| Citation: | Marcin Massalski, Magdalena Nockowska-Rosiak. INVERSE-FREE NEWTON'S METHOD[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(4): 2238-2257. doi: 10.11948/20240428 |
INVERSE-FREE NEWTON'S METHOD
-
Abstract
We present a modification of Newton's method for finding a zero of a multivariable function without an inverse of a matrix in a recurrence. The aim of this paper is twofold: demonstrating at least quadratic convergence of a Newton-type method avoiding matrix inversion under standard assumptions, and then comparing modified and classical Newton's methods numerically.
-
Keywords:
- Newton's method /
- at least quadratic convergence /
- approximate inverse
-

-
References
[1] I. K. Argyros, S. George, S. Regmi and C. I. Argyros, Hybrid Newton-like inverse free algorithms for solving nonlinear equations, Algorithms, 2024, 17(4), 154. doi: 10.3390/a17040154 [2] I. K. Argyros, S. George, S. Shakhno, S. Regmi, M. Havdiak and M. I. Argyros, Asymptotically Newton-type methods without inverses for solving equations, Mathematics, 2024, 12(7), 1069. doi: 10.3390/math12071069 [3] J. D. Blanchard and M. Chamberland, Newton's method without division, Amer. Math. Monthly, 2023, 130(7), 606–617. doi: 10.1080/00029890.2022.2093573 [4] C. G. Broyden, A class of methods for solving nonlinear simultaneous equations, Math. Comput., 1965, 19(92), 577–593. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1965-0198670-6 [5] C. Chun, Iterative methods improving Newton's method by the decomposition method, Comput. Math. Appl., 2005, 50(10–12), 1559–1568. [6] A. Cordero and J. R. Torregrosa, Variants of Newton's method using fifth-order quadrature formulas, Appl. Math. Comput., 2007, 190, 686–698. [7] M. Dallas and S. Pollock, Newton-Anderson at singular points, Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model., 2023, 20(5), 667–692. doi: 10.4208/ijnam2023-1029 [8] D. W. Decker and C. T. Kelley, Expanded convergence domains for Newton's method at nearly singular roots, SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comp., 1985, 6(4), 951–966. doi: 10.1137/0906064 [9] A. Griewank, On solving nonlinear equations with simple singularities or nearly singular solutions, SIAM Rev., 1985, 27(4), 537–563. doi: 10.1137/1027141 [10] H. H. H. Homeier, On Newton-type methods with cubic convergence, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2005, 176(2), 425–432. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2004.07.027 [11] K. Jisheng, L. Yitian and W. Xiuhua, Third-order modification of Newton's method, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2007, 205(1), 1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2006.03.022 [12] C. T. Kelley and R. Suresh, A new acceleration method for Newton's method at singular points, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 1983, 20(5), 1001–1009. doi: 10.1137/0720070 [13] W. Kelley and A. Peterson, Difference Equations, An Introduction with Applications, 2nd ed., Harcourt/Academic Press, San Diego, 2001. [14] Y. Levin and A. Ben-Israel, An inverse-free directional Newton method for solving systems of nonlinear equations, Progress in Analysis, 2003, 1447–1457. [15] R. Lin, H. Ren, Q. Wu, Y. Khan and J. Hu, Convergence analysis of the modified Chebyshev's method for finding multiple roots. Vietnam J. Math., 2022, 50(1), 59–68. doi: 10.1007/s10013-020-00470-8 [16] C. Ma, Y. Wu and Y. Xie, The Newton-type splitting iterative method for a class of coupled Sylvester-like absolute value equation, J. Appl. Anal. Comp., 2024, 14(6), 3306–3331. [17] K. Madhu, D. K. R. Babajee and J. Jayaraman, An improvement to double-step Newton method and its multi-step version for solving system of nonlinear equations and its applications, Numer. Algorithms, 2017, 74(2), 593–607. doi: 10.1007/s11075-016-0163-2 [18] J. J. Moré, B. S. Garbow and K. E. Hillstrom, Testing unconstrained optimization software, ACM Trans. Math. Software, 1981, 7(1), 17–41. doi: 10.1145/355934.355936 [19] J. M. Ortega and W. C. Rheinboldt, Iterative Solution of Nonlinear Equations in Several Variables, Academic Press, New York, 1970. [20] V. Pan and J. Reif, Efficient parallel solution of linear systems, in: Proceedings of the 17th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, December 1985, 1985. [21] V. Pan and R. Schreiber, An improved Newton iteration for the generalized inverse of a matrix, with applications, SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput., 1991, 12(5), 1109–1130. doi: 10.1137/0912058 [22] S. Pollock, Fast convergence to higher-multiplicity zeros, 2019, available as: arXiv: 1911.10647. [23] S. Pollock and H. Schwartz, Benchmarking results for the Newton-Anderson method, Results Appl. Math., 2020, 8, Paper No. 100095. doi: 10.1016/j.rinam.2020.100095 [24] A. Quarteroni, R. Sacco and F. Saleri, Numerical Mathematics, Texts in Applied Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2006. [25] S. Qureshi, I. K. Argyros, H. Jafari, A. Soomro and K. Gdawiec, A highly accurate family of stable and convergent numerical solvers based on Daftardar-Gejji and Jafari decomposition technique for systems of nonlinear equations, MethodsX, 2024, 13, 102865. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2024.102865 [26] S. Qureshi, I. K. Argyros, A. Soomro, K. Gdawiec, A. A. Shaikh and E. Hincal, A new optimal root-finding iterative algorithm: Local and semilocal analysis with polynomiography, Numer. Algorithms, 2024, 95(4), 1715–1745. doi: 10.1007/s11075-023-01625-7 [27] S. Qureshi, F. Chicharro, I. K. Argyros, A. Soomro, J. Alahmadi and E. Hincal, A new optimal numerical root-solver for solving systems of nonlinear equations using local, semi-local, and stability analysis, Axioms, 2024, 13, 341. doi: 10.3390/axioms13060341 [28] G. W. Reddien, On Newton's method for singular problems, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 1978, 15(5), 993–996. doi: 10.1137/0715064 [29] G. W. Reddien, Newton's method and high order singularities, Comput. Math. Appl., 1979, 5(2), 79–86. doi: 10.1016/0898-1221(79)90061-0 [30] G. Schulz, Iterative Berechnung der Reziproken matrix, Z. Angew. Math. Mech., 1933, 13(1), 57–59. doi: 10.1002/zamm.19330130111 [31] Y.-Q. Shen and T. J. Ypma, Newton's method for singular nonlinear equations using approximate left and right nullspaces of the Jacobian, Appl. Numer. Math., 2005, 54(2), 256–265. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2004.09.029 [32] M. Singh, A. K. Verma and R. Agarwal, On an iterative method for a class of 2 point & 3 point nonlinear SBVPs, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2019, 9(4), 1242–1260. [33] E. Suli and D. F. Mayers, An Introduction to Numerical Analysis, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2003. [34] F. Toutounian and F. Soleymani, An iterative method for computing the approximate inverse of a square matrix and the Moore-Penrose inverse of a non-square matrix, Appl. Math. Comput., 2013, 224, 671–680. [35] S. Weerakoon and T. G. I. Fernando, A Variant of Newton's method with accelerated third-order convergence, Appl. Math. Lett., 2000, 13, 87–93. -
-
-
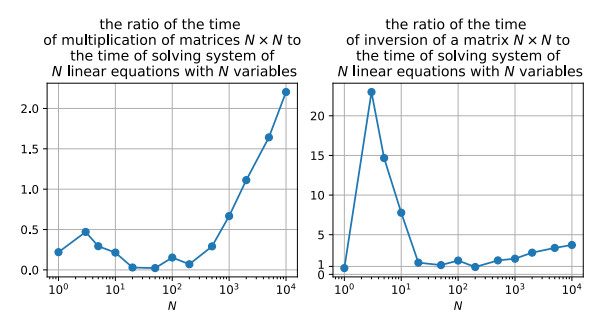
Figure 1.
Comparison of the time of inversion and multiplication of matrices
$ N\times N $ $ N $ $ N $ $ N $ -
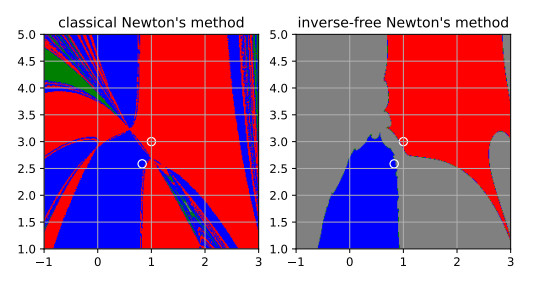
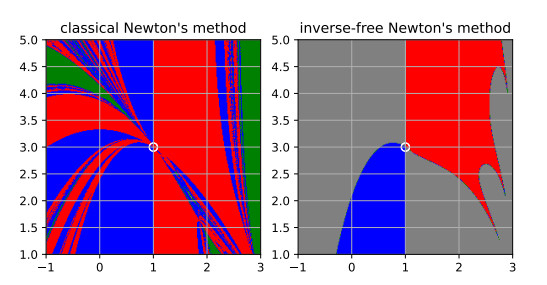
Figure 2.
Basins of attraction for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = \frac{1}{2} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}^{\ast}_+ $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
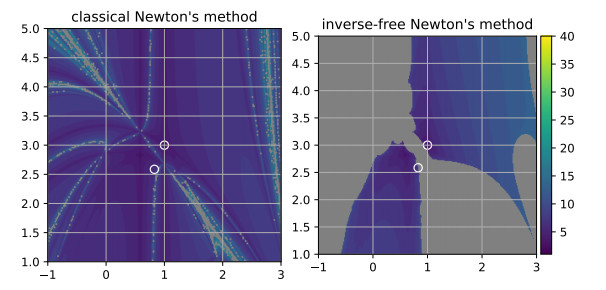
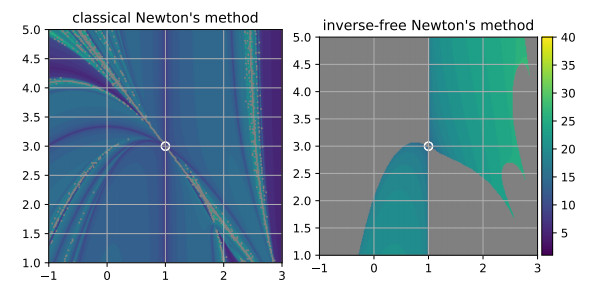
Figure 3.
Basins of attraction for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = \frac{1}{2} $ $ \gamma=10^{-10} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_+^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
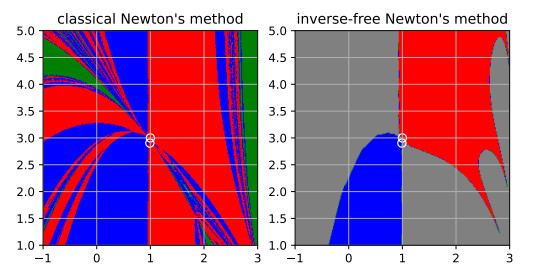
Figure 4.
Basins of attraction for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = 10^{- 1} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}^{\ast}_+ $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
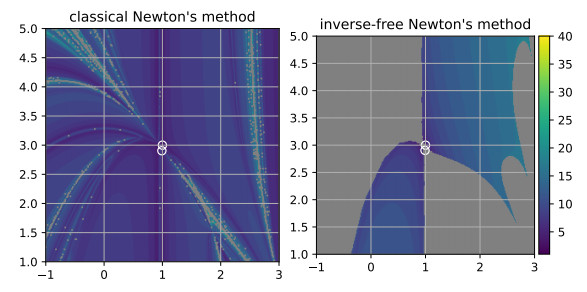
Figure 5.
Basins of attraction for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = 0, 1 $ $ \gamma=10^{-10} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_+^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
Figure 6.
Basins of attraction for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = 10^{- 3} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}^{\ast}_+ $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
Figure 7.
Basins of attraction for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = 10^{-3} $ $ \gamma=10^{-10} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_+^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
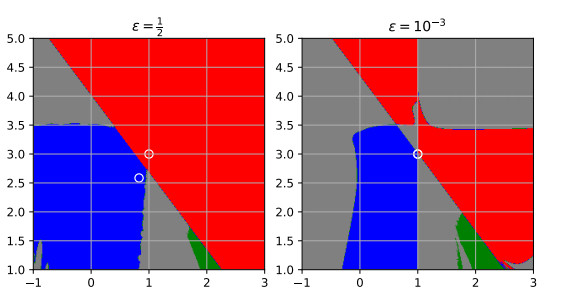
Figure 8.
Basins of attraction inverse-free Newton's method with the first modification for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = \frac{1}{2} $ $ \varepsilon = 10^{- 3} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}^{\ast}_+ $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ -
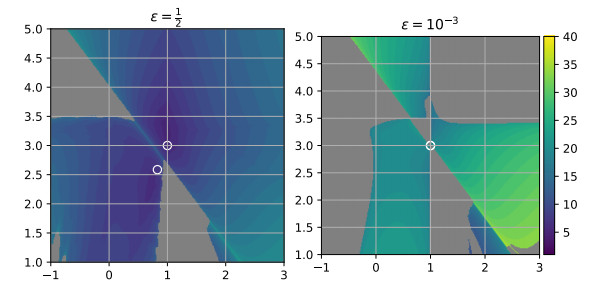
Figure 9.
Basins of attraction inverse-free Newton's method with the first modification for the function
$ {\boldsymbol{{f}}}_{\varepsilon} $ $ \varepsilon = \frac{1}{2} $ $ \varepsilon = 10^{- 3} $ $ \gamma=10^{-10} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_+^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_0^{\ast} $ $ {\boldsymbol{{x}}}_-^{\ast} $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: