jp052471j [25] D. Gillespie and R. S. Eisenberg, Physical descriptions of experimental selectivity measurements in ion channels. European Biophys. J., 2002, 31, 454–466. doi: 10.1007/s00249-002-0239-x [26] D. Gillespie, W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Coupling Poisson-Nernst-Planck and density functional theory to calculate ion flux. J. Phys. : Condens. Matter, 2002, 14, 12129–12145. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/14/46/317 [27] D. Gillespie, W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Crowded Charge in Biological Ion Channels. Nanotech., 2003, 3, 435–438. [28] P. Graf, M. G. Kurnikova, R. D. Coalson and A. Nitzan, Comparison of Dynamic Lattice Monte-Carlo Simulations and Dielectric Self Energy Poisson-Nernst-Planck Continuum Theory for Model Ion Channels. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 2006–2015. doi: 10.1021/jp0355307 [29] L. J. Henderson, The Fitness of the Environment: an Inquiry Into the Biological Significance of the Properties of Matter. Macmillan, New York, 1927. [30] U. Hollerbach, D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Two- and Three-Dimensional Poisson-Nernst-Planck Simulations of Current Flow through Gramicidin-A. J. Comp. Science, 2002, 16, 373–409. [31] U. Hollerbach, D. Chen, W. Nonner and B. Eisenberg, Three-dimensional Poisson-Nernst-Planck Theory of Open Channels. Biophys. J., 1999, 76, A205. [32] Y. Hyon, B. Eisenberg and C. Liu, A mathematical model for the hard sphere repulsion in ionic solutions. Commun. Math. Sci., 2010, 9, 459–475. [33] Y. Hyon, J. Fonseca, B. Eisenberg and C. Liu, A new Poisson-Nernst-Planck equation (PNP-FS-IF) for charge inversion near walls. Biophys. J., 2011, 100, 578a. [34] Y. Hyon, J. Fonseca, B. Eisenberg and C. Liu, Energy variational approach to study charge inversion (layering) near charged walls. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2012, 17, 2725–2743. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2012.17.2725 [35] W. Im, D. Beglov and B. Roux, Continuum solvation model: Electrostatic forces from numerical solutions to the Poisson-Bolztmann equation. Comp. Phys. Comm., 1998, 111, 59–75. doi: 10.1016/S0010-4655(98)00016-2 [36] W. Im and B. Roux, Ion permeation and selectivity of OmpF porin: a theoretical study based on molecular dynamics, Brownian dynamics, and continuum electrodiffusion theory. J. Mol. Biol., 2002, 322, 851–869. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00778-7 [37] J. W. Jerome, Mathematical Theory and Approximation of Semiconductor Models. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1995. [38] J. W. Jerome and T. Kerkhoven, A finite element approximation theory for the drift-diffusion semiconductor model. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 1991, 28, 4030–422. [39] S. Ji and W. Liu, Poisson-Nernst-Planck Systems for Ion Flow with Density Functional Theory for Hard-Sphere Potential: I-V relations and Critical Potentials. Part I: Analysis. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2012, 24, 955–983. doi: 10.1007/s10884-012-9277-y [40] S. Ji and W. Liu, Flux ratios and channel structures. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2019, 31, 1141–1183. doi: 10.1007/s10884-017-9607-1 [41] S. Ji, W. Liu and M. Zhang, Effects of (small) permanent charges and channel geometry on ionic flows via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck models. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2015, 75, 114–135. doi: 10.1137/140992527 [42] Y. Jia, W. Liu and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with Bikerman's local hard-sphere potential: Ion size and valence effects. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2016, 21, 1775–1802. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2016022 [43] M. S. Kilic, M. Z. Bazant and A. Ajdari, Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. Ⅱ. Modified Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations. Phys. Rev. E, 2007, 75, 021503. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.75.021503 [44] M. G. Kurnikova, R. D. Coalson, P. Graf and A. Nitzan, A Lattice Relaxation Algorithm for 3D Poisson-Nernst-Planck Theory with Application to Ion Transport Through the Gramicidin A Channel. Biophys. J., 1999, 76, 642–656. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77232-2 [45] B. Li, Minimizations of electrostatic free energy and the Poisson-Boltzmann equation for molecular solvation with implicit solvent. SIAM J. Math. Anal., 2009, 40, 2536–2566. doi: 10.1137/080712350 [46] B. Li, Continuum electrostatics for ionic solutions with non-uniform ionic sizes. Nonlinearity, 2009, 22, 22, 811–833. [47] G. Lin, W. Liu, Y. Yi and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with a local hard-sphere potential for ion size effects. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2013, 12, 1613–1648. doi: 10.1137/120904056 [48] J. Liu and B. Eisenberg, Poisson-Nernst-Planck-Fermi theory for modeling biological ion channels. J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 141, 12B640. [49] W. Liu, Geometric singular perturbation approach to steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2005, 65, 754–766. doi: 10.1137/S0036139903420931 [50] W. Liu, One-dimensional steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion channels with multiple ion species. J. Differ. Equations, 2009, 246, 428–451. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2008.09.010 [51] W. Liu, A flux ration and a universal property of permanent charge effects on fluxes. Comput. Math. Biophys., 2018, 6, 28–40. doi: 10.1515/cmb-2018-0003 [52] W. Liu and B. Wang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for narrow tubular-like membrane channels. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2010, 22, 413–437. doi: 10.1007/s10884-010-9186-x [53] W. Liu, X. Tu and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck Systems for Ion Flow with Density Functional Theory for Hard-Sphere Potential: I-V relations and Critical Potentials. Part Ⅱ: Numerics. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2012, 24, 985–1004. doi: 10.1007/s10884-012-9278-x [54] H. Lu, J. Li, J. Shackelford, J. Vorenberg and M. Zhang, Ion size effects on individual fluxes via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with Bikerman's local hard-sphere potential: Analysis without electroneutrality boundary conditions. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2018, 23, 1623–1643. [55] M. S. Mock, An example of nonuniqueness of stationary solutions in device models. COMPEL, 1982, 1, 165–174. doi: 10.1108/eb009970 [56] H. Mofidi, B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Effects of diffusion coefficients and permanent charges on reversal potentials in ionic channels. Entropy, 2020, 22, 1–23. [57] W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Ion permeation and glutamate residues linked by Poisson-Nernst-Planck theory in L-type Calcium channels. Biophys. J., 1998, 75, 1287–1305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)74048-2 [58] S. Y. Noskov, S. Berneche and B. Roux, Control of ion selectivity in potassium channels by electrostatic and dynamic properties of carbonyl ligands. Nature, 2004, 431, 830–834. doi: 10.1038/nature02943 [59] S. Y. Noskov and B. Roux, Ion selectivity in potassium channels. Biophys. Chem., 2006, 124, 279–291. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2006.05.033 [60] J. K. Park and J. W. Jerome, Qualitative properties of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: Mathematical study. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1997, 57, 609–630. doi: 10.1137/S0036139995279809 [61] B. Roux, T. W. Allen, S. Berneche and W. Im, Theoretical and computational models of biological ion channels. Quat. Rev. Biophys., 2004, 37, 15–103. doi: 10.1017/S0033583504003968 [62] B. Roux and S. Crouzy, Theoretical studies of activated processes in biological ion channels, in Classical and quantum dynamics in condensed phase simulations, B.J. Berne, G. Ciccotti and D.F. Coker Eds, World Scientific Ltd., 1998, 445–462. [63] I. Rubinstein, Multiple steady states in one-dimensional electrodiffusion with local electroneutrality. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1987, 47, 1076–1093. doi: 10.1137/0147070 [64] I. Rubinstein, Electro-Diffusion of Ions. SIAM Studies in Applied Mathematics, SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, 1990. [65] M. Saraniti, S. Aboud and R. Eisenberg, The Simulation of Ionic Charge Transport in Biological Ion Channels: an Introduction to Numerical Methods. Rev. Comp. Chem., 2005, 22, 229–294. [66] Z. Schuss, B. Nadler and R. S. Eisenberg, Derivation of Poisson and Nernst-Planck equations in a bath and channel from a molecular model. Phys. Rev. E, 2001, 64, 1–14. [67] A. Singer and J. Norbury, A Poisson-Nernst-Planck model for biological ion channels–an asymptotic analysis in a three-dimensional narrow funnel. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2009, 70, 949–968. doi: 10.1137/070687037 [68] A. Singer, D. Gillespie, J. Norbury and R. S. Eisenberg, Singular perturbation analysis of the steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck system: applications to ion channels. European J. Appl. Math., 2008, 19, 541–560. doi: 10.1017/S0956792508007596 [69] H. Steinrück, Asymptotic analysis of the current-voltage curve of a $pnpn$ semiconductor device. IMA J. Appl. Math., 1989, 43, 243–259. doi: 10.1093/imamat/43.3.243 [70] H. Steinrück, A bifurcation analysis of the one-dimensional steady-state semiconductor device equations. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1989, 49, 1102–1121. doi: 10.1137/0149066 [71] L. Sun and W. Liu, Non-localness of excess potentials and boundary value problems of Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ionic flow: a case study. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2018, 30, 779–797. doi: 10.1007/s10884-017-9578-2 [72] Z. Wen, P. W. Bates and M. Zhang, Effects on I-V relations from small permanent charge and channel geometry via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations with multiple cations. Nonlinearity, 2021, 34, 4464–4502. doi: 10.1088/1361-6544/abfae8 [73] Z. Wen, L. Zhang and M. Zhang, Dynamics of classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with multiple cations and boundary layers. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2021, 33, 211–234. doi: 10.1007/s10884-020-09861-4 [74] M. Zhang, Asymptotic expansions and numerical simulations of I-V relations via a steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck system. Rocky MT J. Math., 2015, 45, 1681–1708. [75] M. Zhang, Boundary layer effects on ionic flows via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems. Comput. Math. Biophys., 2018, 6, 14–27. doi: 10.1515/cmb-2018-0002 [76] M. Zhang, Competition between cations via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with nonzero but small permanent charges. Membranes, 2021, 11, 236. doi: 10.3390/membranes11040236 [77] L. Zhang, B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, An effect of large permanent charge: Decreasing flux with increasing transmembrane potential. Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics, 2019, 227, 2575–2601. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2019-700134-7 [78] Q. Zheng, D. Chen and G. Wei, Second-order Poisson-Nernst-Planck solver for ion transport. J. Comput. Phys., 2011, 230, 5239–5262. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.03.020 [79] Q. Zheng and G. Wei, Poisson-Boltzmann-Nernst-Planck model. J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 134, 194101(1–17). doi: 10.1063/1.3581031 [80] S. Zhou, Z. Wang and B. Li, Mean-field description of ionic size effects with nonuniform ionic sizes: A numerical approach. Phy. Rev. E, 2011, 84, 021901(1–13). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.84.021901 -
-
-
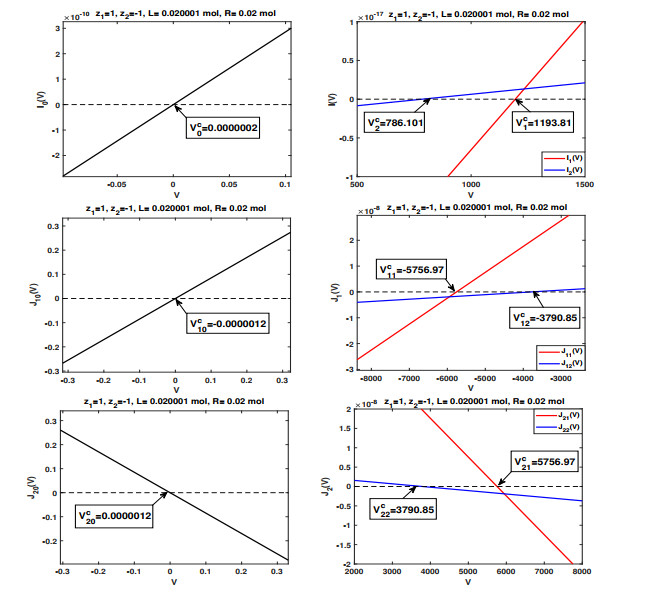
Figure 1. Numerical identifications of the critical potentials
$ V_k^c, \ V^c_{1k} $ and$ V_{2k}^c $ for$ k=0, 1, 2. $ The monotonicity of the functions$ I_k(V) $ ,$ J_{1k}(V) $ and$ J_{2k}(V) $ for$ k=0, 1, 2 $ is shown clearly in each figure. This provides intuitive illustration of Theorem 4.1 with$ 1<x<x^*=339.75691 $ . -
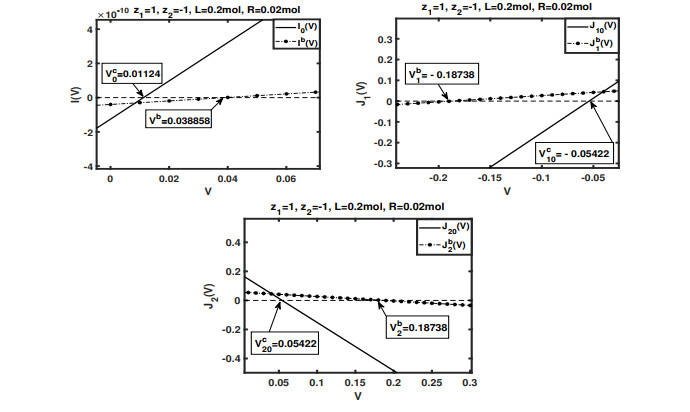
Figure 2. Numerical identifications of the critical potentials
$ V_0^c, \ V^b, V_{10}^c, V_1^b, V_{20}^c $ and$ V_2^b $ with small$ \nu $ . The monotonicity of the functions$ I_0(V), \ J_{10}(V) $ and$ J_{20}(V) $ (solid line in each figure) and the functions$ I^b(V), \ J_1^b(V) $ and$ J_2^b(V) $ (dashed line with star in each figure) can be observed clearly. This provides intuitive illustration of Theorem 4.2. -
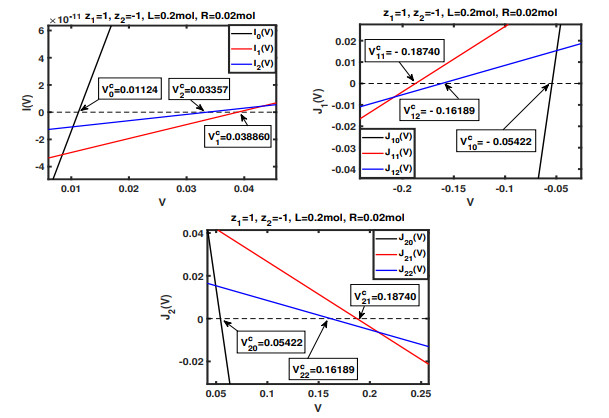
Figure 3. Numerical identifications of the critical potentials
$ V_k^c, \ V^c_{1k} $ and$ V_{2k}^c $ for$ k=0, 1, 2. $ The monotonicity of the functions$ I_k(V) $ ,$ J_{1k}(V) $ and$ J_{2k}(V) $ for$ k=0, 1, 2 $ is shown clearly in each figure for the case with$ L $ close to$ R. $ It is clear that, for$ k=1, 2 $ , the values of$ V_0^c $ and$ V_{k0}^c $ become very small, the values of$ V_k^c\ V_{1k}^c $ and$ V_{2k}^c $ for$ k=1, 2 $ become very large, and the curves$ I_k, \ J_{1k} $ and$ J_{2k} $ become very small as$ L $ close to$ R $ . The observation is consistent with our analytical results stated in Section 4.3.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: