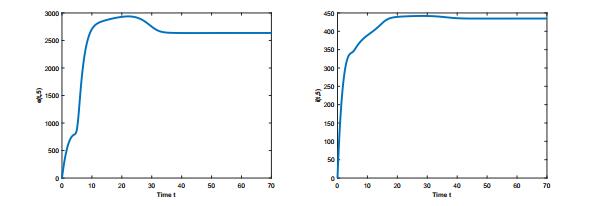
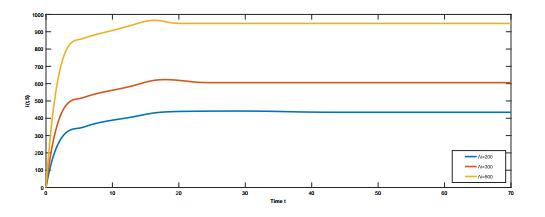
|
[1]
|
V. Akimenko, An age-structured SIR epidemic model with fixed incubation period of infection, Comput. Math. Appl., 2017, 73, 1485-1504. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2017.01.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
R. M. Anderson and R. M. May, Infectious Diseases in Humans: Dynamics and Control, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1991.
Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
S. M. Blower, A. R. Mclean, T. C. Porco et al., The intrinsic transmission dynamics of tuberculosis epidemics, Nat. Med., 1995, 1, 815-821. doi: 10.1038/nm0895-815
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
F. Brauer and P. van den Driessche, Models for transmission of disease with immigration of infectives, Math. Biosci., 2001, 171, 143-154. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(01)00057-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
V. Capasso and G. Serio, A generalization of the Kermack-Mackendric deterministic model, Math. Biosci., 1978, 42, 43-61. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(78)90006-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
C. Castillo Chavez and B. Song, Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2004, 1, 361-404. doi: 10.3934/mbe
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
Y. Chen, J. Yang and F. Zhang, The global stability of an SIRS model with infection age, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2014, 11, 449-469. doi: 10.3934/mbe
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
Y. Chen, S. Zou and J. Yang, Global analysis of an SIR epidemic model with infection age and saturated incidence, Nonlinear Anal.: Real World Appl., 2016, 30, 16-31. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2015.11.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
W. R. Derrick and P. van den Driessche, Homoclinic orbits in a disease transmission model with nonlinear incidence and nonconstant population, Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2003, 3, 299-309. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
X. Duan, S. Yuan, Z. Qiu and J. Ma, Global stability of an SVEIR epidemic model with ages of vaccination and latency, Comput. Math. Appl., 2016, 68, 288-308.
Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
A. Ducrot, P. Magal and O. Seydi, Singular perturbation for an abstract non-densely defined cauchy problem, J. Evol. Equ., 2017, 17, 1089-1128. doi: 10.1007/s00028-016-0374-y
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
W. E. Fitzgibbon, J. J. Morgan, G. F. Webb and Y. Wu, A vector-host epidemic model with spatial structure and age of infection, Nonlinear Anal.: Real World Appl., 2018, 41, 692-705. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2017.11.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
R. Gao, B. Cao, Y. Hu et al., Human infection with a novel avian-origin influenza A(H7N9) virus, N. Engl. J. Med., 2013, 368, 1888-1897.
Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
J. K. Hale, Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs Vol. 25, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1988.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
H. W. Hethcote and P. van den Driessche, Some epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence, J. Math. Biol., 1991, 29, 271-287. doi: 10.1007/BF00160539
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
M. Iannelli, Mathematical Theory of Age-Structured Population Dynamics, Giardini Editori e Stampatori in Pisa, 1995.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
H. Inaba, R. Saito and N. Baca$\ddot{\textrm{e}}$r, An age-structured epidemic model for the demographic transition, Comput. Math. Appl., 2017, 73, 1485-1504. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2017.01.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
W. Kermack and A. McKendrick, A contribution to mathematical theory of epidemics, Proc Roy Soc Lond A, 1927, 115, 700-721. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1927.0118
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
A. Khan and G. Zaman, Global analysis of an age-structured SEIR endemic model, Chaos Soliton. Fract., 2018, 108, 154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2018.01.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
A. Korobeinikov, Lyapunov functions and global properties for SEIR and SEIS epidemic models, Math. Med. Biol., 2004, 21, 75-83. doi: 10.1093/imammb/21.2.75
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
A. Korobeinikov and P. K. Maini, Nonlinear incidence and stability of infectious disease models, Math. Med. Biol., 2005, 22, 113-128. doi: 10.1093/imammb/dqi001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
J. Li and F. Brauer, Continuous-time age-structured models in population dynamics and epidemiology, in: F. Brauer, P. van den Driessche and J. Wu (Eds), Mathematical Epidemiology, Lecture Notes in Mathematics Vol. 1945, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008.
Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
J. Li, Y. Yang, Y. Xiao and S. Liu, A class of Lyapunov functions and the global stability of some epidemic models with nonlinear incidence, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2016, 6(1), 38-46.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
M. Y. Li and J. Muldowney, Global stability for the SEIR model in epidemiology, Math. Biosci., 1995, 12, 155-164.
Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
L. Liu, J. Wang and X. Liu, Global stability of an SEIR epidemic model with age-dependent latency and relapse, Nonlinear Anal.: Real World Appl., 2015, 24, 18-35. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2015.01.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
S. Liu, X. Xie and J. Tang, Competing population model with nonlinear intraspecific regulation and maturation delays, Int. J. Biomath., 2012, 5, 1260007:1-22. doi: 10.1142/S1793524512600078
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
W. M. Liu, S. A. Levin and X. Iwasa, Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behaviour of SIRS epidemiological models, J. Math. Biol., 1986, 23, 187-204. doi: 10.1007/BF00276956
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
P. Magal, C. C. McCluskey and G. F. Webb, Lyapunov functional and global asymptotic stability for an infection-age model, Appl. Anal., 2010, 89, 1109-1140. doi: 10.1080/00036810903208122
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
R. M. May and R. M. Anderson, Regulation and stability of host-parasite population interactions: Ⅱ. destabilizing processes, J. Anim. Ecol., 1978, 249-267.
Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
C. C. McCluskey, Global stability for an SEI model of infectious disease with age structure and immigration of infecteds, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2016, 13, 381-400.
Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
S. J. Olsen, H. L. Chang, T. Y. Cheung et al, Transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome on aircraft, N. Engl. J. Med., 2003, 349, 2416-2422.
Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
R. Ross, The Prevention of Malaria, John Murray, London, 1911.
Google Scholar
|
|
[33]
|
G. Rost and J. Wu, SEIR epidemiological model with varying infectivity and infinite delay, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2008, 5, 389-402. doi: 10.3934/mbe
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[34]
|
R. P. Sigdel and C. C. McCluskey, Global stability for an SEI model of infectious disease with immigration, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 243, 684-689.
Google Scholar
|
|
[35]
|
H. L. Smith, Subharmonic bifurcation in an SIR epidemic model, J. Math. Biol., 1983, 17, 163-177. doi: 10.1007/BF00305757
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[36]
|
H. L. Smith and H. R. Thieme, Dynamical Systems and Population Persistence, Graduate Studies in Mathematics Vol. 118, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 2011.
Google Scholar
|
|
[37]
|
B. Soufiane and T. M. Touaoula, Global analysis of an infection age model with a class of nonlinear incidence rates, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2016, 434, 1211-1239. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.09.066
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[38]
|
K. Styblo, D. Frencly and T. Petty, Tuberculosis control and surveillance, Recent Adv. Respir. Med., 1986, 4, 77-108.
Google Scholar
|
|
[39]
|
J. Wang, M. Guo and S. Liu, SVIR epidemic model with age structure in susceptibility, vaccination effects and relapse, IMA J. Appl. Math., 2018, 82, 945-970.
Google Scholar
|
|
[40]
|
J. Wang, R. Zhang and T. Kuniya, The dynamics of an SVIR epidemiological model with infection age, IMA J. Appl. Math., 2016, 81, 321-343. doi: 10.1093/imamat/hxv039
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[41]
|
L. Wang and X. Wang, Influence of temporary migration on the transmission of infectious diseases in a migrants' home village, J. Theoret. Biol., 2012, 300, 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.01.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[42]
|
X. Wang, S. Liu, L. Wang and W. Zhang, An epidemic patchy model with entry-exit screening, Bull. Math. Biol., 2015, 77, 1237-1255. doi: 10.1007/s11538-015-0084-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[43]
|
G. F. Webb, An age-dependent epidemic model with spatial diffusion, Arch. Ration. Mech. An., 1980, 75, 91-102. doi: 10.1007/BF00284623
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[44]
|
G. F. Webb, Theory of Nonlinear Age-Dependent Population Dynamics, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1985.
Google Scholar
|
|
[45]
|
G. F. Webb and C. J. Browne, A model of the Ebola epidemics in West Africa incorporating age of infection, J. Biol. Dyna., 2016, 10, 18-30. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2015.1090632
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[46]
|
World Health Organization, Fact sheets on Tuberculosis, www.who.int/tb. Accessed March 2019.
Google Scholar
|
|
[47]
|
Y. Yang, S. Tang, X. Ren et al., Global stability and optimal control for a tuberculosis model with vaccination and treatment, Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2016, 21, 1009-1022. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[48]
|
H. Yu, S. Cauchemez et al., Transmission dynamics, border entry screening, and school holidays during the 2009 influenza A (H1N1) pandemic, Emerg. Infect. Dis., 2012, 18, 758-766. doi: 10.3201/eid1805.110356
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[49]
|
T. Zhang and Z. Teng, Pulse vaccination delayed SEIRS epidemic model with saturation incidence, Appl. Math. Model, 2008, 32, 1403-1416. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2007.06.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|




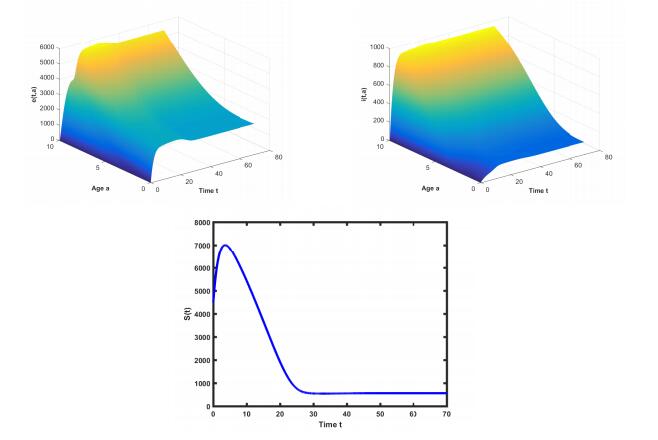

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: