| Citation: | Lu-Lu Yan, Fan Yang, Xiao-Xiao Li. THE FRACTIONAL TIKHONOV REGULARIZATION METHOD FOR SIMULTANEOUS INVERSION OF THE SOURCE TERM AND INITIAL VALUE IN A SPACE-FRACTIONAL ALLEN-CAHN EQUATION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(4): 2257-2282. doi: 10.11948/20230364 |
THE FRACTIONAL TIKHONOV REGULARIZATION METHOD FOR SIMULTANEOUS INVERSION OF THE SOURCE TERM AND INITIAL VALUE IN A SPACE-FRACTIONAL ALLEN-CAHN EQUATION
-
Abstract
In this paper, we consider the inverse problem for identifying the source term and initial value simultaneously in a space-fractional Allen-Cahn equation. This problem is ill-posed, i.e., the solution of this problem does not depend continuously on the data. The fractional Tikhonov method is used to solve this problem. Under the a priori and the a posteriori regularization parameter choice rules, the error estimates between the regularization solutions and the exact solutions are obtained, respectively. Different numerical examples are presented to illustrate the validity and effectiveness of our method.
-

-
References
[1] S. M. Allen and J. W. Cahn, A microscopic theory for antiphase boundary motion and its application to antiphase domain coarsening, Acta Metall., 1979, 27(6), 1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(79)90196-2 [2] Q. Du, C. Liu and X. Wang, A phase field approach in the numerical study of the elastic bending energy for vesicle membranes, J. Comput. Phys., 2004, 198(2), 450–468. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2004.01.029 [3] L. C. Evans, H. M. Soner and P. E. Souganidis, Phase transitions and generalized motion by mean curvature, Commun. Pure Appl. Math., 1992, 45(9), 1097–1123. doi: 10.1002/cpa.3160450903 [4] L. C. Evans and J. Spruck, Motion of level sets by mean curvature, J. Differ. Geom., 1991, 33(3), 635–681. [5] X. F. Yang, Error analysis of stabilized semi-implicit method of Allen-Cahn equation, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems - B, 2009, 11(4), 1057–1070. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2009.11.1057 [6] T. Tang and J. Yang, Implicit-explicit scheme for the Allen-Cahn equation preserves the maximum principle, J. Comput. Math., 2016, 34(5), 471–781. [7] J. W. Choi, H. G. Lee, et al., An unconditionally gradient stable numerical method for solving the Allen-Cahn equation, Physica A, 2009, 388(9), 1791–1803. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2009.01.026 [8] T. Hou, D. Xiu and W. Jiang, A new second-order maximum-principle preserving finite difference scheme for Allen-Cahn equations with periodic boundary conditions, Appl. Math. Lett., 2020, 104(0), 106265. [9] H. Zhang, J. Yan, X. Qian, et al., On the preserving of the maximum principle and energy stability of high-order implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta schemes for the space-fractional Allen-Cahn equation, Numer. Algorithms, 2021, 88(3), 1309–1336. doi: 10.1007/s11075-021-01077-x [10] T. Hou, T. Tang and J. Yang, Numerical analysis of fully discretized Crank-Nicolson scheme for fractional-in-space Allen-Cahn equations, J. Sci. Comput., 2017, 72(3), 1214–1231. doi: 10.1007/s10915-017-0396-9 [11] D. He, K. Pan and H. Hu, A spatial fourth-order maximum principle preserving operator splitting scheme for the multi-dimensional fractional Allen-Cahn equation, Appl. Numer. Math., 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.apnum.2019.12.018. [12] H. Chen and H. Sun, A dimensional splitting exponential time differencing scheme for multidimensional fractional Allen-Cahn equations, J. Sci. Comput., 2021, 87(1), 1–25. doi: 10.1007/s10915-020-01404-9 [13] H. Chen and H. Sun, Second-order maximum principle preserving Strang's splitting schemes for anisotropic fractional Allen-Cahn equations, Numer. Algorithms, 2022, 90(2), 749–771. doi: 10.1007/s11075-021-01207-5 [14] F. Yang, Y. P. Ren and X. X. Li, Landweber iterative method for identifying a space-dependent source for the time-fractional diffusion equation, Bound. Value Probl., 2017, 2017(1), 163. doi: 10.1186/s13661-017-0898-2 [15] F. Yang, X. Liu and X. X. Li, Landweber iterative regularization method for identifying the unknown source of the time-fractional diffusion equation, Adv. Differ. Equ., 2017, 2017(1), 388. doi: 10.1186/s13662-017-1423-8 [16] H. Jafari, A. Babaei and S. Banihashemi, A novel approach for solving an inverse reaction-diffusion-convection problem, J. Optimiz. Theory App., 2019, 183(2), 688–704. doi: 10.1007/s10957-019-01576-x [17] F. Yang and C. L. Fu, The quasi-reversibility regularization method for identifying the unknown source for time fractional diffusion equation, Appl. Math. Model., 2015, 39(5–6), 1500–1512. [18] F. Yang, C. L. Fu and X. X. Li, The inverse source problem for time fractional diffusion equation: Stability analysis and regularization, Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng., 2015, 23(6), 969–996. doi: 10.1080/17415977.2014.968148 [19] F. Yang, C. L. Fu and X. X. Li, A mollification regularization method for unknown source in time-fractional diffusion equation, Int. J. Comput. Math., 2014, 91(7), 1516–1534. doi: 10.1080/00207160.2013.851787 [20] Z. Qian and X. L. Feng, A fractional Tikhonov method for solving a Cauchy problem of Helmholtz equation, Appl. Anal., 2017, 96(10), 1656–1668. doi: 10.1080/00036811.2016.1254776 [21] Q. Yang, F. Liu and I. Turner, Numerical methods for fractional partial differential equations with riesz space fractional derivatives, Appl. Math. Model., 2010, 34(1), 200–218. [22] E. Klann and R. Ramlau, Regularization by fractional filter methods and data smoothing, Inverse Prol., 2008, 24(2), 025018. [23] X. M. Xue and X. T. Xiong, A fractional Tikhonov regularization method for identifying a space-dependent source in the time-fractional diffusion equation, Appl. Math. Comput., 2019. DOI: 10.1016/j.amc.2018.12.063. [24] Z. J. Zhang, W. H. Deng and H. T. Fan, Finite difference schemes for the tempered fractional Laplacian, Numer. Math. Theor. Meth. Appl., 2019, 12(2), 492–516. [25] M. E. Hochstenbach and L. Reichel, Fractional Tikhonov regularization for linear discrete ill-posed problems, BIT., 2011, 51(1), 197–215. -
-
-
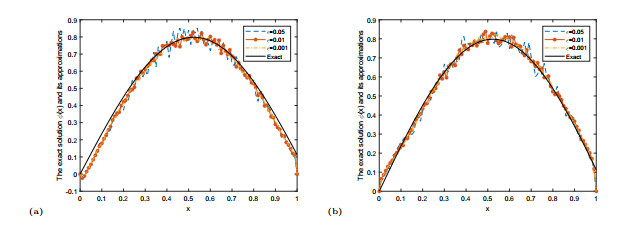
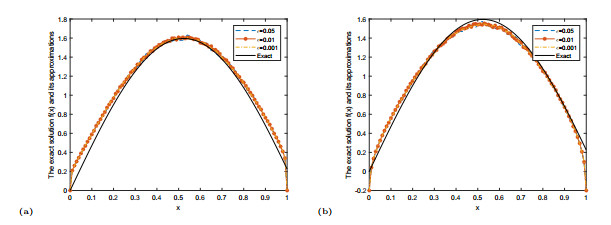
Figure 1.
The exact solution
$ f(x) $ $ f^{\delta}_{\mu}(x) $ $ \alpha=0.3 $ $ \alpha=0.7 $ -
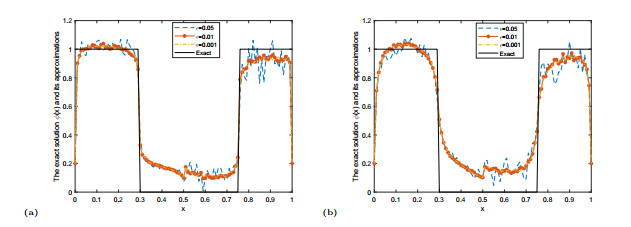
Figure 2.
The exact solution
$ \varphi(x) $ $ \varphi^{\delta}_{\mu}(x) $ $ \alpha=0.3 $ $ \alpha=0.7 $ -
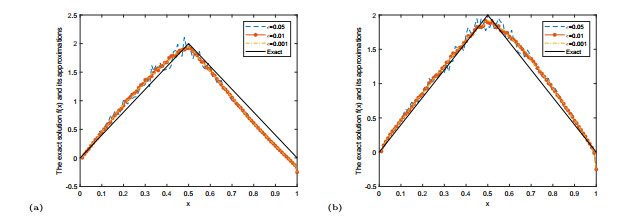
Figure 3.
The exact solution
$ f(x) $ $ f^{\delta}_{\mu}(x) $ $ \alpha=0.3 $ $ \alpha=0.55 $ -
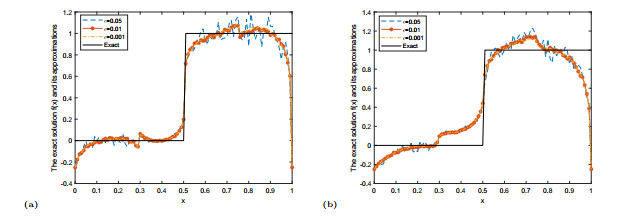
Figure 4.
The exact solution
$ \varphi(x) $ $ \varphi^{\delta}_{\mu}(x) $ $ \alpha=0.3 $ $ \alpha=0.55 $ -
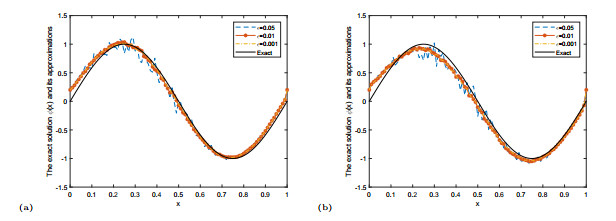
Figure 5.
The exact solution
$ f(x) $ $ f^{\delta}_{\mu}(x) $ $ \alpha=0.3 $ $ \alpha=0.45 $ -
Figure 6.
The exact solution
$ \varphi(x) $ $ \varphi^{\delta}_{\mu}(x) $ $ \alpha=0.3 $ $ \alpha=0.45 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: