| Citation: | Zisheng Liu, Ting Zhang. CONVERGENCE ANALYSIS ON THE ALTERNATING DIRECTION METHOD OF MULTIPLIERS FOR THE COSPARSE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(6): 3061-3077. doi: 10.11948/20230407 |
CONVERGENCE ANALYSIS ON THE ALTERNATING DIRECTION METHOD OF MULTIPLIERS FOR THE COSPARSE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM
-
Abstract
From a dual perspective of the sparse representation model, Nam et al. proposed the cosparse analysis model. In this paper, we aim to investigate the convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) for the cosparse optimization problem. First, we examine the variational inequality representation of the cosparse optimization problem by introducing auxiliary variables. Second, ADMM is used to solve cosparse optimization problem. Finally, by utilizing a tight frame with a uniform row norm and building upon lemmas and the strict contraction theorem, we establish a worst-case $\mathcal{O}(1/t)$ convergence rate in the ergodic sense. The experimental results verify the practicability and convergence of the ADMM in solving cosparse optimization problems.
-

-
References
[1] M. V. Afonso, J. M. Bioucas-Dias and M. A. T. Figueiredo, Fast image recovery using variable splitting and constrained optimization, IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2010, 19(9), 2345–2356. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2047910 [2] M. M. Alves, J. Eckstein, M. Geremia and J. G. Melo, Relative-error inertial-relaxed inexact versions of Douglas-Rachford and ADMM splitting algorithms, Comput. Optim. Appl., 2020, 75, 389–422. doi: 10.1007/s10589-019-00165-y [3] J. Bai, X. Chang, J. Li and F. Xu, Convergence revisit on generalized symmetric ADMM, Optim., 2021, 70, 149–168. doi: 10.1080/02331934.2019.1704754 [4] S. Boyd, N. Parikh, E. Chu, et al., Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers, Found. Trends Mach. Learn., 2011, 3(1), 1–122. [5] S. Boyd, N. Parikh, E. Chu, et al., Distributed optimization and statistical learning via alternating direction method of multipliers, in Found. Trends Mach. Learn., 2010, 3(1), 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [6] S. Boyd and L. Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization, Cambridge, U. K, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2004. [7] A. M. Bruckstein, D. L. Donoho and M. Elad, From sparse solutions of systems of equations to sparse modeling of signals and images, SIAM Rev., 2009, 51, 34–81. doi: 10.1137/060657704 [8] E. J. Candés and T. Tao, Decoding by linear programming, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 2004, 51(12), 4203–4215. [9] A. L. Casanovas, G. Monaci, P. Vandergheynst and R. Gribonval, Blind audiovisual source separation based on sparse representations, IEEE Trans. Multimedia, 2010, 12(5), 358–371. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2010.2050650 [10] T. Chan and R. Glowinski, Finite Element Approximation and Iterative Solution of a Class of Mildly Non-Linear Elliptic Equations, Stanford: Computer Science Department, Stanford University, 1978. [11] D. L. Donoho, Compressed sensing, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 2006, 52(4), 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [12] J. Eckstein and W. Yao, Understanding the convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers: Theoretical and computational perspectives, Pacific J. Optim., 2015, 11, 619–644. [13] M. Elad, Sparse and Redundant Representations: From Theory to Applications in Signal and Image Prcoessing, Springer Press, 2010. [14] M. Elad and M. Aharon, Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries, IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2006, 15(12), 3736–3745. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.881969 [15] M. Elad, J. L. Starck, P. Querre and D. L. Donoho, Simultaneous cartoon and texture image inpainting using morphological component analysis (MCA), Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal., 2005, 19(3), 340–358. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2005.03.005 [16] S. Foucart and H. Rauhut, A Mathematical Introduction to Compressive Sensing, Springer, New York, 2013. [17] R. Giryes, S. Nam, M. Elad, et al., Greedy-like algorithms for the cosparse analysis model, Linear Algebra Appl., 2014, 441(15), 22–60. [18] V. K. Goyal, J. Kovacevic and J. A. Kelner, Quantized frame expansions with erasures, Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal., 2001, 10(3), 203–233. doi: 10.1006/acha.2000.0340 [19] D.-R. Han, A survey on some recent developments of alternating direction method of multipliers, J. Oper. Res. Soc. China, 2022, 10, 1–52. doi: 10.1007/s40305-021-00368-3 [20] B. He, On the convergence properties of alternating direction method of multipliers, Numer. Math. J. Chin. Univ., (Chine. Ser.), 2017, 39, 81–96. [21] B. He, F. Ma and X. Yuan, Convergence study on the symmetric version of ADMM with large step sizes, SIAM J. Imaging sciences, 2016, 9(3), 1467–1501. doi: 10.1137/15M1044448 [22] B. He and X. Yuan, On the $O(1/n)$ convergence rate of the Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method, SIAM J. Numer. Anal, 2012, 130(3), 702–709. [23] S. Hu and Z. Huang, Alternating direction method for bi-quadratic programming, J. Glob. Optim., 2011, 51(3), 429–446. doi: 10.1007/s10898-010-9635-4 [24] Z. Huang, G. Lin and N. Xiu, Several developments of variational inequalities and complementarity problems, bilevel programming and MPEC, Oper. Res., 2014, 18(1), 113–133. [25] Z. Jia, G. Xue, X. Cai and D. Han, The convergence rate analysis of the symmetric ADMM for the nonconvex separable optimization problems, J. Ind. Manag. Optim., 2021, 17(4), 1943–1971. doi: 10.3934/jimo.2020053 [26] M. S. Kotzagiannidis and M. E. Davies, Analysis vs synthesis with structure - an investigation of union of subspace models on graphs, Appl. Comput. Harmon Anal., 2022, 60, 293–332. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2022.03.002 [27] J. Li, Z. Liu and W. Li, The reweighed greedy analysis pursuit algorithm for the cosparse analysis model, IEEE. The 2015 11th International Conference on Natural Computation, 2015, 1018–1022. [28] D. Li and M. Xue, Bases and Frames in Banach Spaces, Science Press, Beijing, 2007. (in Chinese). [29] Z. Liu, J. Li, W. Li and P. Dai, A modified greedy analysis pursuit algorithm for the cosparse analysis model, Numer. Algor., 2017, 74, 867–887. doi: 10.1007/s11075-016-0174-z [30] S. Mallat, A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing, Third Edition: The Sparse Way, Academic Press, 2008. [31] I. Mishra and S. Jain, Soft computing based compressive sensing techniques in signal processing: A comprehensive review, J. Intell. Syst., 2021, 30, 312–326. [32] S. Nam, M. Davies, M. Elad and R. Gribonval, Cosparse analysis modeling-uniqueness and algorithms, in: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2011, Prague, Czech Republic, May, 2011, 5804–5807. [33] S. Nam, M. Davies, M. Elad and R. Gribonval, The cosparse analysis model and algorithms, Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal., 2013, 34(1), 30–56. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2012.03.006 [34] M. D. Plumbley, T. Blumensath, L. Daudet, et al., Sparse representations in audio and music: From coding to source separation, Proc. IEEE., 2010, 98(6), 995–1005. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030345 [35] H. Song, X. Ren, Y. Lai and H. Meng, Sparse analysis recovery via iterative cosupport detection estimation, IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 38386–38395. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3063798 [36] J. L. Starck, F. Murtagh and M. J. Fadili, Sparse Image and Signal Processing-Wavelets, Curvelets, Morphological Diversity, Cambridge University Press, 2010. [37] T. Tirer and R. Giryes, Generalizing CoSaMP to signals from a union of low dimensional linear subspaces, Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal., 2020, 49(1), 99–122. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2018.11.005 [38] Y. Tsaig and D. L. Donoho, Extensions of compressed sensing, Signal Processing, 2006, 86(3), 549–571. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.05.029 [39] J. Xie, A. Liao and Y. Lei, A new accelerated alternating minimization method for analysis sparse recovery, Signal Process., 2018, 145, 167–174. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.12.010 [40] T. Zhao, C. E. Yonina, B Amir and N. Arye, Smoothing and decomposition for analysis sparse recovery, IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 2014, 62(7), 1762–1774. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2304932 -
-
-
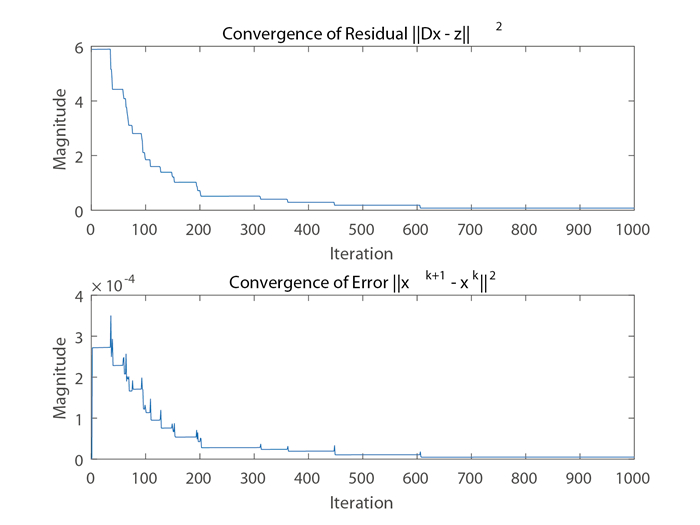
Figure 1.
The residuals and errors curves with
$ d=128, n=140, m=256, \ell=118 $ -
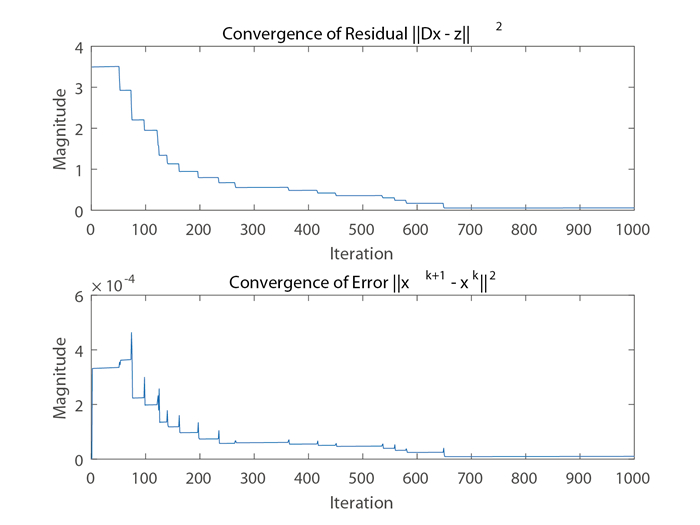
Figure 2.
The residuals and errors curves with
$ d=256, n=512, m=512, \ell=230 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: