| Citation: | Sobirjon Shoyimardonov. NEIMARK-SACKER BIFURCATION AND STABILITY ANALYSIS IN A DISCRETE PHYTOPLANKTON-ZOOPLANKTON SYSTEM WITH HOLLING TYPE Ⅱ FUNCTIONAL RESPONSE[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2023, 13(4): 2048-2064. doi: 10.11948/20220345 |
NEIMARK-SACKER BIFURCATION AND STABILITY ANALYSIS IN A DISCRETE PHYTOPLANKTON-ZOOPLANKTON SYSTEM WITH HOLLING TYPE Ⅱ FUNCTIONAL RESPONSE
-
Abstract
In this paper, we study discrete-time model of phytoplankton-zooplankton with Holling type Ⅱ predator functional response. It is shown that Neimark-Sacker bifurcation occurs at the one of positive fixed points for certain parameter chosen as a bifurcation parameter. The existence and local stability of the positive fixed points of the model are proved. By considering theoretical results in the concrete example, it was obtained interesting dynamics of this system, which is not investigated in its corresponding continuous system.
-

-
References
[1] J. Chattopadhayay, R. R. Sarkar and S. Mandal, Toxin-producing plankton may act as a biological control for planktonic blooms-Field study and mathematical modelling, J. Theor. Biol., 2002, 215(3), 333-344. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2001.2510 [2] J. Chen and H. Zhang, The qualitative analysis of two species predator-prey model with Holling type Ⅲ functional response, Appl. Math. Mech., 1986, 77(1), 77-86. [3] K. Cheng, Uniqueness of a limit cycle for a predator-prey system, SIAM J. Math. Anal., 1981, 12(4), 541-548. doi: 10.1137/0512047 [4] W. Cheng and L. Wang, Stability and Neimark-Sacker bifurcation of a semi-discrete population model, Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2014, 4(4), 419-435. doi: 10.11948/2014024 [5] S. Chen, H. Yang and J. Wei, Global dynamics of two phytoplankton-zooplankton models with toxic substances effect, Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2019, 9(3), 796-809. doi: 10.11948/2156-907X.20180187 [6] R. L. Devaney, An Introduction to Chaotic Dynamical System, Westview Press, 2003. [7] J. Guckenheimer and P. Holmes, Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcations of Vector Fields, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1983. [8] Y. Hong, Global dynamics of a diffusive phytoplankton-zooplankton model with toxic substances effect and delay, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2022, 19(7), 6712-6730. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022316 [9] S. B. Hsu, On global stability of a predator-prey system, Math. Biosci., 1978, 39(1-2), 1-10. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(78)90025-1 [10] S. B. Hsu, A survey of constructing lyapunov functions for mathematical models in population biology, Taiwanese J. Math., 2005, 9(2), 151-173. [11] S. B. Hsu and T. Huang, Global stability for a class of predator-prey systems, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1995, 55(3), 763-863. doi: 10.1137/S0036139993253201 [12] W. Ko and K. Ryu, Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response incorporating a prey refuge, J. Differential Equations, 2006, 231(2), 534-550. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2006.08.001 [13] Y. A. Kuznetsov, Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory, 2nd Ed., Springer-Verlag, New York, 1998. [14] T. Liao, The impact of plankton body size on phytoplankton-zooplankton dynamics in the absence and presence of stochastic environmental fluctuation, Chaos, Solitons Fractals, 2022. DOI: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111617. [15] R. Peng and J. Shi, Non-existence of non-constant positive steady states of two Holling type-Ⅱ predator-prey systems: Strong interaction case, J. Differential Equations, 2009, 247(3), 866-886. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2009.03.008 [16] C. Robinson, Dynamical Systems: Stability, Symbolic Dynamics, and Chaos, 2nd Ed., Boca Raton, London, New York, 1999. [17] U. A. Rozikov and S. K. Shoyimardonov, Ocean ecosystem discrete time dynamics generated by $\ell$-Volterra operators, International Journal of Biomathematics, 2019, 12(2), 1950015-1-24. doi: 10.1142/S1793524519500153 [18] U. A. Rozikov, S. K. Shoyimardonov and R. Varro, Planktons discrete-time dynamical systems, Nonlinear studies, 2021, 28(2), 585-600. [19] M. Sajib, I. Sirajul, A. B. Haider and A. Sonia, A mathematical model applied to investigate the potential impact of global warming on marine ecosystems, Appl. Math. Model., 2022, 101, 19-37. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2021.08.026 [20] J. Wang, Spatiotemporal patterns of a homogeneous diffusive predator-prey system with Holling type Ⅲ functional response, J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2017, 29(4), 1383-1409. doi: 10.1007/s10884-016-9517-7 [21] S. Winggins, Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003. [22] J. Zhou and C. Mu, Coexistence states of a Holling type-Ⅱ predator-prey system, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2010, 369(2), 555-563. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.04.001 [23] Q. Zhao, S. Liu and X. Niu, Dynamic behavior analysis of a diffusive plankton model with defensive and offensive effects, Chaos, Solitons Fractals, 2019, 129, 94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2019.08.015 -
-
-
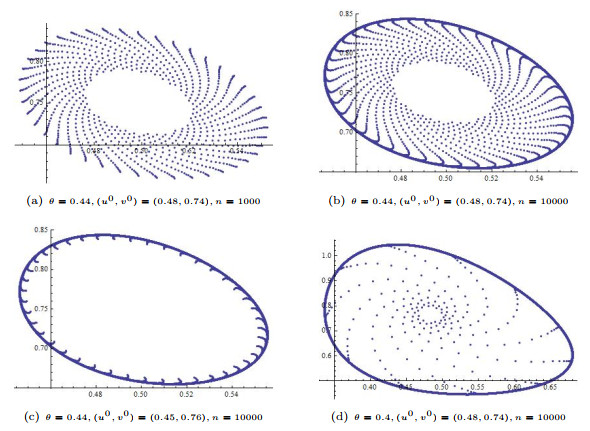
Figure 1.
Phase portraits for the system (1.4) with
$ c=1, \beta=4, r=10/9, \theta_0=4/9\approx0.4444..., (u^0, v^0)=(0.6, 0.75). $ -
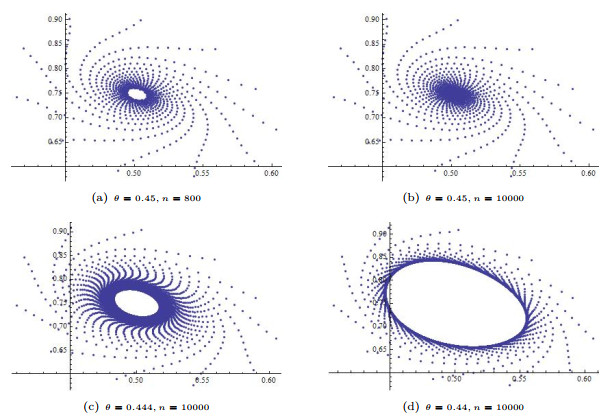
Figure 2.
Phase portraits for the system (1.4) with
$ c=1, \beta=4, r=10/9, \theta_0=4/9\approx0.4444.... $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: