| Citation: | Wenjing Liu, Yancong Xu, Libin Rong. PREDATOR DISCRIMINATION PROMOTES THE COEXISTENCE OF PREY AND PREDATOR[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(3): 1579-1597. doi: 10.11948/20230301 |
PREDATOR DISCRIMINATION PROMOTES THE COEXISTENCE OF PREY AND PREDATOR
-
Abstract
The predator discrimination of prey may affect the density of both prey and predator populations, which, in turn, could influence the coexistence of discriminated prey species. This paper investigates the dynamics of a three-dimensional predator-prey model, which includes unobvious predator discrimination of prey, using a dynamical system approach. We study the existence, local and global stability of equilibria and further discuss the presence and conditions of forward bifurcation in the system. Finally, numerical simulations are performed to illustrate the theoretical results. The findings suggest that prey diversity favors predator discrimination of prey and enhances the coexistence of all species.
-

-
References
[1] R. S. Cantrell and C. Cosner, On the dynamics of predator-prey models with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2001, 257(1), 206–222. doi: 10.1006/jmaa.2000.7343 [2] P. Chesson, Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity, Annual review of Ecology and Systematics, 2000, 31(1), 343–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.31.1.343 [3] J. H. P. Dawes and M. O. Souza, A derivation of Holling's type Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ functional responses in predator-prey systems, Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2013, 327, 11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2013.02.017 [4] K. P. Hadeler and C. Castillo-Chavez, A core group model for disease transmission, Mathematical Biosciences, 1995, 128, 41-55. [5] E. D. Houde and R. C. Schekter, Feeding by marine fish larvae: developmental and functional responses, Environmental Biology of Fishes, 1980, 5, 315–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00005186 [6] S. B. Hsu, S. P. Hubbell and P. Waltman, A contribution to the theory of competing predators, Ecological Monographs, 1978, 48(3), 337–349. doi: 10.2307/2937235 [7] S. B. Hsu, S. P. Hubbell and P. Waltman, Competing predators, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1978, 35(4), 617–625. doi: 10.1137/0135051 [8] S. B. Hsu, T. W. Hwang and Y. Kuang, Global analysis of the Michaelis-Menten-type ratio-dependent predator-prey system, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2001, 42, 489–506. doi: 10.1007/s002850100079 [9] G. Huang, W. Ma and Y. Takeuchi, Global properties for virus dynamics model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response, Applied Mathematics Letters, 2009, 22(11), 1690–1693. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2009.06.004 [10] J. Huang, S. Ruan and J. Song, Bifurcations in a predator-prey system of Leslie type with generalized Holling type Ⅲ functional response, Journal of Differential Equations, 2014, 257(6), 1721–1752. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.04.024 [11] G. Iwashita, A. Yamawo and M. Kondoh, Predator discrimination of prey promotes the predator-mediated coexistence of prey species, Royal Society Open Science, 2022, 9(12), 220859. doi: 10.1098/rsos.220859 [12] W. Ko and K. Ryu, Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response incorporating a prey refuge, Journal of Differential Equations, 2006, 231(2), 534–550. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2006.08.001 [13] A. L. Koch, Competitive coexistence of two predators utilizing the same prey under constant environmental conditions, Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1974, 44(2), 387–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90169-6 [14] V. Krivan and O. J. Schmitz, Adaptive foraging and flexible food web topology, Evolutionary Ecology Research, 2003, 5(5), 623–652. [15] Y. Kuang and E. Beretta, Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 1998, 36, 389–406. doi: 10.1007/s002850050105 [16] Y. Kuznetsov, Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1995. [17] Y. Lamontagne, C. Coutu and C. Rousseau, Bifurcation analysis of a predator-prey system with generalised Holling type Ⅲ functional response, Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations, 2008, 20(3), 535–571. doi: 10.1007/s10884-008-9102-9 [18] Q. Li, L. Zhang and P. Zhou, Global bifurcation for a class of Lotka-Volterra competitive systems, Journal of Nonlinear Modeling and Analysis, 2023, 5, 720–739. [19] X. Q. Lin, Y. C. Xu, D. Z. Gao and G. H. Fan, Bifurcation and overexploitation in Rosenzweig-MacArthur model, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-B, 2023, 28(1), 690–706. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2022094 [20] M. Liu, C. Z. Bai and Y. Jin, Population dynamical behavior of a two-predator-one-prey stochastic model with time delay, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 2017, 37(5), 2513. doi: 10.3934/dcds.2017108 [21] A. J. Lotka, Elements of Physical Biology, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1925. [22] R. J. Pakeman, Multivariate identification of plant functional response and effect traits in an agricultural landscape, Ecology, 2011, 92(6), 1353–1365. doi: 10.1890/10-1728.1 [23] L. A. Real, The kinetics of functional response, The American Naturalist, 1977, 111(978), 289–300. doi: 10.1086/283161 [24] G. T. Skalski and J. F. Gilliam, Functional responses with predator interference: Viable alternatives to the Holling type Ⅱ model, Ecology, 2001, 82(11), 3083–3092. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[3083:FRWPIV]2.0.CO;2 [25] Y. V. Tyutyunov and L. I. Titova, Ratio-dependence in predator-prey systems as an edge and basic minimal model of predator interference, Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2021, 9, 725041. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2021.725041 [26] R. K. Upadhyay and S. N. Raw, Complex dynamics of a three species food-chain model with Holling type Ⅳ functional response, Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2011, 16(3), 553–374. doi: 10.15388/NA.16.3.14098 [27] R. R. Vance, Predation and resource partitioning in one-predator–two-prey model communities, The American Naturalist, 1978, 112(987), 797–813. doi: 10.1086/283324 [28] V. Volterra, Fluctuations in the abundance of a species considered mathematically, Nature, 1926, 118(2972), 558–560. doi: 10.1038/118558a0 [29] J. P. Wang and M. X. Wang, Boundedness and global stability of the two-predator and one-prey models with nonlinear prey-taxis, Z. Angew. Math. Phys., 2018, 69, 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s00033-017-0895-4 [30] Q. Wang, B. X. Dai and Y. M. Chen, Multiple periodic solutions of an impulsive predator-prey model with Holling-type Ⅳ functional response, Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2009, 49(9–10), 1829–1836. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2008.09.008 [31] T. Wen, Y. C. Xu, M. He and L. B. Rong, Modelling the dynamics in a predator-prey system with Allee effects and anti-predator behavior, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst, 2023, 22(116), 1–50. [32] S. Wiggins and D. S. Mazel, Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos, American Institute of Physics, 2013. [33] Y. C. Xu, L. J. Wei, X. Y. Jiang and Z. R. Zhu, Complex dynamics of a SIRS epidemic model with the influence of hospital bed number, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-B, 2021, 26(12), 6229–6252. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2021016 [34] Y. Yang, F. W. Meng and Y. C. Xu, Global bifurcation analysis in a predator-prey system with simplified Holling Ⅳ functional response and antipredator behavior, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2023, 46(5), 6135–6153. doi: 10.1002/mma.8896 [35] A. Zegeling, H. L. Wang and G. Z. Zhu, Uniqueness of limit cycles in a predator-prey model with sigmoid functional response, Journal of Nonlinear Modeling and Analysis, 2023, 5, 790–802. [36] Z. R. Zhu, R. C. Wu, Y. Yang and Y. C. Xu, Modelling HIV dynamics with cell-to-cell transmission and CTL response, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2023, 46(6), 6506–6528. doi: 10.1002/mma.8921 -
-
-
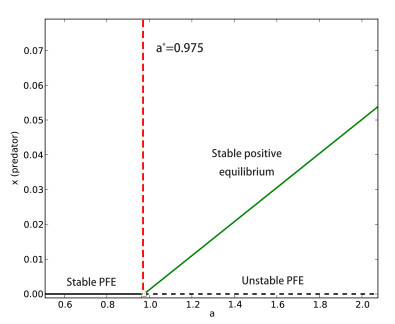
Figure 1.
The positive equilibrium
$ E^* $ $ bk_2-1=0 $ $ bk_2-1 > 0 $ $ -1 < bk_2-1 < 0 $ -
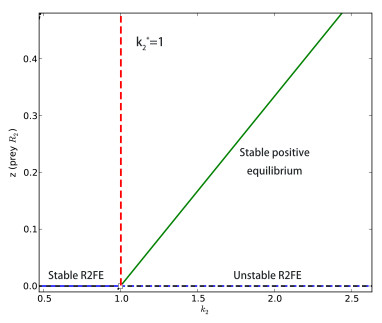
Figure 2.
Forward bifurcation diagram of the concentration of predator with respect to
$ a $ $ 0 < a\leq \frac{1}{k_1} $ $ c > \frac{bk_2-1}{bk_1} $ -
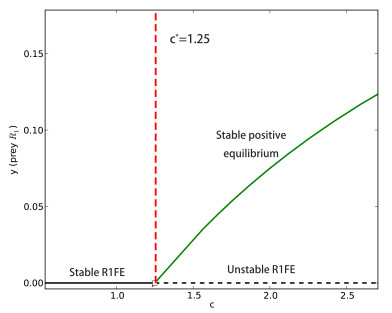
Figure 3.
Forward bifurcation diagram of the concentration of predator with respect to
$ c $ $ 0 < a\leq \frac{1}{k_1} $ $ c > 0 $ -
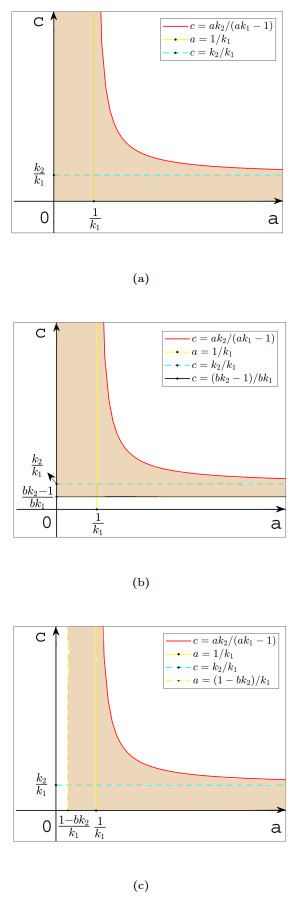
Figure 4.
Forward bifurcation diagram of the concentration of predator with respect to
$ a $ $ c > \frac{bk_2-1}{bk_1} $ $ ak_1 > 1 $ $ a=1, b=2, c=1 $ $ k_1=2 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: