| Citation: | Weixuan Shi, Sha Lu, Jianzhong Zhang. IMPULSIVE CONTROL FOR A PLANT-PEST-NATURAL ENEMY MODEL WITH STAGE STRUCTURE[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(1): 261-285. doi: 10.11948/20240083 |
IMPULSIVE CONTROL FOR A PLANT-PEST-NATURAL ENEMY MODEL WITH STAGE STRUCTURE
-
Abstract
For integrated pest management (IPM), we propose a generalized stage-structured plant-pest-natural enemy system with impulsive spraying pesticide and releasing natural enemies at different fixed moment. By the stroboscopic maps, we obtain two types of periodic solutions: the plant-pest-extinction and the pest-extinction. The sufficient conditions for the global attractivity of a pest-extinction periodic solution and permanence of the system are obtained by comparison theorem and stroboscopic technique. Moreover, numerical simulations are inserted to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the theoretical results, which show that the impulsive control plays a key role on the permanence of the system.
-
Keywords:
- Impulsive control /
- stage-structure /
- global attractivity /
- permanence
-

-
References
[1] O. Akmana, T. Comar and M. Hendersona, An analysis of an impulsive stage structured integrated pest management model with refuge effect, Chaos, Soliton. & Fract., 2018, 111, 44–54. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2018.03.039 [2] D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeonov, Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications, Longman Scientific and Technical, New York, 1993. [3] Q. J. Chen, Z. J. Liu, Y. S. Tan, et al., Analysis of a stochastic hybrid population model with impulsive perturbations and allee effect, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2023, 69(1), 565–587. doi: 10.1007/s12190-022-01752-9 [4] Y. P. Chen, Z. J. Liu and M. Haque, Analysis of a leslie-gower-type prey-predator model with periodic impulsive perturbations, Commun. Nonlinear Sci., 2009, 14(8), 3412–3423. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2008.12.019 [5] P. Cull, Global stability of population models, B. Math. Biol., 1981, 43(1), 47–58. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8240(81)80005-5 [6] B. Dubey and A. Kumar, Dynamics of prey-predator model with stage structure in prey including maturation and gestation delays, Nonlinear Dynam., 2019, 96(4), 2653–2679. doi: 10.1007/s11071-019-04951-5 [7] P. Georgescu and G. Morosanu, Impulsive perturbations of a three-trophic prey-dependent food chain system, Math. Comput. Model., 2008, 48(7), 975–997. [8] M. P. Hoffmann and A. C. Frodsham, Natural Enemies of Vegetable Insect Pests, Cooperative Extension, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, 1993. [9] G. X. Hu and K. H. Tian, On hybrid stochastic population models with impulsive perturbations, J. Biol. Dynam., 2019, 13(1), 385–406. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2019.1609607 [10] S. C. Hu, V. Lakshmikantham and S. Leela, Impulsive differential systems and the pulse phenomena, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 1989, 137(2), 605–612. doi: 10.1016/0022-247X(89)90266-7 [11] H. F. Huo, F. H. Zhang and H. Xiang, Spatiotemporal dynamics for impulsive eco-epidemiological model with crowley-martin type functional response, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2022, 19(12), 12180–12211. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022567 [12] K. S. Jatav and J. Dhar, Hybrid approach for pest control with impulsive releasing of natural enemies and chemical pesticides: A plant-pest-natural enemy model, Nonlinear Anal.-Hybri., 2014, 12, 79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2013.11.011 [13] V. Kumar, J. Dhar and H. S. Bhatti, Stage-structured plant-pest-natural enemy interaction dynamics incorporating gestation delay for both pest and natural enemy, Model. Earth Syst. Env., 2019, 5(1), 59–69. doi: 10.1007/s40808-018-0518-x [14] V. Kumari, S. Chauhan and J. Dhar, Controlling pest by integrated pest management: A dynamical approach, Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag., 2020, 5(4), 769–786. [15] V. Lakshmikantham, D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeonov, Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations, World Scientific, Singapor, 1989. [16] W. J. Li, J. C. Ji and L. H. Huang, Global dynamic behavior of a predator-prey model under ratio-dependent state impulsive control, Appl. Math. Model., 2020, 77, 1842–1859. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.09.033 [17] W. X. Li and K. Wang, Optimal harvesting policy for general stochastic logistic population model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2010, 368(2), 420–428. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.04.002 [18] J. Liu, J. Hu and P. Yuen, Extinction and permanence of the predator-prey system with general functional response and impulsive control, Appl. Math. Model., 2020, 88, 55–67. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.06.033 [19] Y. J. Niu, D. Liao and P. Wang, Stochastic asymptotical stability for stochastic impulsive differential equations and it is application to chaos synchronization, Commun. Nonlinear Sci., 2012, 17(2), 505–512. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.07.011 [20] Y. Z. Pei, Y. Yang and C. G. Li, Dynamics of an impulsive control system which prey species share a common predator, Chaos, Soliton. & Fract., 2009, 41(5), 2429–2436. [21] X. Y. Song, M. Y. Hao and X. Z. Meng, A stage-structured predator-prey model with disturbing pulse and time delays, Appl. Math. Model., 2009, 33(1), 211–223. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2007.10.020 [22] J. A. Souza and L. H. Takamoto, Lyapunov stability for impulsive control affine systems, J. Differ. Equations, 2019, 266(7), 4232–4267. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2018.09.033 [23] J. T. Sun, H. B. Chen and L. Yang, Variational methods to fourth-order impulsive differential equations, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2011, 35(1), 323–340. [24] S. Y. Tang, Y. N. Xiao, L. S. Chen, et al., Integrated pest management models and their dynamical behaviour, B. Math. Biol., 2005, 67(1), 115–135. doi: 10.1016/j.bulm.2004.06.005 [25] L. S. Wang, R. Xu and G. H. Feng, A stage-structured predator-prey system with impulsive effect and holling type-Ⅱ functional response, Journal of Mathematical Research and Exposition, 2011, 31(1), 147–156. [26] H. G. Yu, S. M. Zhong, M. Ye, et al., Mathematics and dynamic analysis of an ecological model with impulsive control strategy and distributed time delay, Math. Comput. Model., 2009, 50(11), 1622–1635. [27] B. Zeng and Z. H. Liu, Existence results for impulsive feedback control systems, Nonlinear Anal.-Hybri., 2019, 33, 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2019.01.008 [28] Q. Q. Zhang, S. Y. Tang and X. F. Zou, Rich dynamics of a predator-prey system with state-dependent impulsive controls switching between two means, J. Differ. Equations, 2023, 364, 336–377. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2023.03.030 [29] S. W. Zhang and D. J. Tan, Dynamics of a stochastic predator-prey system in a polluted environment with pulse toxicant input and impulsive perturbations, Appl. Math. Model., 2015, 39(20), 6319–6331. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2014.12.020 -
-
-
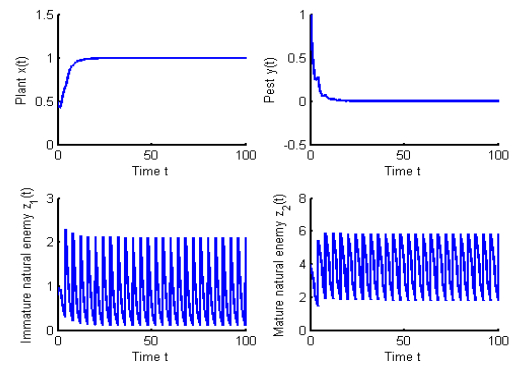
Figure 1.
Dynamical behavior of system (1.2) without impulsive control.
-
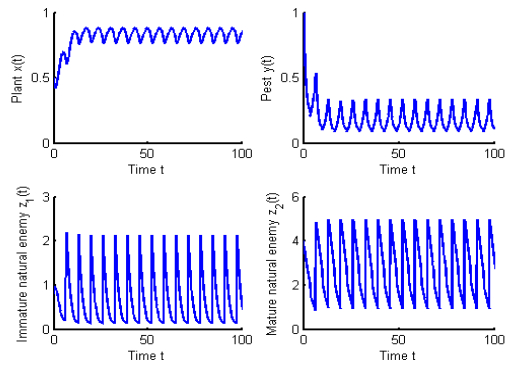
Figure 2.
The pest-extinction periodic solution
$ (1, 0, \widetilde{z }_1(t), \widetilde{z}_2(t)) $ $ T=4 < T_{\max}=4.7364 $ -
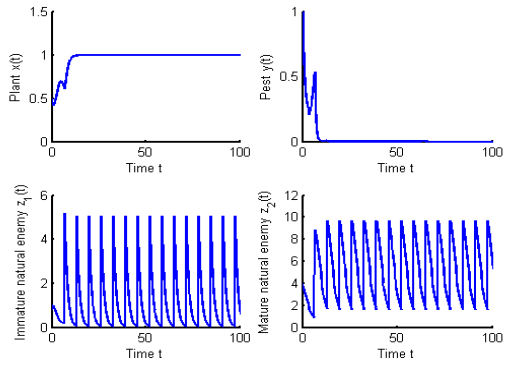
Figure 3.
System (1.2) is permanent for
$ T=6.5 > T_{\max}=4.7364 $ -
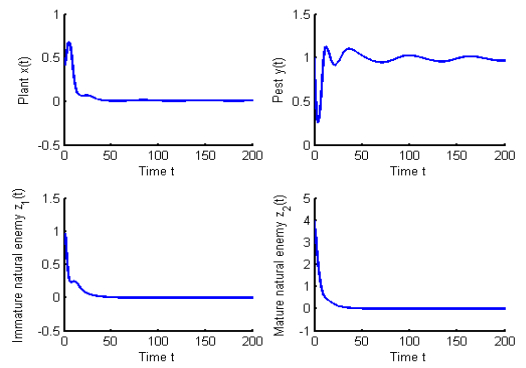
Figure 4.
The coexistence of populations transfer to extinction of pests for
$ T=6.5 $ $ \mu _1=5 $ $ \mu_2=8 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: