| Citation: | Qianjun Chen, Zijian Liu, Yuanshun Tan, Jin Yang. ANALYSIS OF A STOCHASTIC NONAUTONOMOUS HYBRID POPULATION MODEL WITH IMPULSIVE PERTURBATIONS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2023, 13(5): 2365-2386. doi: 10.11948/20220108 |
ANALYSIS OF A STOCHASTIC NONAUTONOMOUS HYBRID POPULATION MODEL WITH IMPULSIVE PERTURBATIONS
-
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a stochastic nonautonomous hybrid population model with Allee effect, Markovian switching and impulsive perturbations and investigate its stochastic dynamics. We first establish sufficient conditions for the extinction and permanence. Then, we study some asymptotic properties and the lower- and upper-growth rates of the positive solutions. Finally, by performing numerical simulations we verify the main results and analyze the impact on the system from the Allee effect, the Markovian switching and the impulsive perturbations.
-
Keywords:
- Allee effect /
- markovian switching /
- impulsive perturbations /
- permanence /
- extinction
-

-
References
[1] W. J. Anderson, Continuous-time Markov Chains: An Application-Oriented Approach, Springer, New York, 2012. [2] G. Arthi, R. Sivasangari and Y. Ma, Existence and controllability for impulsive fractional stochastic evolution systems with state-dependent delay, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2023, 13(1), 95–115. [3] L. Berec, E. Angulo and F. Courchamp, Multiple Allee effects and population management, Trends in Ecol. Evolut., 2007, 22(4), 185–191. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2006.12.002 [4] Y. Deng and M. Liu, Analysis of a stochastic tumor-immune model with regime switching and impulsive perturbations, Appl. Math. Modell., 2020, 78, 482–504. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.10.010 [5] B. Dennis, Allee effects: population growth, critical density, and the chance of extinction, Natural Resource Modeling, 1989, 3(4), 481–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-7445.1989.tb00119.x [6] L. Donald, Persistence of dynamical systems under random perturbations, J. Siam Review, 1975, 17(4), 605–640. doi: 10.1137/1017070 [7] A. Freedman, Stochastic Differential Equations and their Applications, Academic Press, San Diego, 1976. [8] T. C. Gard, Introduction to Stochastic Differential Equations, Marcel Dekker Inc New York, 1988, 84(408), 19–19. [9] J. Golec and S. Sathananthan, Stability analysis of a stochastic logistic model, J. Math. Comput. Modell., 2003, 38(5–6), 585–593. doi: 10.1016/S0895-7177(03)90029-X [10] J. Hou, Z. Teng and S. Gao, Permanence and global stability for nonautonomous N-species Lotka-Valterra competitive system with impulses, Nonlinear Anal. : RWA, 2010, 11(3), 1882–1896. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2009.04.012 [11] W. Ji, Permanence and extinction of a stochastic hybrid population model with Allee effect, Physica A: Sta. Mec. Appl., 2019, 533, 122075. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.122075 [12] D. Jiang, N. Shi and X. Li, Global stability and stochastic permanence of a non-autonomous logistic equation with random perturbation, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2008, 340(1), 588–597. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2007.08.014 [13] X. Jiang, L. Zu, D. Jiang, et al., Analysis of a Stochastic Holling Type Ⅱ Predator-Prey Model Under Regime Switching, Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc., 2020, 43(3), 2171–2197. doi: 10.1007/s40840-019-00798-6 [14] Y. Jiang, Z. Liu, J. Yang, et al., Dynamics of a stochastic Gilpin-Ayala population model with Markovian switching and impulsive perturbations, Adv. Differ. Equ., 2020, 2020(1), 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s13662-019-2438-0 [15] R. Z. Khasminskii, C. Zhu and G. Yin, Stability of regime-switching diffusions, Stochastic Process. Appl., 2007, 117(8), 1037–1051. doi: 10.1016/j.spa.2006.12.001 [16] D. Kuang, Q. Yin and J. Li, Stationary distribution and extinction of stochastic HTLV-I infection model with CTL immune response under regime switching, J. Nonlinear Model. Anal., 2020, 2(4), 585–600. [17] X. Li, A. Gray, D. Jiang, et al., Sufficient and necessary conditions of stochastic permanence and extinction for stochastic logistic populations under regime switching, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2011, 376(1), 11–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.10.053 [18] X. Li and G. Yin, Logistic models with regime switching: permanence and ergodicity, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2016, 441(2), 593–611. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2016.04.016 [19] A. Liebhold and J. Bascompte, The Allee effect, stochastic dynamics and the eradication of alien species, Ecology Letters, 2003, 6(2), 133–40. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00405.x [20] B. Liu, X. Liu and X. Liao, Existence and uniqueness and stability of solutions for stochastic impulsive systems, J. Syst. Sci. & Complexity, 2007, 20(1), 149–158. [21] M. Liu and M. Deng, Permanence and extinction of a stochastic hybrid model for tumor growth, Appl. Math. Lett., 2019, 94, 66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2019.02.016 [22] M. Liu and M. Deng, Analysis of a stochastic hybrid population model with Allee effect, Appl. Math. Comput., 2020, 364, 124582. [23] M. Liu and K. Wang, Persistence and extinction in stochastic non-autonomous logistic systems, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2011, 375(2), 443–457. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.09.058 [24] M. Liu and K. Wang, On a stochastic logistic equation with impulsive perturbations, Comput. Math. Appl., 2012, 63(5), 871–886. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2011.11.003 [25] M. Liu and K. Wang, Dynamics and simulations of a logistic model with impulsive perturbations in a random environment, Math. Comput. Simulat., 2013, 92, 53–75. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2013.04.011 [26] Q. Luo and X. Mao, Stochastic population dynamics under regime switching, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2007, 334(1), 69–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.12.032 [27] X. Mao and C. Yuan, Stochastic Differential Equations with Markovian Switching, Imperial College Press, London, 2006. [28] J. Shi and R. Shivaji, Persistence in reaction diffusion models with weak allee effect, J. Math. Biol., 2006, 52(6), 807–829. doi: 10.1007/s00285-006-0373-7 [29] L. Shu, X. Shu, Q. Zhu and F. Xu, Existence and exponential stability of mild solutions for second-order neutral stochastic functional differential equation with random impulses, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2021, 11(1), 59–80. [30] J. Wang, J. Shi and J. Wei, Predator-prey system with strong Allee effect in prey, J. Math. Biol., 2011, 62(3), 291–331. doi: 10.1007/s00285-010-0332-1 [31] R. Wu, Dynamics of stochastic hybrid Gilpin-Ayala system with impulsive perturbations, J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl., 2017, 10(2), 436–450. doi: 10.22436/jnsa.010.02.10 [32] Z. Wu, P. Cheng, Z. Wei, et al., Ginzburg-Landau equations with random switching and impulsive perturbations, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 2019, 79, 104912. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2019.104912 [33] X. Yu, S. Yuan and T. Zhang, Persistence and ergodicity of a stochastic single species model with Allee effect under regime switching, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 2018, 59, 359–374. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.11.028 [34] S. Zhang, X. Meng, T. Feng, et al., Dynamics analysis and numerical simulations of a stochastic non-autonomous predator-prey system with impulsive effects, Nonlinear Anal. : Hybrid Systems, 2017, 26, 19–37. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.04.003 -
-
-
Figure 1.
Figure (a) represents the trajectory of the solution of subsystem (5.1a). It is shown that population
$ x $ -
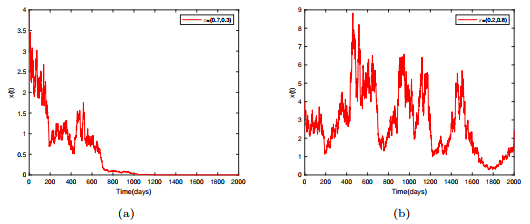
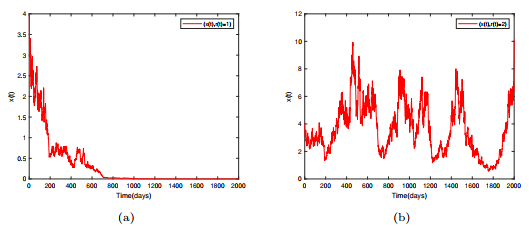
Figure 2.
Trajectories of system (5.1) switching between states 1 and 2. Figure (a) represents the trajectory of the stationary distribution
$ \pi=(\pi_1, \pi_2)=(0.7, 0.3) $ $ x $ $ \pi=(\pi_1, \pi_2)=(0.2, 0.8) $ -
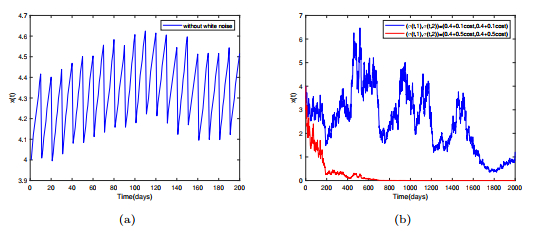
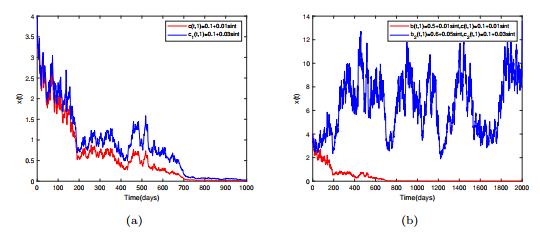
Figure 3.
Trajectories of system (5.1) switching between states 1 and 2, the stationary distribution of Markov chain is
$ \pi=(\pi_1, \pi_2)=(0.7, 0.3) $ $ (\sigma(t, 1), \sigma(t, 2))=(0.5-0.1\cos t, 0.4+0.1\cos t) $ $ (\sigma(t, 1), \sigma(t, 2))=(0.8-0.1\cos t, 0.8+0.1\cos t) $ -
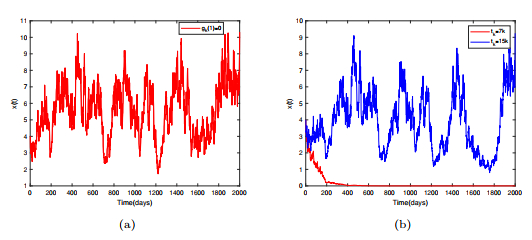
Figure 4.
Trajectories of system (5.1). Figure (a) represents the trajectory of the solution of subsystem (5.1a). It shows that population
$ x $ $ \pi=(\pi_1, \pi_2)=(0.7, 0.3) $ -
Figure 5.
Figure (a) represents the trajectory of the solution of subsystem (5.1a) with
$ g_k(1)=1.05 $ $ x $ $ g_k(2)=0.8 $ -
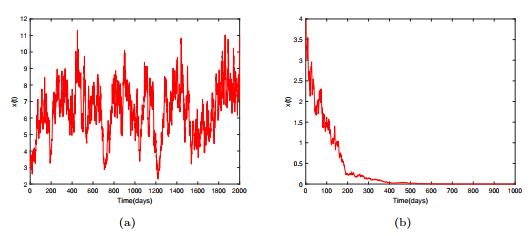
Figure 6.
Figures represent the trajectory of the solution of subsystem (5.1a).




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: