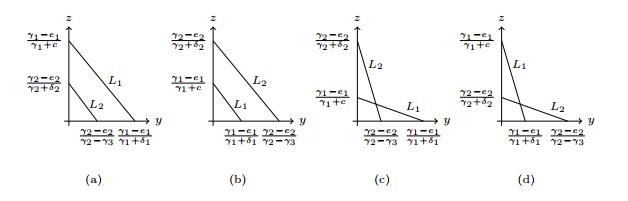
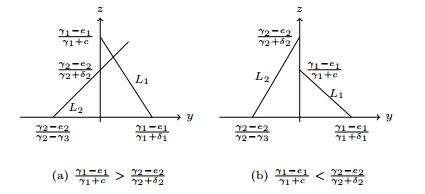
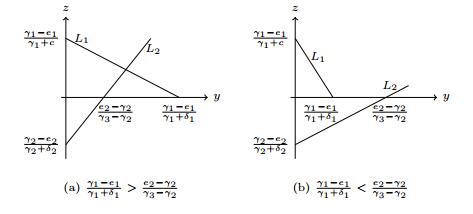
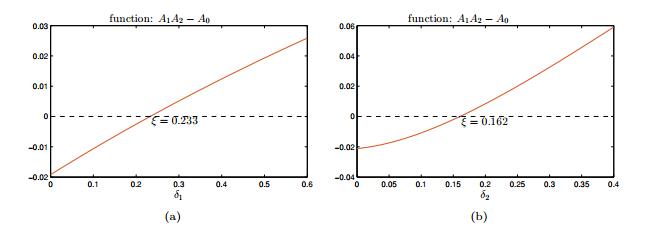
|
[1]
|
A. Atabaigi, Bifurcation and chaos in a discrete time predator-prey system of Leslie type with generalized Holling type Ⅲ functional response, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2017, 7(2), 411-426.
Google Scholar
|
|
[2]
|
P. Amarasekare, Coexistence of intraguild predators and prey in resource-rich environments, Ecol., 2008, 89(10), 2786-2797. doi: 10.1890/07-1508.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[3]
|
P. Abrams, S. Fung, Prey persistence and abundance in systems with intraguild predation and type-2 functional response, J. Theor. Biol., 2010, 264, 1033-1042. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.02.045
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[4]
|
D. Bolnick, Can intraspecific competition drive disruptive selection? an experimental test in natural populations of sticklebacks, Evol., 2004, 58(3), 608-618.
Google Scholar
|
|
[5]
|
F. Brauer, C. Castillo Chavez, Mathematical Models in Population Biology and Epidemiology (Second Edition), Springer, New York, 2012.
Google Scholar
|
|
[6]
|
G. Butler, H. Freedman, P. Waltman, Uniformly persistent systems, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 1986, 96(3), 425-430. doi: 10.1090/S0002-9939-1986-0822433-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[7]
|
S. Chow, C. Li, D. Wang, Normal Forms and Bifurcation of Planar Vector Fields, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1994.
Google Scholar
|
|
[8]
|
C. Dye, Intraspecific competition amongst larval Aedes aegypti food exploitation or chemical interference, Ecol. Entomol., 1982, 7, 39-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2311.1982.tb00642.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[9]
|
H. Freedman, P. Waltman, Persistence in models of three interacting predator-prey populations, Math. Biosci., 1984, 68(2), 213-231. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(84)90032-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[10]
|
H. Freedman, S. Ruan, M. Tang, Uniform persistence and flows near a closed positively invariant set, J. Dynam. Diff. Eqs., 1994, 6(4), 583-600. doi: 10.1007/BF02218848
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[11]
|
M. Freeze, Y. Chang, W. Feng, Analysis of dynamics in a complex food chain with ratio-dependent functional response, JAAC, 2014, 4(1), 69-87.
Google Scholar
|
|
[12]
|
C. Holling, The components of predation as revealed by a study of small mammal predation of the European Pine Sawfly, Can. Entomol., 1959, 91, 293-320. doi: 10.4039/Ent91293-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[13]
|
R. Holt, G. Polis, A theoretical framework for intraguild predation, Am. Nat., 1997, 149, 745-764. doi: 10.1086/286018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[14]
|
R. Han, B. Dai, Spatiotemporal dynamics and Hopf bifurcation in a delayed diffusive intraguild predation model with Holling Ⅱ functional response, Int. J. Bifurcat.Chaos, 2016, 26(12), 1-31.
Google Scholar
|
|
[15]
|
R. Han, B. Dai, Spatiotemporal dynamics and spatial pattern in a diffusive intraguild predation model with delay effect, Appl. Math. Comput., 2017, 312, 177-201.
Google Scholar
|
|
[16]
|
R. Han, B. Dai, L. Wang, Delay induced spatiotemporal patterns in a diffusive intraguild predation model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2018, 15(3), 595-627.
Google Scholar
|
|
[17]
|
S. Hsu, S. Ruan, T. Yang, Analysis of three species Lotka-Volterra food web models with omnivory, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2015, 426(2), 659-687.
Google Scholar
|
|
[18]
|
T. Hanse, N. Stenseth, H. Henttonen, J. Tast, Interspecific and intraspecific competition as causes of direct and delayed density dependence in a fluctuating vole population, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1999, 96, 986-991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.3.986
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[19]
|
A. Korobeinikov, Stability of ecosystem: global properties of a general predator-prey model, Math. Medic. Biol., 2009, 26, 309-321. doi: 10.1093/imammb/dqp009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[20]
|
Y. Kuznetsov, Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory (Third Edition), Springer, New York, 2004.
Google Scholar
|
|
[21]
|
Y. Kang, L. Wedekin, Dynamics of a intraguild predation model with generalist or specialist predator, J. Math. Biol., 2013, 67(5), 1227-1259. doi: 10.1007/s00285-012-0584-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[22]
|
M. Van Kleunen, M. Fischer, B. Schmid, Effects of intraspecific competition on size variation and reproductive allocation in a clonal plant, OIKOS, 2001, 94, 515-524. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2001.940313.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[23]
|
Z. Li, B. Dai, Global dynamics of delayed intraguild predation model with intraspecific competition, Int. J. Biomath., 2018, 11(8), 1-39.
Google Scholar
|
|
[24]
|
K. Mischaikow, H. Smith, H. Thieme, Asymptotically autonomous semiflows: chain recurrence and Lyapunov functions, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc., 1995, 347(5), 1669-1685. doi: 10.1090/tran/1995-347-05
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[25]
|
C. Pao, Nonlinear parabolic and elliptic equations, Plenum Press, New York and London, 1992.
Google Scholar
|
|
[26]
|
G. Polis, R. Holt, Intraguild predation: the dynamics of complex trophic interactions, Trends Ecol. Evol., 1992, 7, 151-154. doi: 10.1016/0169-5347(92)90208-S
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[27]
|
M. Peng, Z. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Liu, Hopf bifurcation analysis for a delayed predator-prey system with a prey refuge and selective harvesting, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2018, 8(3), 982-997.
Google Scholar
|
|
[28]
|
S. Ruan, Oscillations in plankton models with nutrient recycling, J. Theor. Biol., 2001, 208(1), 15-26.
Google Scholar
|
|
[29]
|
H. Shu, X. Hu, L. Wang, J. Watmough, Delay induced stability switch, multitype bistability and chaos in an intraguild predation model, J. Math. Biol., 2015, 71, 1269-1298. doi: 10.1007/s00285-015-0857-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[30]
|
A. Verdy, P. Amarasekare, Alternative stable states in communities with intraguild predation, J. Theor. Biol., 2010, 262(1), 116-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.09.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[31]
|
Y. Wang, D. DeAngelis, Stability of an intraguild predation system with mutual predation, Commun. Nonl. Sci. Numer. Simul., 2016, 33, 141-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.09.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
[32]
|
Y. Wang, W. Jiang, Bifurcations in a delayed differential-algebraic plankton economic system, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2017, 7(4), 1431-1447.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: