| Citation: | Jin Wen, Yun-Long Liu, Xue-Juan Ren, Donal O'Regan. A REGULARIZATION METHOD FOR BACKWARD PROBLEMS OF SINGULARLY PERTURBED PARABOLIC AND FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION EQUATIONS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(4): 2212-2237. doi: 10.11948/20240424 |
A REGULARIZATION METHOD FOR BACKWARD PROBLEMS OF SINGULARLY PERTURBED PARABOLIC AND FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION EQUATIONS
-
Abstract
In this paper, backward problems of singularly perturbed parabolic and fractional diffusion equations are studied from the additional temperature data at fixed time $ t=T$. We analyze the ill-posedness of these two inverse problems, and apply the quasi-reversibility regularization method to solve these problems. Then we obtain the convergence rates of logarithmic and Hölder types for the backward problems. Finally, several one- and two-dimensional numerical examples are given to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method.
-

-
References
[1] A. Y. Bomba and O. A. Fursachik, Inverse singularly perturbed problems of convection-diffusion type in quadrangular curvilinear domains, Mat. Metodi Fiz.-Mekh. Polya, 2009, 52(3), 59–66. [2] X. Cai, D. L. Cai, R. Q. Wu and K. H. Xie, High accuracy non-equidistant method for singular perturbation reaction-diffusion problem, Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2009, 30, 175–182. doi: 10.1007/s10483-009-0205-8 [3] P. Carter, A stabilizing effect of advection on planar interfaces in singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion equations, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2024, 84(3), 1227–1253. doi: 10.1137/23M1610872 [4] D. Chaikovskii, A. Liubavin and Y. Zhang, Asymptotic expansion regularization for inverse source problems in two-dimensional singularly perturbed nonlinear parabolic PDEs, CSIAM Trans. Appl. Math., 2023, 4(4), 721–757. doi: 10.4208/csiam-am.SO-2022-0017 [5] D. Chaikovskii and Y. Zhang, Convergence analysis for forward and inverse problems in singularly perturbed time-dependent reaction-advection-diffusion equations, J. Comput. Phys., 2022, 470, Paper No. 111609, 32. [6] J. Dardé, Iterated quasi-reversibility method applied to elliptic and parabolic data completion problems, Inverse Probl. Imaging, 2016, 10(2), 379–407. doi: 10.3934/ipi.2016005 [7] A. M. Denisov, Approximate solution of an inverse problem for a singularly perturbed integro-differential heat equation, Comput. Math. Math. Phys., 2023, 63(5), 837–844. doi: 10.1134/S0965542523050081 [8] A. M. Denisov, Approximation of the solution of an inverse problem for a singularly perturbed system of partial differential equations, Differ. Equ., 2023, 59(6), 762–768. doi: 10.1134/S0012266123060058 [9] J. R. Dorroh and X. P. Ru, The application of the method of quasi-reversibility to the sideways heat equation, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 1999, 236(2), 503–519. doi: 10.1006/jmaa.1999.6462 [10] N. V. Duc, N. V. Thang and N. T. Thành, The quasi-reversibility method for an inverse source problem for time-space fractional parabolic equations, J. Differential Equations, 2023, 344, 102–130. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2022.10.029 [11] L. Eldén, Approximations for a Cauchy problem for the heat equation, Inverse Problems, 1987, 3, 263–273. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/3/2/009 [12] S. Haber, Boundary Value Problem for a Singularly Perturbed Differential Equation, ProQuest LLC, Ann Arbor, MI, Thesis (Ph. D.)–Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1955. [13] S. Haber and N. Levinson, A boundary value problem for a singularly perturbed differential equation, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 1955, 6, 866–872. doi: 10.1090/S0002-9939-1955-0074634-3 [14] S. I. Kabanikhin, Inverse and Ill-posed Problems: Theory and Applications, Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin, 2012, vol. 55, xvi+459. [15] S. Karasuljić and H. Ljevaković, On construction of a global numerical solution for a semilinear singularly-perturbed reaction diffusion boundary value problem, Mat. Bilten, 2020, 44(2), 131–148. [16] A. A. Kilbas, H. M. Srivastava and J. J. Trujillo, Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations, in: North-Holland Mathematics Studies, Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam, 2006, vol. 204, p. xvi+523. [17] N. Kumar, S. Toprakseven, N. Singh Yadav and J. Y. Yuan, A Crank-Nicolson WG-FEM for unsteady 2D convection-diffusion equation with nonlinear reaction term on layer adapted mesh, Appl. Numer. Math., 2024, 201, 322–346. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2024.03.013 [18] R. Lattès and J.-L. Lions, The Method of Quasi-Reversibility. Applications to Partial Differential Equations, Modern Analytic and Computational Methods in Science and Mathematics, American Elsevier Publishing Co., Inc., New York, 1969. [19] T. T. Le and L. H. Nguyen, T.-P. Nguyen and W. Powell, The quasi-reversibility method to numerically solve an inverse source problem for hyperbolic equations, J. Sci. Comput., 2021, 87(3), Paper No. 90, 23. [20] Y. S. Li and T. Wei, An inverse time-dependent source problem for a time-space fractional diffusion equation, Appl. Math. Comput., 2018, 336, 257–271. [21] T. Linss, Maximum-norm error analysis of a non-monotone FEM for a singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion problem, BIT, 2007, 47(2), 379–391. doi: 10.1007/s10543-007-0118-z [22] G. Q. Liu and Y. C. Su, A uniformly convergent difference scheme for the singular perturbation problem of a high order elliptic differential equation, Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1996, 17(5), 413-421. doi: 10.1007/BF00131089 [23] D. V. Lukyanenko, A. A. Borzunov and M. A. Shishlenin, Solving coefficient inverse problems for nonlinear singularly perturbed equations of the reaction-diffusion-advection type with data on the position of a reaction front, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2021, 99, Paper No. 105824, 10. [24] D. V. Lukyanenko, V. B. Grigorev, V. T. Volkov and M. A. Shishlenin, Solving of the coefficient inverse problem for a nonlinear singularly perturbed two-dimensional reaction-diffusion equation with the location of moving front data, Comput. Math. Appl., 2019, 77(5), 1245–1254. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2018.11.005 [25] D. V. Lukyanenko, M. A. Shishlenin and V. T. Volkov, Solving of the coefficient inverse problems for a nonlinear singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion-advection equation with the final time data, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2018, 54, 233–247. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.06.002 [26] D. V. Lukyanenko, M. A. Shishlenin and V. T. Volkov, Asymptotic analysis of solving an inverse boundary value problem for a nonlinear singularly perturbed time-periodic reaction-diffusion-advection equation, J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl., 2019, 27(5), 745–758. doi: 10.1515/jiip-2017-0074 [27] D. V. Lukyanenko, V. T. Volkov, N. N. Nefedov, L. Recke and K. Schneider, Analytic-numerical approach to solving singularly perturbed parabolic equations with the use of dynamic adapted meshes, Model. Anal. Inf. Sist., 2016, 23(3), 334–341. doi: 10.18255/1818-1015-2016-3-334-341 [28] Z. Mao and L. B. Liu, A moving grid algorithm for a strongly coupled system of singularly perturbed convection-diffusion problems, Math. Appl. (Wuhan), 2018, 31(3), 653–660. [29] M. A. Mohye, J. B. Munyakazi and T. G. Dinka, A second order numerical method for two-parameter singularly perturbed time-delay parabolic problems, J. Math. Model., 2023, 11(4), 745–766. [30] I. Podlubny, Fractional Differential Equations, An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of their Solution and Some of their Applications, in: Mathematics in Science and Engineering, Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, CA, 1999, vol. 198, p. xxiv+340. [31] Z. Qian, C.-L. Fu and R. Shi, A modified method for a backward heat conduction problem, Appl. Math. Comput., 2007, 185(1), 564–573. [32] A. Seal, S. Natesan and S. Toprakseven, A dimensional-splitting weak Galerkin finite element method for 2d time-fractional diffusion equation, J. Sci. Comput., 2024, 98(3), Paper No. 56, 26. [33] G. I. Shishkin and L. P. Shishkina, A stable standard difference scheme for a singularly perturbed convection-diffusion equation under computer perturbations, Tr. Inst. Mat. Mekh., 2014, 20(1), 322–333. [34] C. M. Song, H. Li and J. N. Li, Initial boundary value problem for the singularly perturbed Boussinesq-type equation, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., 2013, 709–717. [35] S. Toprakseven, A weak Galerkin finite element method for time fractional reaction-diffusion-convection problems with variable coefficients, Appl. Numer. Math., 2021, 168, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2021.05.021 [36] S. Toprakseven and S. Dinibutun, A weak Galerkin finite element method for parabolic singularly perturbed convection-diffusion equations on layer-adapted meshes, Electron. Res. Arch., 2024, 32(8), 5033–5066. doi: 10.3934/era.2024232 [37] S. Toprakseven and N. Srinivasan, An efficient weak Galerkin FEM for third-order singularly perturbed convection-diffusion differential equations on layer-adapted meshes, Appl. Numer. Math., 2024, 204, 130–146. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2024.06.009 [38] R. Vulanović and L. Teofanov, A modification of the Shishkin discretization mesh for one-dimensional reaction diffusion problems, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2013, 220, 104–116. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2013.05.055 [39] J. G. Wang and T. Wei, An iterative method for backward time-fractional diffusion problem, Numer. Methods Partial Differential Equations, 2014, 30(6), 2029–2041. doi: 10.1002/num.21887 [40] J. G. Wang and T. Wei, Quasi-reversibility method to identify a space-dependent source for the time-fractional diffusion equation, Appl. Math. Model., 2015, 39(20), 6139–6149. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2015.01.019 [41] J. Wen, L. M. Huang and Z. X. Liu, A modified quasi-reversibility method for inverse source problem of Poisson equation, Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng., 2021, 29(12), 2098–2109. doi: 10.1080/17415977.2021.1902516 [42] J. Wen, Z. Y. Li and Y. P. Wang, Solving the backward problem for time-fractional wave equations by the quasi-reversibility regularization method, Adv. Comput. Math., 2023, 49(6), Paper No. 80, 26. [43] J. Wen, Y. L. Liu and D. O'Regan, An efficient iterative quasi-reversibility method for the inverse source problem of time-fractional diffusion equations, Numerical Heat Transfer Part B-Fundamentals, 2024. [44] J. Wen, X. J. Ren and S. J. Wang, Simultaneous determination of source term and initial value in the heat conduction problem by modified quasi-reversibility regularization method, Numerical Heat Transfer Part B-Fundamentals, 2022, 82(3–4), 112–127. [45] J. Wen, X. J. Ren and S. J. Wang, Simultaneous determination of source term and the initial value in the space-fractional diffusion problem by a novel modified quasi-reversibility regularization method, Physica Scripta, 2023, 98(2), 025201. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/acaa68 [46] J. Wen, C. W. Yue, Z. X. Liu and D. O'Regan, A fractional Landweber iteration method for simultaneous inversion in a time-fractional diffusion equation, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2023, 13(6), 3374–3402. [47] F. Yang and C. L. Fu, Two regularization methods to identify time-dependent heat source through an internal measurement of temperature, Math. Comput. Modelling, 2011, 53(5–6), 793–804. [48] F. Yang and C. L. Fu, A mollification regularization method for the inverse spatial-dependent heat source problem, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2014, 255, 555–567. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2013.06.012 [49] Z. Q. Zhang and T. Wei, Identifying an unknown source in time-fractional diffusion equation by a truncation method, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2013, 219(11), 5972–5983. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2012.12.024 -
-
-
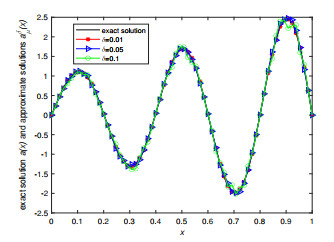
Figure 1.
Exact solution and its approximation for Example 5.1 when
$ \varepsilon=0.001 $ -
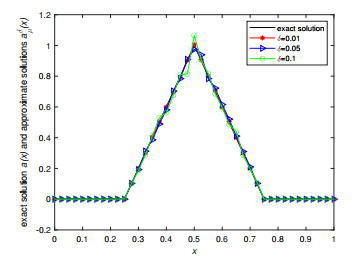
Figure 2.
Exact solution and its approximation for Example 5.2 when
$ \varepsilon=0.003 $ -
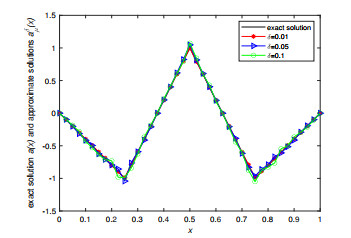
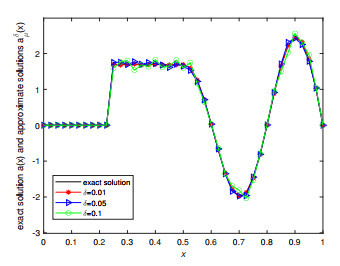
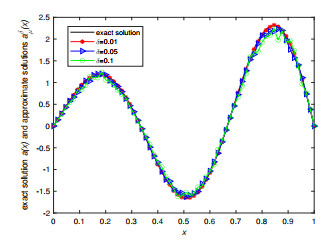
Figure 3.
Exact solution and its approximation for Example 5.3 when
$ \varepsilon=0.005 $ -
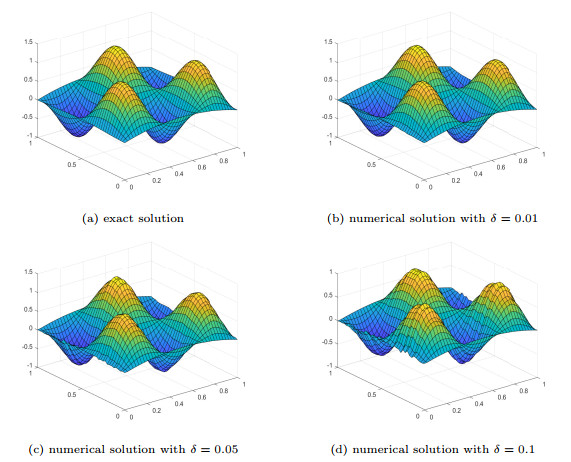
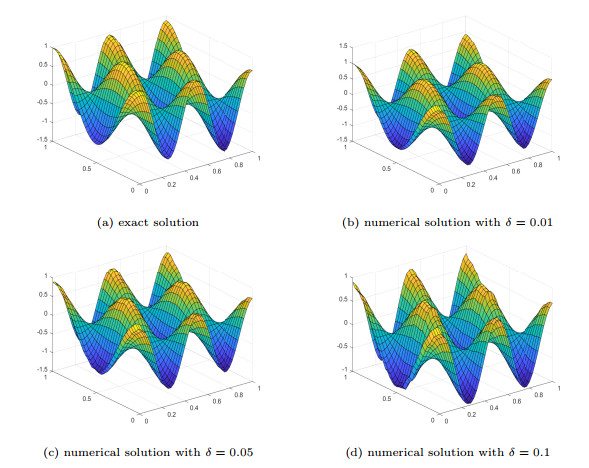
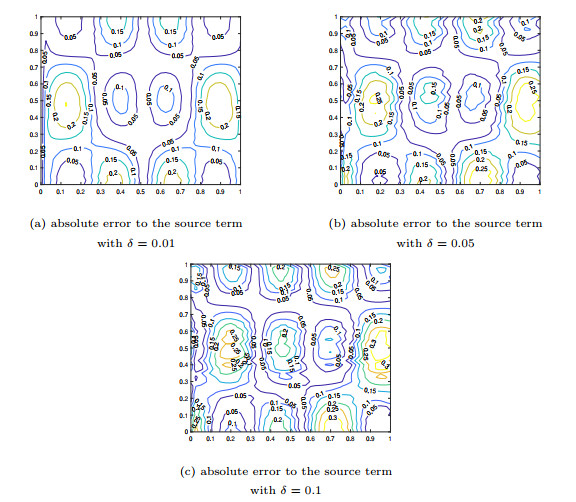
Figure 4.
Numerical results for source term in Example 5.4.
-
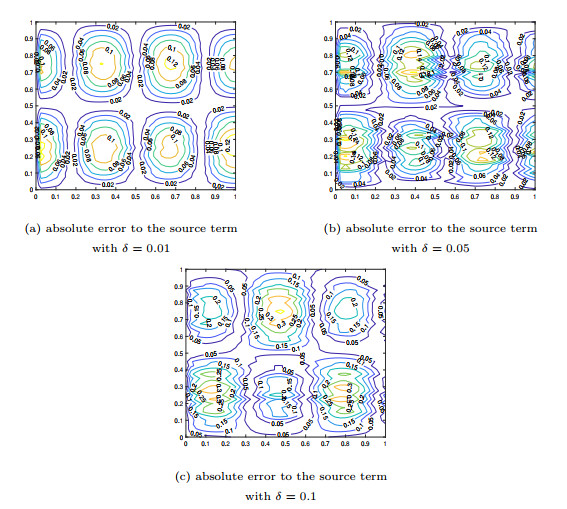
Figure 5.
The comparison of the numerical effects between the exact source term and its computed approximations for Example 5.4.
-
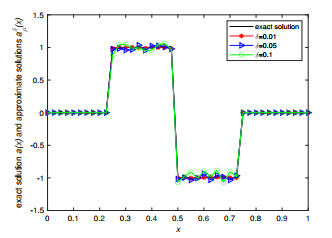
Figure 6.
Exact solution and its approximation for Example 5.5 when
$ \varepsilon=0.001, \alpha=0.8 $ -
Figure 7.
Exact solution and its approximation for Example 5.6 when
$ \varepsilon=0.004, \alpha=0.8 $ -
Figure 8.
Exact solution and its approximation for Example 5.7 when
$ \varepsilon=0.008, \alpha=0.8 $ -
Figure 9.
Numerical results for source term in Example 5.8 when
$ \alpha=0.8 $ -
Figure 10.
The comparison of the numerical effects between the exact source term and its computed approximations for Example 5.8 when
$ \alpha=0.8 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: