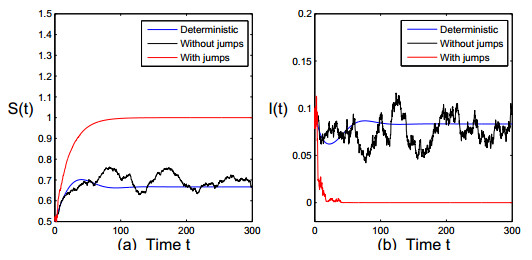
|
[1]
|
J. Bao, X. Mao, G. Yin, et al., Competitive Lotka-Volterra population dynamics with jumps, Nonlinear Anal., 2011, 74, 6601–6616. doi: 10.1016/j.na.2011.06.043
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
A. Bhadra, E.L. Ionides, K. Laneri, et al., Malaria in Northwest India: data analysis via partially observed stochastic differential equation models driven by Lévy noise, J. Amer. Stat. Assoc., 2011, 106, 440–451. doi: 10.1198/jasa.2011.ap10323
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
Y. Cai, Y. Kang, M. Banerjee, et al., A stochastic SIRS epidemic model with infectious force under intervention strategies, J. Diff. Equat., 2015, 259, 7463–7502. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2015.08.024
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
A. Gray, D. Greenhalgh, L. Hu, X. Mao, J. Pan, A stochastic differential equation SIS epidemic model, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2011, 71, 876–902. doi: 10.1137/10081856X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
C. Ji, D. Jiang, Threshold behaviour of a stochastic SIR model, Appl. Math. Model., 2014, 38, 5067–5079. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2014.03.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
D. Jiang, N. Shi, Y. Zhao, Existence, uniqueness and global stability of positive solutions to the Food-Limited population model with random perturbation, Math. Comput. Model., 2005, 42, 651–658. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2004.03.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
W. Kermack, A. McKendrick, Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics (Part Ⅰ), Proc. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, 1927, 115, 700–721. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1927.0118
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
A. Lahrouz, L. Omari, Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with non-linear incidence, Statist. Probab. Lett., 2013, 83, 960–968. doi: 10.1016/j.spl.2012.12.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
D. Li, J. Cui, M. Liu, et al., The evolutionary dynamics of stochastic epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate, Bull. Math. Biol., 2015, 77, 1705–1743. doi: 10.1007/s11538-015-0101-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
D. Li, J. Cui, G. Song, Permanence and extinction for a single-species system with jump-diffusion, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2015, 430, 438–464. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.04.050
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
M. Liu, K. Wang, Dynamics of a Leslie-Gower Holling-type Ⅱ predator-prey system with Lévy jumps. Nonl. Anal., 2013, 85, 204–213.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
X. Mao, G. Marion, E. Renshaw, Environmental Brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics, Stoch. Process. Appl., 2002, 97, 95–110. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4149(01)00126-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
R.M. May, Stability and complexity in model ecosystems, Princeton Univ. Press, New Jersey, 1973.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
T. Tang, Z. Teng, Z. Li, Threshold behavior in a class of stochastic SIRS epidemic models with nonlinear incidence, Stoch. Anal. Appl., 2015, 33, 994–1019. doi: 10.1080/07362994.2015.1065750
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
E. Tornatore, S.M. Buccellato, P. Vetro, Stability of a stochastic SIR system, Phys. A., 2005, 354, 111–126. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2005.02.057
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
Y. Zhao, D. Jiang, The threshold of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with saturated incidence, Appl. Math. Lett., 2014, 34, 90–93. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2013.11.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
B. Zheng, X. Meng, T. Zhang, A new way of investigating the asymptotic behaviour of a stochastic SIS system with multiplicative noise, Appl. Math. Lett., 2019, 87, 80–86. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2018.07.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
J. Zhou, Y. Yang, T. Zhang, Global stability of a discrete multigroup SIR model with nonlinear incidence rate, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2017, 40, 5370–5379. doi: 10.1002/mma.v40.14
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
J. Zhou, Y. Yang, T. Zhang, Global dynamics of a reaction-diffusion waterborne pathogen model with general incidence rate, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2018, 466, 835-859. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2018.06.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




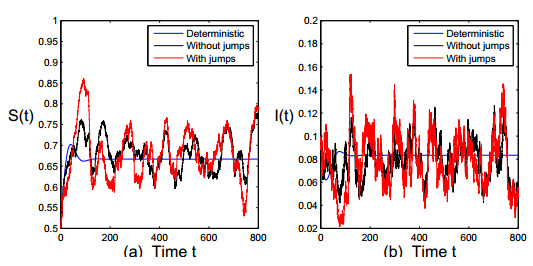

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: