| Citation: | Wenjun Yu, Hailong Shen, Xinhui Shao. A CLASS OF COORDINATE DESCENT METHODS WITH ANGLE PROBABILITY FOR SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(5): 2935-2958. doi: 10.11948/20240569 |
A CLASS OF COORDINATE DESCENT METHODS WITH ANGLE PROBABILITY FOR SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS
-
Abstract
In order to resolve large-scale linear systems, we construct the new probability criterion based on the angle between hyperplanes and propose the randomized coordinate descent method with the angle probability criterion. Furthermore, we propose the randomized extended coordinate descent method with the angle probability criterion, which allows to solve underdetermined linear systems. The convergence properties of the two methods are analyzed from the expectation perspective and upper bounds on their convergence rate are derived when the matrix is full rank. Lastly, we conduct numerical experiments to verify the efficacy of our new methods.
-

-
References
[1] Z. -Z. Bai, L. Wang and W. -T. Wu, On convergence rate of the randomized gauss-seidel method, Linear Algebra and its Applications, 2021, 611, 237-252. doi: 10.1016/j.laa.2020.10.028 [2] Z. -Z. Bai and W. -T. Wu, On greedy randomized kaczmarz method for solving large sparse linear systems, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2018, 40(1), A592-A606. doi: 10.1137/17M1137747 [3] Z. -Z. Bai and W. -T. Wu, On greedy randomized coordinate descent methods for solving large linear least-squares problems, Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications, 2019, 26(4), e2237. doi: 10.1002/nla.2237 [4] P. Breheny and J. Huang, Coordinate descent algorithms for nonconvex penalized regression, with applications to biological feature selection, The Annals of Applied Statistics, 2011, 5(1), 232. [5] T. A. Davis and Y. Hu, The university of florida sparse matrix collection, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS), 2011, 38(1), 1-25. [6] K. Du, Tight upper bounds for the convergence of the randomized extended kaczmarz and gauss-seidel algorithms, Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications, 2019, 26(3), e2233. doi: 10.1002/nla.2233 [7] K. Du and X. -H. Sun, A doubly stochastic block gauss-seidel algorithm for solving linear equations, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2021, 408, 126373. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2021.126373 [8] Y. -J. Guan, W. -G. Li, L. -L. Xing and T. -T. Qiao, A note on convergence rate of randomized kaczmarz method, Calcolo, 2020, 57, 1-11. doi: 10.1007/s10092-019-0350-3 [9] D. Leventhal and A. S. Lewis, Randomized methods for linear constraints: Convergence rates and conditioning, Mathematics of Operations Research, 2010, 35(3), 641-654. doi: 10.1287/moor.1100.0456 [10] Y. Liu, X. -L. Jiang and C. -Q. Gu, On maximum residual block and two-step gauss-seidel algorithms for linear least-squares problems, Calcolo, 2021, 58, 1-32. doi: 10.1007/s10092-020-00392-4 [11] Z. Lu and L. Xiao, On the complexity analysis of randomized block-coordinate descent methods, Mathematical Programming, 2015, 152, 615-642. doi: 10.1007/s10107-014-0800-2 [12] A. Ma, D. Needell and A. Ramdas, Convergence properties of the randomized extended gauss-seidel and kaczmarz methods, SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2015, 36(4), 1590-1604. doi: 10.1137/15M1014425 [13] I. Necoara, A random coordinate descent method for large-scale resource allocation problems, in 2012 IEEE 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), IEEE, 2012, 4474-4479. [14] Y. Nesterov, Efficiency of coordinate descent methods on huge-scale optimization problems, SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2012, 22(2), 341-362. doi: 10.1137/100802001 [15] Y. -Q. Niu and B. Zheng, A new randomized gauss-seidel method for solving linear least-squares problems, Applied Mathematics Letters, 2021, 116, 107057. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2021.107057 [16] Y. -Q. Niu and B. Zheng, A randomized sparse kaczmarz solver for sparse signal recovery via minimax-concave penalty, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2024, 47, 6431-6445. doi: 10.1002/mma.9927 [17] P. Richtárik and M. Takáč, Iteration complexity of randomized block-coordinate descent methods for minimizing a composite function, Mathematical Programming, 2014, 144(1), 1-38. [18] A. Rodomanov and D. Kropotov, A randomized coordinate descent method with volume sampling, SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2020, 30(3), 1878-1904. doi: 10.1137/19M125532X [19] J. M. Steele, The Cauchy-Schwarz Master Class: An Introduction to the Art of Mathematical Inequalities, Cambridge University Press, 2004. [20] T. Strohmer and R. Vershynin, A randomized kaczmarz algorithm with exponential convergence, Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2009, 15(2), 262-278. doi: 10.1007/s00041-008-9030-4 [21] L. -Z. Tan and X. -P. Guo, On multi-step greedy randomized coordinate descent method for solving large linear least-squares problems, Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2023, 42(1), 37. doi: 10.1007/s40314-022-02163-z [22] N. Wu and H. Xiang, On the generally randomized extended gauss-seidel method, Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2022, 172, 382-392. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2021.10.018 [23] Q. Wu, M. Li, J. Zhu, et al., Dp-rbadabound: A differentially private randomized block-coordinate adaptive gradient algorithm for training deep neural networks, Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 211, 118574. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118574 [24] W. Wu, Convergence of the randomized block gauss-seidel method, SIAM Undergraduate Research Online, 2018, 11, 369-382. [25] J. Zhang and J. Guo, On relaxed greedy randomized coordinate descent methods for solving large linear least-squares problems, Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2020, 157, 372-384. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2020.06.014 [26] A. Zouzias and N. M. Freris, Randomized extended kaczmarz for solving least squares, SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2013, 34(2), 773-793. doi: 10.1137/120889897 -
-
-
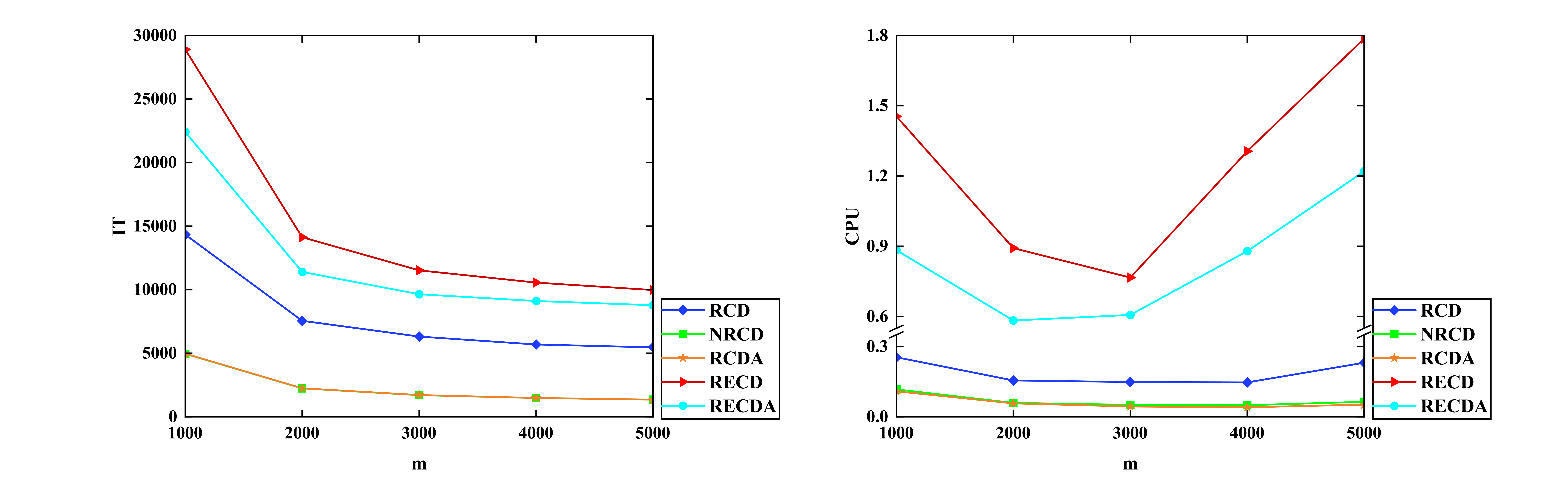
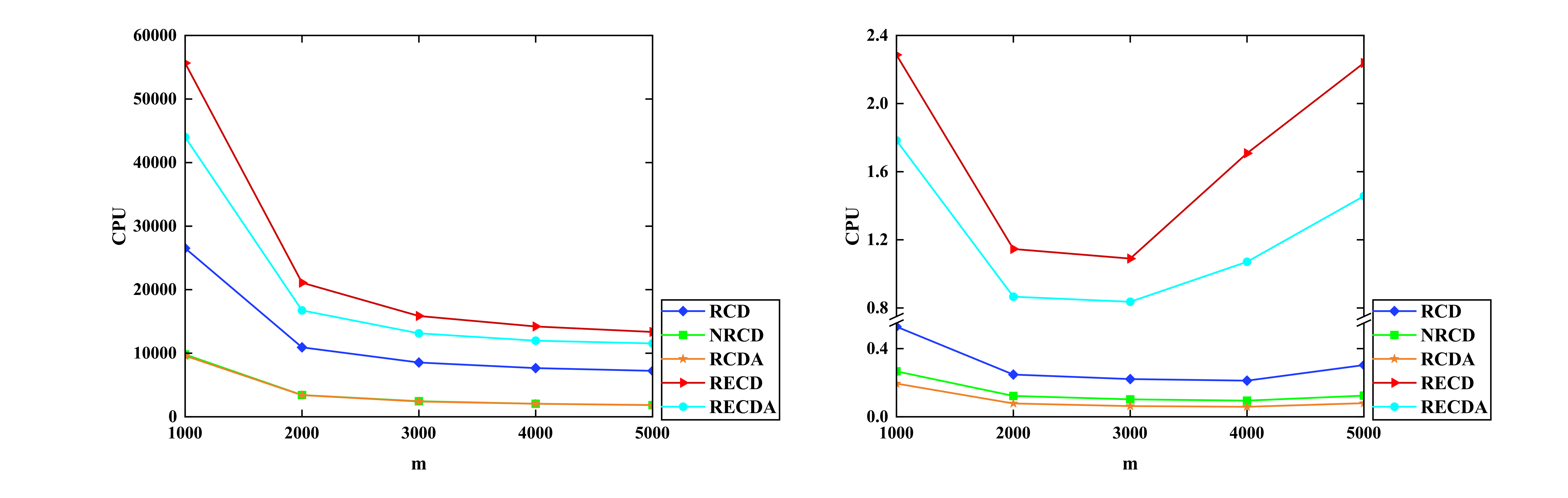
Figure 1.
IT and CPU versus
$ m $ $ n $ -
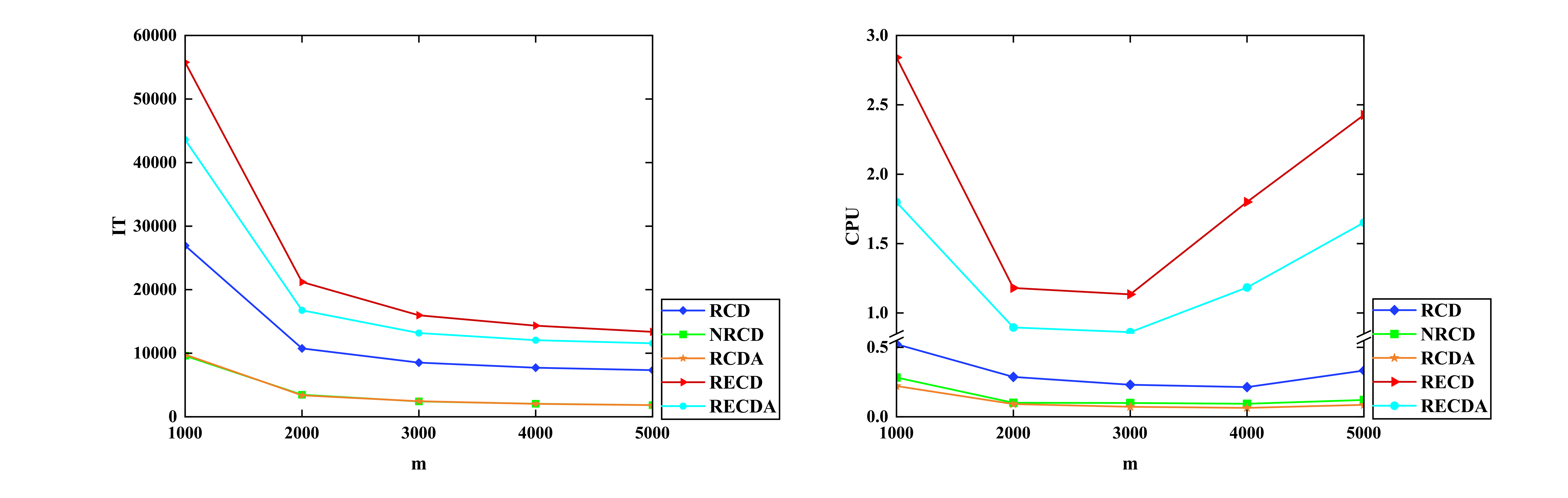
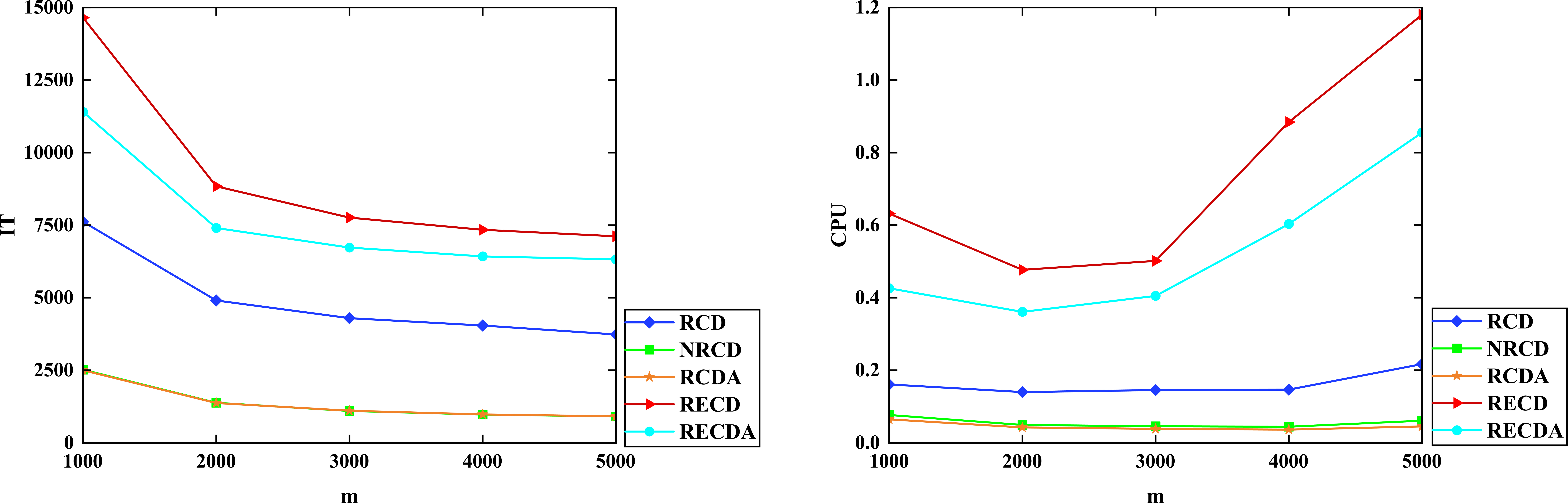
Figure 2.
IT and CPU versus
$ m $ $ n $ -
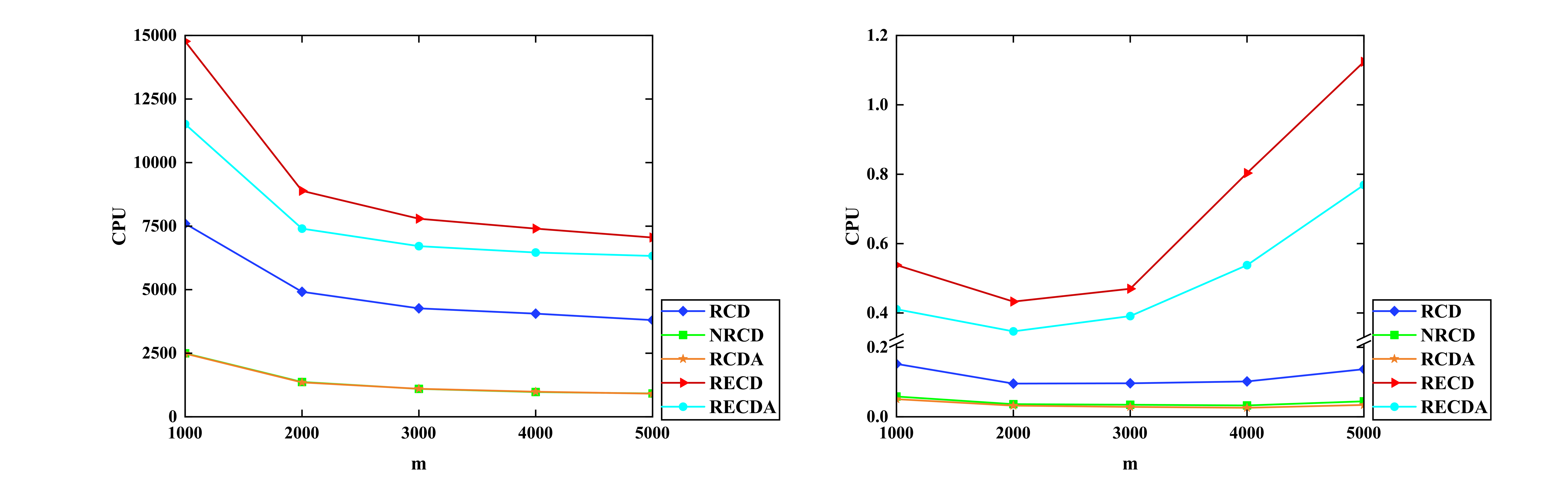
Figure 3.
IT and CPU versus
$ m $ $ n $ -
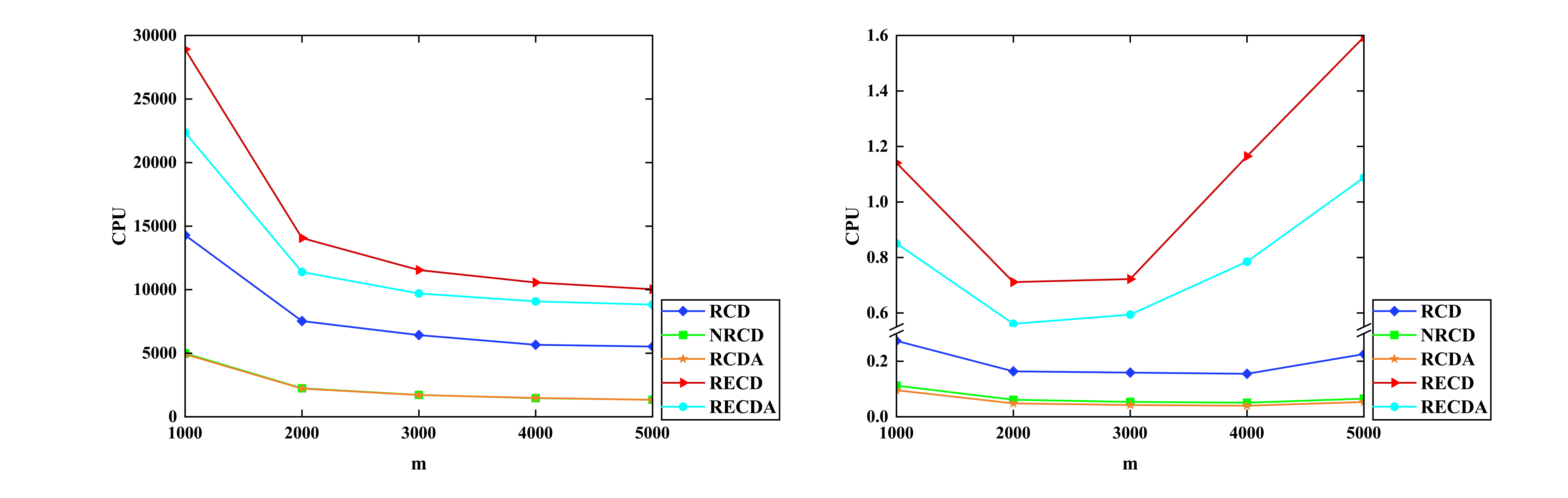
Figure 4.
IT and CPU versus
$ m $ $ n $ -
Figure 5.
IT and CPU versus
$ m $ $ n $ -
Figure 6.
IT and CPU versus
$ m $ $ n $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: