| Citation: | Yue Tang, Inkyung Ahn, Zhigui Lin. THE SEIR MODEL WITH PULSE AND DIFFUSION OF VIRUS IN THE ENVIRONMENT[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2023, 13(6): 3606-3631. doi: 10.11948/20230207 |
THE SEIR MODEL WITH PULSE AND DIFFUSION OF VIRUS IN THE ENVIRONMENT
-
Abstract
This paper addresses a reaction-diffusion problem featuring impulsive effects under Neumann boundary conditions. The model simulates the periodic eradication of viruses in an environment. Initially, we establish the well-posedness of the reaction-diffusion model. We define the basic reproduction number $R_0$ for the problem in the absence of pulsing and compute the principal eigenvalue of the corresponding elliptic eigenvalue problem. Utilizing Lyapunov functionals and Green's first identity, we derive the global threshold dynamics of the system. Specifically, when $R_0 < 1$, the disease-free equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable; conversely, if $R_0 > 1$, the system exhibits uniform persistence, and the endemic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable. Additionally, we consider the generalized principal eigenvalues for the problem with pulsing and provide sufficient conditions for the stability of both the disease-free equilibrium and the positive periodic solution. Finally, we corroborate our theoretical findings through numerical simulations, particularly discussing the impacts of periodic environmental cleaning.
-

-
References
[1] N. Ahmed, S. S. Tahira, M. Rafiq, et al., Positivity preserving operator splitting nonstandard finite difference methods for SEIR reaction diffusion model, Open Math., 2019, 17, 313-330 doi: 10.1515/math-2019-0027 [2] L. J. Allen, B. M. Bolker, Y. Lou, et al., Asymptotic profiles of the steady states for an SIS epidemic reaction-diffusion model, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., 2008, 21(1), 1-20 doi: 10.3934/dcds.2008.21.1 [3] R. J. Boer and A. S. Perelson, Quantifying T lymphocyte turnover, J. Theo. Biol., 2013, 327, 45-87 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.12.025 [4] J. M. Boyce, Environmental contamination makes an important contribution to hospital infection, J. Hosp. Infect., 2007, 65, 50-54 doi: 10.1016/S0195-6701(07)60015-2 [5] J. M. Boyce, G. Potter-Bynoe, C. Chenevert, et al., Environmental contamination due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: possible infection control implications, Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol., 1997, 18(9), 622-627 doi: 10.2307/30141488 [6] R. S. Cantrell and C. Cosner, Spatial Ecology Via Reaction-Diffusion Equations, John Wiley Sons, New York, 2004 [7] F. Capone, V. De Cataldis and R. De Luca, On the Stability of a SEIR Reaction Diffusion Model for Infections Under Neumann Boundary Conditions, Acta Appl. Math., 2014, 132(1), 165-176 doi: 10.1007/s10440-014-9899-7 [8] S. J. Dancer, Importance of the environment in meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus acquisition: the case for hospital cleaning, Lancet Infect. Dis., 2008, 8(2), 101-113 doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70241-4 [9] S. J. Dancer, The role of environmental cleaning in the control of hospital acquired infection, J. Hosp. Infect., 2009, 73(4), 378-385 doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2009.03.030 [10] A. Haase, K. Henry, M. Zupancic, et al., Quantitative image analysis of HIV-1 infection in lymphoid tissue, Science, 1996, 274(5289), 985-989 doi: 10.1126/science.274.5289.985 [11] J. K. Hale, Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems, American Mathematical Society Providence, Providence, Rhode Island, 1988 [12] X. Z. Li, G. Gupur and G. T. Zhu, Threshold and stability results for an age-structured SEIR epidemic model, Comput. Math. Appl., 2001, 42(6-7), 883-907 [13] Y. J. Lou and X. Q. Zhao, A reaction-diffusion malaria model with incubation period in the vector population, J. Math. Biol., 2011, 62(4), 543-568 doi: 10.1007/s00285-010-0346-8 [14] S. Nakaoka, S. Iwami and K. Sato, Dynamics of HIV infection in lymphoid tissue network, J. Math. Biol., 2016, 72(4), 909-938 doi: 10.1007/s00285-015-0940-x [15] D. F. Pang and Y. N. Xiao, The SIS model with diffusion of virus in the environment, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2019, 16(4), 2852-2874 doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019141 [16] M. Pedersen and Z. G. Lin, The profile near blowup time for solutions of diffusion systems coupled with localized nonlinear reactions, Nonlinear Anal., 2002, 50(7), 1013-1024 doi: 10.1016/S0362-546X(01)00798-2 [17] R. Peng, Asymptotic profiles of the positive steady state for an SIS epidemic reaction-diffusion model. Part Ⅰ, J. Diff. Equ., 2009, 247(4), 1096-1119 doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2009.05.002 [18] R. Peng and X. Q. Zhao, A reaction-diffusion SIS epidemic model in a time-periodic environment, Nonlinearity, 2009, 25(5), 1451-1471 [19] L. Q. Pu, Z. G. Lin and Y. Lou, A West Nile virus nonlocal model with free boundaries and seasonal succession, J. Math. Biol., 2023, 86(2), 1-52 [20] L. B. Rong and A. S. Perelson, Asymmetric division of activated latently infected cells may explain the decay kinetics of the HIV-1 latent reservoir and intermittent viral blips, Math. Biosci., 2009, 217(1), 77-87 doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2008.10.006 [21] H. L. Smith, Monotone Dynamical Systems: An Introduction to the Theory of Competitive and Cooperative Systems, American Mathematical Society Providence, Providence, Rhode Island, 1995 [22] H. L. Smith and X. Q. Zhao, Robust persistence for semidynamical systems, Nonlinear Anal., 2001, 47(9), 6169-6179 doi: 10.1016/S0362-546X(01)00678-2 [23] F. B. Wang, Y. Huang and X. F. Zou, Global dynamics of a PDE in-host viral model, Appl. Anal., 2014, 93(11), 2312-2329 doi: 10.1080/00036811.2014.955797 [24] J. L. Wang and J. Yang, T. Kuniya, Dynamics of a PDE viral infection model incorporating cell-to-cell transmission, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2016, 444(2), 1542-1564 doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2016.07.027 [25] S. L. Wang, X. Y. Song and Z. H. Ge, Dynamics analysis of a delayed viral infection model with immune impairment, Appl. Math. Model., 2011, 35(10), 4877-4885 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2011.03.043 [26] W. D. Wang and X. Q. Zhao, Basic reproduction numbers for reaction-diffusion epidemic models, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2012, 11(4), 1652-1673 doi: 10.1137/120872942 [27] X. Wang, Y. N. Xiao, J. R. Wang, et al., A mathematical model of effects of environmental contamination and presence of volunteers on hospital infections in China, J. Theo. Biol., 2012, 293, 161-173 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.10.009 [28] X. Y. Wang, J. Y. Yang and X. F. Luo, Asymptotical profiles of a viral infection model with multi-target cells and spatial diffusion, Comput. Math. Appl., 2019, 77(2), 389-406 [29] D. J. Weber and W. A. Rutala, Role of environmental contamination in the transmission of vancomycin-resistant enterococci, Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol., 1997, 18(5), 306-309 doi: 10.1086/647616 [30] R. Xu and C. W. Song, Dynamics of an HIV infection model with virus diffusion and latently infected cell activation, Nonlinear Anal., 2022, 67, 103618 doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2022.103618 [31] C. Y. Yang and J. Wang, Basic reproduction numbers for a class of reaction-diffusion epidemic models, Bull. Math. Biol., 2020, 82(8), 1-25 [32] L. Zhang, Z. C. Wang and X. Q. Zhao, Threshold dynamics of a time periodic reaction-diffusion epidemic model with latent period, J. Diff. Equ., 2015, 258(9), 3011-3036 doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.12.032 [33] M. Y. Zhang, J. GE and Z. G. Lin, Logistic diffusion problem and its analysis on three types of domains, Journal of Guangxi Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 41(01), 17-23 [34] X. Q. Zhao, Dynamical Systems in Population Biology, Springer, New York, 2017 [35] X. Q. Zhao, Basic Reproduction Ratios for Periodic Compartmental Models with Time Delay, J. Dyn. Diff. Equ., 2017, 29(1), 67-82. doi: 10.1007/s10884-015-9425-2 -
-
-
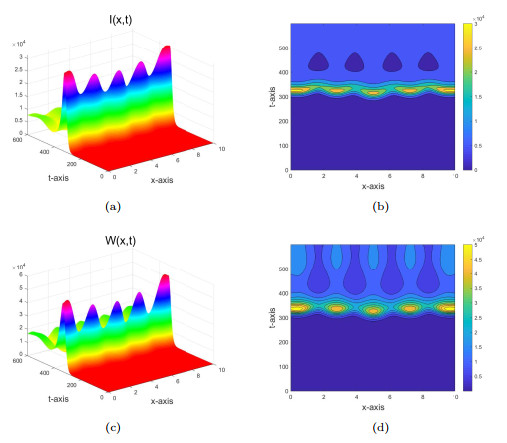
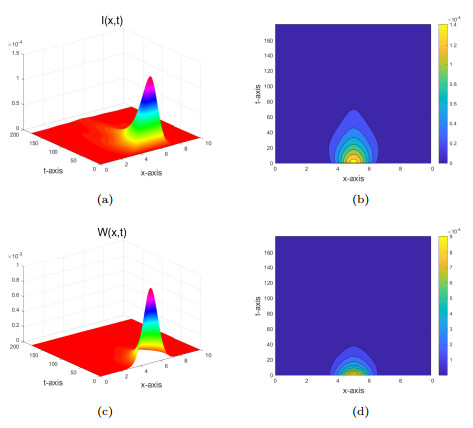
Figure 1.
Choose
$ b_0=0.05 $ $ (R_0<1) $ $ I(x, t) $ $ W(x, t) $ -
Figure 2.
Choose
$ b_0=0.12 $ $ (R_0>1) $ $ I(x, t) $ $ W(x, t) $ -
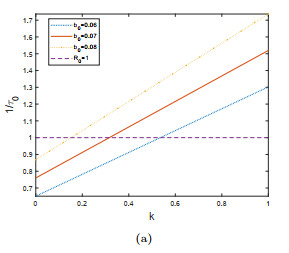
Figure 3.
Choose
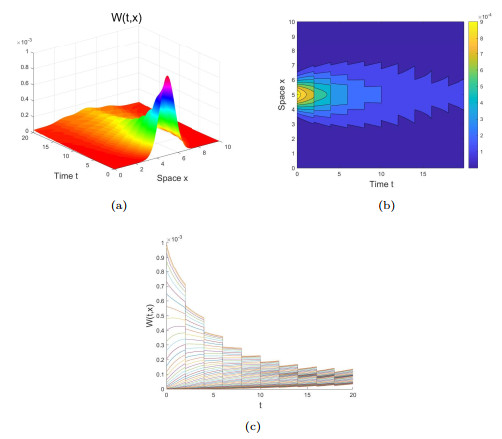
$ b_0=0.06, 0.07, 0.08 $ $ k $ $ \frac{1}{\tau_0} $ -
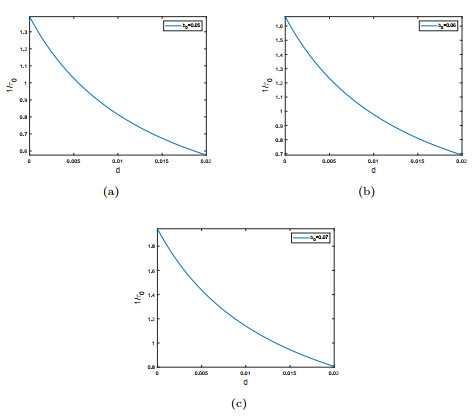
Figure 4.
Fix parameters in (4.1). The relation between
$ d $ $ \frac{1}{\tau_0} $ $ (a)\, b_0=0.05;\ (b)\, b_0=0.06;\ (c)\, b_0=0.07 $ -
Figure 5.
$ \lambda_*>0 $ -
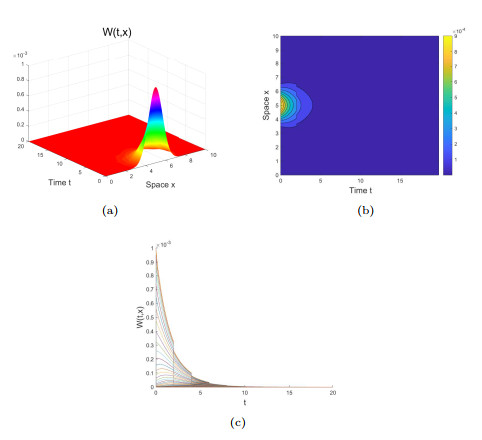
Figure 6.
$ \lambda^*<0 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: