| Citation: | Jiandong Zhao, Tonghua Zhang. DYNAMICS OF TWO PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH POWER LAW RELATION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2023, 13(1): 233-248. doi: 10.11948/20220026 |
DYNAMICS OF TWO PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH POWER LAW RELATION
-
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a predator-prey model with power law relation based on the model in [Hatton et al, The predator-prey power law: Biomass scaling across terrestrial and aquatic biomes, Science 349(2015), aac6284], and analyze the global dynamics of both models. We obtain that Hatton's model is persistent for power less than 1, and there exists a separatrix near the origin such that solutions of the model above it are driven to the origin and the ones below it are far away from origin for power greater than 1. However, our model is persistent for all power and has the same singularity as that of Hatton's model at the origin for power greater than 1, which indicate that the prey and predator will coexist or extinct eventually. Furthermore, in our model, the prey will be stable at its carrying capacity and the predator will be extinct for power less than 1, and the prey will be stable at its carrying capacity or both the prey and predator will be extinct for power greater than 1.
-
Keywords:
- Predator-prey model /
- power law /
- equilibrium /
- stability /
- Hopf bifurcation
-

-
References
[1] V. Ajraldi, M. Pittavino and E. Venturino, Modeling herd behavior in population systems, Nonlinear Anal. : Real World Appl., 2011, 12(4), 2319–2338. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2011.02.002 [2] R. Arditi and L. R. Ginzburg, Coupling in predator-prey dynamics: ratio-dependence, J. Theor. Biol., 1989, 139(3), 311–326. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5193(89)80211-5 [3] F. J. Ayala, M. E. Gilpin and J. G. Ehrenfeld, Competition between species: Theoretical models and experimental tests, Theor. Popul. Biol., 1973, 4(3), 331–356. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(73)90014-2 [4] F. S. Berezovskaya, A. S. Novozhilov and G. P. Karev, Population models with singular equilibrium, Math. Biosci., 2007, 208(1), 270–299. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.10.006 [5] A. A. Berryman, The origins and evolution of predator-prey theory, Ecology, 1992, 73(5), 1530–1535. doi: 10.2307/1940005 [6] K. Boyadzhiev and V. H. Moll, The integrals in Gradshteyn and Ryzhik, Part 26: The exponential integral, SCIENTIA Series A: Mathematical Sciences, 2015, 26, 19–30. [7] F. Brauer and C. Castillo-Chavez, Mathematical Models in Population Biology and Epidemiology, Springer, New York, 2012. [8] P. A. Braza, Predator-prey dynamics with square root functional responses, Nonlinear Anal. : Real World Appl., 2012, 13(4), 1837–1843. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2011.12.014 [9] J. Chattopadhyay, S. Chatterjee and E. Venturino, Patchy agglomeration as a transition from monospecies to recurrent plankton blooms, J. Theor. Biol., 2008, 253(2), 289–295. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.03.008 [10] L. Chen and F. Chen, Dynamical analysis of a predator-prey model with square root functional response, J. Nonlinear Funct. Anal., 2015, Article ID 8. [11] L. Chen, F. Chen and L. Chen, Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response incorporating a constant prey refuge, Nonlinear Anal. : Real World Appl., 2010, 11(1), 246–252. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.10.056 [12] P. Feng, Analysis of a delayed predator-prey model with ratio-dependent functional response and quadratic harvesting, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 44(1–2), 251–262. doi: 10.1007/s12190-013-0691-z [13] M. E. Gilpin and F. J. Ayala, Global models of growth and competition, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1973, 70(12), 3590–3593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3590 [14] I. A. Hatton, K. S. McCann, J. M. Fryxell, T. J. Davies, M. S merlak, A. R. E. Sinclair and M. Loreau, The predator-prey power law: Biomass scaling across terrenstrial and aquatic biomes, Science, 2015, 349(6252), aac6284. doi: 10.1126/science.aac6284 [15] C. S. Holling, The functional response of invertebrate predators to prey density, Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 1966, 98(48), 5–86. [16] S. B. Hsu, Ordinary Differential Equations with Applications (2nd Edition), World Scientific, Singapore, 2013. [17] S. B. Hsu and T. Huang, Global stability for a class of predator-prey systems, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1995, 55(3), 763–783. doi: 10.1137/S0036139993253201 [18] S. B. Hsu, T. Huang and Y. Kuang, Global analysis of the Michaelis-Menten-type ratio-dependent predator-prey system, J. Math. Biol., 2001, 42(6), 489–506. doi: 10.1007/s002850100079 [19] C. Ji, D. Jiang and Y. Zhao, Qualitative analysis of stochastic ratio-dependent predator-prey systems, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2019, 9(2), 475–500. [20] C. Jost, O. Arino and R. Arditi, About deterministic extinction in ratio-dependent predator-prey models, Bull. Math. Biol., 1999, 61(1), 19–32. doi: 10.1006/bulm.1998.0072 [21] Y. Kuang and E. Beretta, Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system, J. Math. Biol., 1998, 36(4), 389–406. doi: 10.1007/s002850050105 [22] Q. Liu, D. Jiang, T. Hayat and A. Alsaedi, Dynamics of a stochastic predator-prey model with distributed delay and Markovian switching, Phys. A, 2019, 527, 121264. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.121264 [23] X. Liu and Y. Lou, Global dynamics of a predator-prey model, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2010, 371(1), 323–340. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.05.037 [24] A. J. Lotka, Contribution to the theory of periodic reaction, J. Phys. Chem., 1910, 14(3), 271–274. doi: 10.1021/j150111a004 [25] J. Lv, X. Zou and Y. Li, Dynamical properties of a stochastic predator-prey model with functional response, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2020, 10(4), 1242–1255. [26] X. Meng, R. Liu, L. Liu and T. Zhang, Evolutionary analysis of a predator-prey community under natural and artificial selections, Appl. Math. Model., 2015, 39(2), 574–585. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2014.06.016 [27] J. D. Murray, Mathematical Biology Ⅰ: An Introduction (Third Edition), Springer, New York, 2002. [28] C. E. H. Pimentel, P. M. Rodriguez and L. A. Valencia, A note on a stage-specific predator-prey stochastic model, Phys. A, 2020, 553, 124575. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2020.124575 [29] H. Qi and X. Meng, Threshold behavior of a stochastic predator-prey system with prey refuge and fear effect, Appl. Math. Lett., 2021, 113, 106846. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2020.106846 [30] E. Sáez and E. González-Olivares, Dynamics of a predator-prey model, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1999, 59(5), 1867–1878. doi: 10.1137/S0036139997318457 [31] K. Sun, T. Zhang and Y. Tian, Theoretical study and control optimization of an integrated pest management predator-prey model with power growth rate, Math. Biosci., 2016, 279, 13–26. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2016.06.006 [32] X. Tang, Y. Song and T. Zhang, Turing-Hopf bifurcation analysis of a predator-prey model with herd behavior and cross-diffusion, Nonlinear Dyn., 2016, 86(1), 73–89. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2873-3 [33] E. Venturino and S. Petrovskii, Spatiotemporal behavior of a prey-predator system with a group defense for prey, Ecol. Complex., 2013, 14, 37–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2013.01.004 [34] C. Viberti and E. Venturino, An ecosystem with Holling type Ⅱ response and predators' genetic variability, Math. Model. Anal., 2014, 19(3), 371–394. doi: 10.3846/13926292.2014.925518 [35] V. Volterra, Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero d'individui in specie animali conviventi, Memorie Royal Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei, 1926, 2, 31–113. [36] D. Xiao and L. S. Jennings, Bifurcations of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with constant rate harvesting, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2005, 65(3), 737–753. doi: 10.1137/S0036139903428719 [37] D. Xiao and S. Ruan, Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system, J. Math. Biol., 2001, 43(3), 268–290. doi: 10.1007/s002850100097 [38] M. Xiao and J. Cao, Hopf bifurcation and non-hyperbolic equilibrium in a ratio-dependent predator-prey model with linear harvesting rate: Analysis and computation, Math. Comput. Model., 2009, 50(3–4), 360–379. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2009.04.018 [39] C. Xu, S. Yuan amd T. Zhang, Global dynamics of a predator-prey model with defence mechanism for prey, Appl. Math. Lett., 2016, 62, 42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2016.06.013 [40] Y. Yang and T. Zhang, Dynamic analysis of a modified stochastic predator-prey system with general ratio-dependent functional response, Bull. Korean Math. Soc., 2016, 53(1), 103–117. doi: 10.4134/BKMS.2016.53.1.103 [41] S. Zhang, T. Zhang and S. Yuan, Dynamics of a stochastic predator-prey model with habitat complexity and prey aggregation, Ecol. Complex., 2021, 45, 100889. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2020.100889 [42] T. Zhang, W. Ma, X. Meng and T. Zhang, Periodic solution of a prey-predator model with nonlinear state feedback control, Appl. Math. Comput., 2015, 266, 95–107. [43] T. Zhang, Y. Xing, H. Zang and M. Han, Spatio-temporal dynamics of a reaction-diffusion system for a predator-prey model with hyperbolic mortality, Nonlinear Dyn., 2014, 78(1), 265–277. doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1438-6 -
-
-
Figure 1.
Dynamical behavior of (1.2) for
$ k=0.75 $ $ r=0.8 $ $ g=0.5 $ $ m=1 $ -
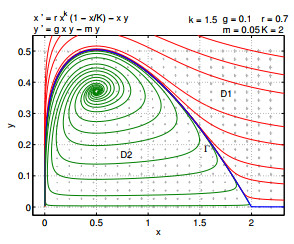
Figure 2.
Dynamical behavior of (1.4) with
$ k=1.5 $ $ r=0.7 $ $ K=2 $ $ g=0.1 $ $ m=0.05 $ -
Figure 3.
Dynamical behavior of (1.2) for
$ k=1.5 $ -
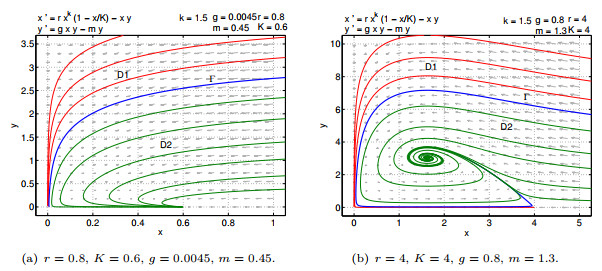
Figure 4.
Dynamical behavior of (1.4) for
$ k=0.75 $ -
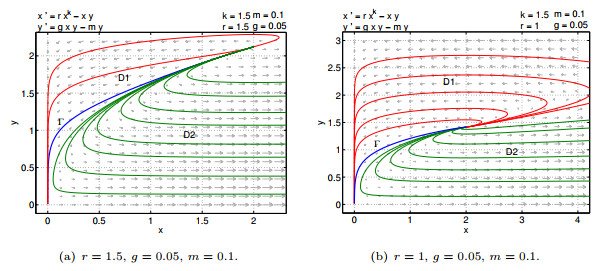
Figure 5.
Dynamical behavior of (1.4) for
$ k=1.5 $





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: