| Citation: | Long Yan, Hongguo Xu, Weishi Liu. POISSON-NERNST-PLANCK MODELS FOR THREE ION SPECIES: MONOTONIC PROFILES VS. OSCILLATORY PROFILES[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(3): 1211-1233. doi: 10.11948/20220195 |
POISSON-NERNST-PLANCK MODELS FOR THREE ION SPECIES: MONOTONIC PROFILES VS. OSCILLATORY PROFILES
-
Abstract
We consider ionic flows through an ion channel via a quasi-one-dimensional classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck model. The specific biological setup involves ionic solutions with three ion species and the permanent charge is set to be zero. It is known that, for ionic flows with two ion species, the spatial profiles of the electric potential and the ion concentrations are monotonic, independent of boundary conditions. For ionic flows with three or more ion species with at least three different valences, depending on the boundary conditions, the profiles could be oscillatory. In this work, for ionic mixtures with two cation species of different valences and one anion species, we will provide a complete classification in terms of boundary conditions on when the profiles are monotonic and when they are oscillatory. This would be an important step for studies including nonzero permanent charges.
-
Keywords:
- Ion channel /
- ion flow /
- PNP models /
- three ion species /
- monotonic vs. oscillatory spatial profiles
-

-
References
[1] N. Abaid, R. S. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Asymptotic expansions of I-V relations via a Poisson-Nernst-Planck system, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2008, 7, 1507–1526. doi: 10.1137/070691322 [2] V. Barcilon, D. Chen, R. S. Eisenberg and J. W. Jerome, Qualitative properties of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: Perturbation and simulation study, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1997, 57, 631–648. doi: 10.1137/S0036139995312149 [3] P. Bates, Z. Wen and M. Zhang, Small permanent charge effects on individual fluxes via Poisson-Nernst-Planck models with multiple cations, J. Nonl. Sci., 2021, 31(3), Paper No. 55, 62 pp. [4] M. Bazant, K. Chu and B. Bayly, Current-Voltage relations for electrochemical thin films, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2005, 65, 1463–1484. doi: 10.1137/040609938 [5] F. Bezanilla, The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels, Phys. Rev., 2000, 80, 555–592. [6] J. J. Bikerman, Structure and capacity of the electrical double layer, Philos. Mag., 1942, 33, 384–397. doi: 10.1080/14786444208520813 [7] D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Charges, currents and potentials in ionic channels of one conformation, Biophys. J., 1993, 64, 1405–1421. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81507-8 [8] R. S. Eisenberg, Ion channels as devices, J. Comp. Electro., 2003, 2, 245–249. [9] R. S. Eisenberg, Proteins, channels, and crowded ions, Biophys. Chem., 2003, 100, 507–517. [10] B. Eisenberg, Y. Hyon and C. Liu, Energy variational analysis of ions in water and channels: Field theory for primitive models of complex ionic fluids, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 133, 104104(1–23). [11] B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion channels with permanent charges, SIAM J. Math. Anal., 2007, 38, 1932–1966. doi: 10.1137/060657480 [12] B. Eisenberg, W. Liu and H. Xu, Reversal permanent charge and reversal potential: Case studies via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck models, Nonlinearity, 2015, 28, 103–128. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/28/1/103 [13] D. Gillespie, W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Coupling Poisson-Nernst-Planck and density functional theory to calculate ion flux, J. Phys. : Condens. Matter, 2002, 14, 12129–12145. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/14/46/317 [14] D. Gillespie, W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Density functional theory of charged, hard-sphere fluids, Phys. Rev. E, 2003, 68, 0313503(1–10). [15] B. Hille, Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes (3rd ed. ), Sinauer Associates Inc., 2001. [16] A. L. Hodgkin, The ionic basis of electrical activity in nerve and muscle, Biol. Rev., 1951, 26, 339–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1951.tb01204.x [17] A. L. Hodgkin and A. F. Huxley, Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo, J. Physol., 1952, 116, 449–472. [18] A. L. Hodgkin, A. F. Huxley and B. Katz, Ionic currents underlying activity in the giant axon of the squid, Arch. Sci. Physiol., 1949, 3, 129–150. [19] A. L. Hodgkin and B. Katz, The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid, J. Physiol., 1949, 108, 37–77. [20] W. Huang, W. Liu and Y. Yu, Permanent charge effects on ionic flow: A numerical study of flux ratios and their bifurcation, Commun. Comput. Phys., 2021, 30, 486–514. doi: 10.4208/cicp.OA-2020-0057 [21] Y. Hyon, B. Eisenberg and C. Liu, A mathematical model for the hard sphere repulsion in ionic solutions, Commun. Math. Sci., 2010, 9, 459–475. [22] W. Im, D. Beglov and B. Roux, Continuum solvation model: Electrostatic forces from numerical solutions to the Poisson-Boltzmann equation, Comp. Phys. Comm., 1998, 111, 59–75. doi: 10.1016/S0010-4655(98)00016-2 [23] S. Ji, B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Flux ratios and channel structures, J. Dynam. Differential Equation, 2019, 31, 1141–1183. doi: 10.1007/s10884-017-9607-1 [24] S. Ji and W. Liu, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with density functional theory for hard-sphere potential: I-V relations and critical potentials. Part I: Analysis, J. Dynam. Differential Equations, 2012, 24, 955–983. doi: 10.1007/s10884-012-9277-y [25] S. Ji, W. Liu and M. Zhang, Effects of (small) permanent charge and channel geometry on ionic flows via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck models, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2015, 75, 114–135. doi: 10.1137/140992527 [26] G. Lin, W. Liu, Y. Yi and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with a local hard-sphere potential for ion size effects, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2013, 12, 1613–1648. doi: 10.1137/120904056 [27] W. Liu, Geometric singular perturbation approach to steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2005, 65, 754–766. doi: 10.1137/S0036139903420931 [28] W. Liu, One-dimensional steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion channels with multiple ion species, J. Differential Equations, 2009, 246, 428–451. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2008.09.010 [29] W. Liu, A flux ratio and a universal property of permanent charges effects on fluxes, Comput. Math. Biophys., 2018, 6, 28–40. doi: 10.1515/cmb-2018-0003 [30] W. Liu, X. Tu and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with density functional theory for hard-sphere potential: I-V relations and critical potentials. Part Ⅱ: Numerics, J. Dynam. Differential Equations, 2012, 24, 985–1004. doi: 10.1007/s10884-012-9278-x [31] W. Liu and B. Wang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for narrow tubular-like membrane channels, J. Dynam. Differential Equations, 2010, 22, 413–437. doi: 10.1007/s10884-010-9186-x [32] W. Liu and H. Xu, A complete analysis of a classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck model for ionic flow, J. Differential Equations, 2015, 258, 1192–1228. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.10.015 [33] H. Mofidi, B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Effects of diffusion coefficients and permanent charge on reversal potentials in ionic channels, Entropy, 2020, 22, 325(1–23). [34] H. Mofidi and W. Liu, Reversal potential and reversal permanent charge with unequal diffusion coefficients via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck models, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2020, 80, 1908–1935. doi: 10.1137/19M1269105 [35] W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Ion permeation and glutamate residues linked by Poisson-Nernst-Planck theory in L-type Calcium channels, Biophysical J., 1998, 75, 1287–1305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)74048-2 [36] Y. Rosenfeld, Free-energy model for the inhomogeneous hard-sphere fluid mixture and Density-Functional Theory of freezing, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1989, 63, 980–983. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.980 [37] Y. Rosenfeld, Free energy model for the inhomogeneous fluid mixtures: Yukawa-charged hard spheres, general interactions, and plasmas, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 8126–8148. doi: 10.1063/1.464569 [38] I. Rubinstein, Multiple steady states in one-dimensional electrodiffusion with local electroneutrality, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1987, 47, 1076–1093. doi: 10.1137/0147070 [39] I. Rubinstein, Electro-Diffusion of Ions, SIAM Studies in Applied Mathematics, SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, 1990. [40] B. Sakmann and E. Neher, Single Channel Recording (2nd ed. ), Plenum, 1995. [41] A. Singer and J. Norbury, A Poisson-Nernst-Planck model for biological ion channels–an asymptotic analysis in a three-dimensional narrow funnel, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2009, 70, 949–968. doi: 10.1137/070687037 [42] A. Singer, D. Gillespie, J. Norbury and R. S. Eisenberg, Singular perturbation analysis of the steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck system: applications to ion channels, Eur. J. Appl. Math., 2008, 19, 541–560. doi: 10.1017/S0956792508007596 [43] L. Sun and W. Liu, Non-localness of excess potentials and boundary value problems of Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ionic flow: A case study, J. Dynam. Differential Equations, 2018, 30, 779–797. doi: 10.1007/s10884-017-9578-2 [44] N. Sun and W. Liu, Flux ratios for effects of permanent charges on ionic flows with three ion species: New phenomena from a case study, J. Dynam. Differential Equations, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10884-021-10118-x. doi: 10.1007/s10884-021-10118-x [45] H. H. Ussing, Interpretation of the exchange of radio-sodium in isolated muscle, Nature, 1947, 160, 262–263. doi: 10.1038/160262a0 [46] X. Wang, D. He, J. Wylie and H. Huang, Singular perturbation solutions of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems, Phys. Rev. E, 2014, 89, 022722(1–14). [47] L. Zhang, B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, An effect of large permanent charge: Decreasing flux with increasing transmembrane potential, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics, 2019, 227, 2575–2601. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2019-700134-7 [48] L. Zhang and W. Liu, Effects of large permanent charges on ionic flows via Poisson-Nernst-Planck models, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2020, 19, 1993–2029. doi: 10.1137/19M1289443 [49] M. Zhang, Asymptotic expansions and numerical simulations of I-V relations via a steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck system, Rocky Mountain J. Math., 2015, 45, 1681–1708. [50] Q. Zheng and G. Wei, Poisson-Boltzmann-Nernst-Planck model, J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 134, 194101(1–17). -
-
-
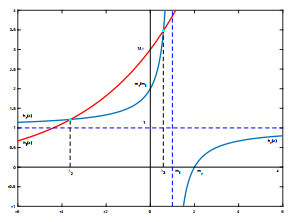
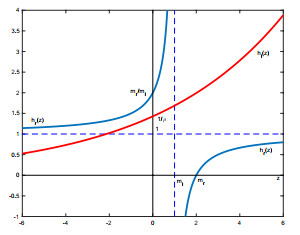
Figure 1. Graphs in Case (b)
$ m_r<m_l $ : first for$ \rho m_r<m_l $ , second for$ \rho m_r=m_l $ , third for$ \rho m_r>m_l $ . -
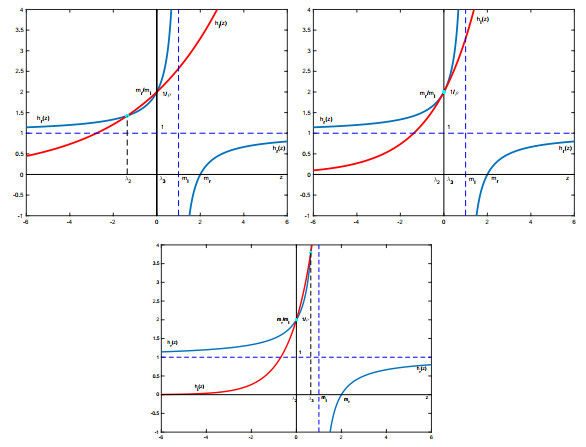
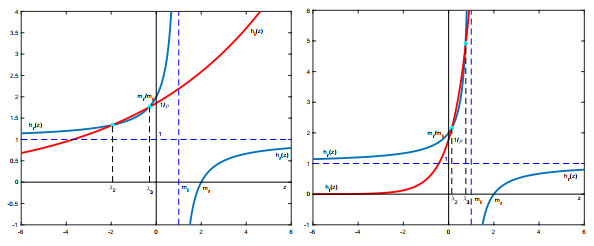
Figure 2. Graphs of Subcase (c1)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r<m_l $ . -
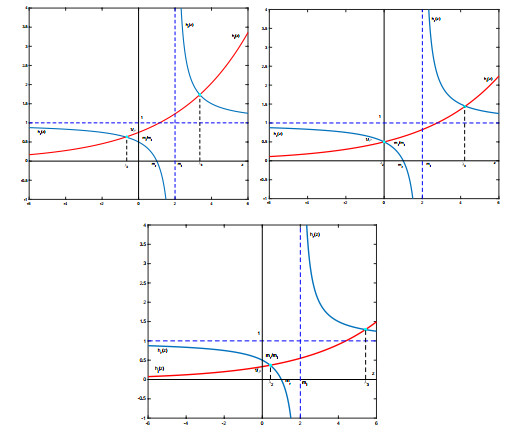
Figure 3. Graphs in Subcase (c2)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r=m_l $ : first for$ V<{1\over m_l}-{1\over m_r} $ , second for$ V={1\over m_l}-{1\over m_r} $ , third for$ V>{1\over m_l}-{1\over m_r} $ . -
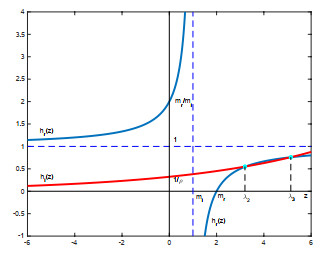
Figure 4. Graphs in Subcase (c3)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r>m_l $ in smaller double root situation: first for$ V<{1\over m_l}-{1\over m_r} $ , second for$ V>{1\over m_l}-{1\over m_r} $ . -
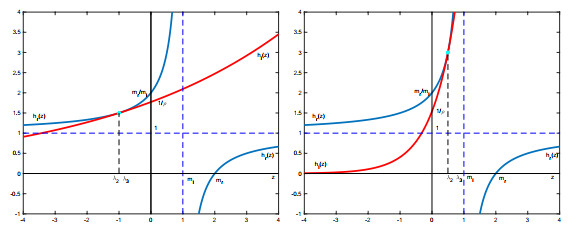
Figure 5. Graphs in Subcase (c3)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r>m_l $ in larger double root situation. -
Figure 6. Graphs in Subcase (c3)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r>m_l $ with$ \rho(t)<\rho<\rho(1/t) $ : roots in complex conjugate pair. -
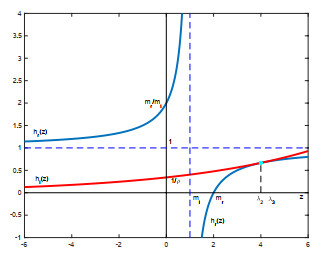
Figure 7. Graphs in Subcase (c3)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r>m_l $ with$ m_l/m_r<\rho<\rho(t) $ : real roots with same sign. -
Figure 8. Graphs in Subcase (c3)
$ m_r>m_l $ and$ \rho m_r>m_l $ with$ \rho>\rho(1/t) $ : real roots$ \lambda_2, \lambda_3>m_r $ . -
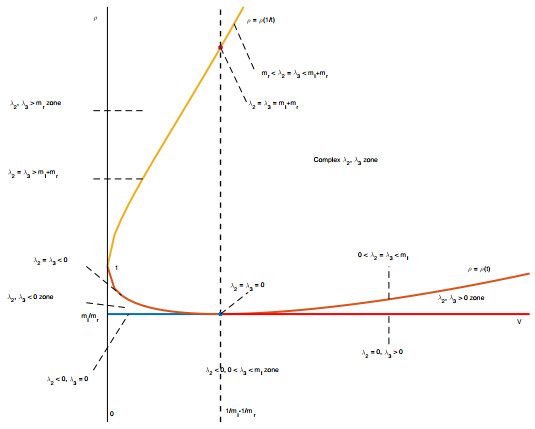
Figure 9. Case (c) (
$ m_r>m_l $ ): relation between$ \rho $ and$ V $ and zeros of$ h(z) $ .




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: