| Citation: | Jie Bai, Chayu Yang, Xueying Wang, Jin Wang. MODELING THE WITHIN-HOST DYNAMICS OF CHOLERA: BACTERIAL-VIRAL-IMMUNE INTERACTION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2021, 11(2): 690-710. doi: 10.11948/20190241 |
MODELING THE WITHIN-HOST DYNAMICS OF CHOLERA: BACTERIAL-VIRAL-IMMUNE INTERACTION
-
Abstract
We present a mathematical model to investigate the within-host dynamics of cholera.We formulate a system of nonlinear differential equations to describe the evolution and interplay of the pathogenic bacteria at different stages, the viruses, and the immune response inside the human body.Our analysis shows that the basic reproduction number of this model is determined collectively by the bacterial, viral and immune reproduction numbers, and that the bacterial-viral-immune interaction shapes the complex dynamics of cholera infection within a human host.
-
Keywords:
- Cholera modeling /
- within-host dynamics /
- equilibrium analysis
-

-
References
[1] M. Ali, A. R. Nelson, A. L. Lopez, and D. A. Sack, Updated global burden of cholera in endemic countries, PLoS. Negl. Trop. Dis., 2015, 9(6), e0003832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003832 [2] A. Bechette, T. Stojsavljevic, M. Tessmer et al., Mathematical modeling of bacteria-virus interactions in Lake Michigan incorporating phosphorus content, J. Great Lakes Res., 2013, 39, 646-654. doi: 10.1016/j.jglr.2013.09.003 [3] B. Boldin and O. Diekmann, Superinfections can induce evolutionarily stable coexistence of pathogens, J. Math. Biol., 2008, 56, 635-672. doi: 10.1007/s00285-007-0135-1 [4] V. Capasso and S. L. Paveri-Fontana, A mathematical model for the 1973 cholera epidemic in the European Mediterranean region, Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique, 1979, 27(2), 121-132. [5] C. Castillo-Chavez and B. Song, Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2004, 1(2), 361-404. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2004.1.361 [6] X. Cen, Z. Feng and Y. Zhao, Emerging disease dynamics in a model coupling within- host and between-host systems, J. Theor. Biol., 2014, 361, 141-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.07.030 [7] D. Coombs, M. A. Gilchrist and C. L. Ball, Evaluating the importance of within-and between-host selection pressures on the evolution of chronic pathogens, Theor. Popul. Biol., 2007, 72, 576-591. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2007.08.005 [8] Z. Feng, J. Velasco-Hernandez and B. Tapia-Santos, A mathematical model for coupling within-host and between-host dynamics in an environmentally-driven infectious disease, Math. Biosci., 2013, 241(1), 49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2012.09.004 [9] Z. Feng, J. Velasco-Hernandez, B. Tapia-Santos et al., A model for coupling within-host and between-host dynamics in an infectious disease, Nonlinear Dyn., 2012, 68, 401-411. doi: 10.1007/s11071-011-0291-0 [10] W. Garira, D. Mathebula and R. Netshikweta, A mathematical modelling framework for linked within-host and between-host dynamics for infections with free-living pathogens in the environment, Math. Biosci., 2014, 256, 58-78. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2014.08.004 [11] M. A. Gilchrist and D. Coombs, Evolution of virulence: Interdependence, constraints, and selection using nested models, Theor. Popul. Biol., 2006, 69, 145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2005.07.002 [12] M. A. Gilchrist and A. Sasaki, Modeling host-parasite coevolution: a nested approach based on mechanistic models, J. Theor. Biol., 2002, 218, 289-308. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2002.3076 [13] D. M. Hartley, J. G. Morris and D. L. Smith, Hyperinfectivity: a critical element in the ability of V. cholerae to cause epidemics? PLoS Med., 2006, 3, 0063-0069. [14] D. He, X. Wang, D. Gao, and J. Wang, Modeling the 2016-2017 Yemen cholera outbreak with the impact of limited medical resources, J. Theor. Biol., 2018, 451, 80-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.04.041 [15] H. W. Hethcote, The mathematics of infectious diseases, SIAM Rev., 2000, 42(4), 599-653. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500371907 [16] M. Martcheva, S. Lenhart, S. Eda, D. Klinkenberg et al., An immuno-epidemiological model for Johne's disease in cattle, Vet. Res., 2015, 46(1), 69. doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0190-3 [17] M. Martcheva and X. Li, Linking immunological and epidemiological dynamics of HIV: the case of super-infection, J. Biol. Dyn., 2013, 7(1), 161-182. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2013.820358 [18] N. Mideo, S. Alizon and T. Day, Linking within- and between-host disease dynamics in the evolutionary epidemiology of infectious diseases, Trends Ecol. Evol., 2008, 23(9), 511-517. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2008.05.009 [19] Z. Mukandavire, S. Liao, J. Wang et al., Estimating the reproductive numbers for the 2008-2009 cholera outbreaks in Zimbabwe, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2011, 108(21), 8767-8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019712108 [20] E. J. Nelson, J. B. Harris, J. G. Morris et al., Cholera transmission: the host, pathogen and bacteriophage dynamics, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2009, 7(10), 693-702. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2204 [21] D. Posny and J. Wang, Modelling cholera in periodic environments, J. Biol. Dyn., 2014, 8(1), 1-19. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2014.896482 [22] M. Shen, Y. Xiao and L. Rong, Global stability of an infection-age structured HIV-1 model linking within-host and between-host dynamics, Math. Biosci., 2015, 263, 37-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2015.02.003 [23] Z. Shuai and P. van den Driessche, Global stability of infectious disease models using Lyapunov functions, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2013, 73(4), 1513-1532. doi: 10.1137/120876642 [24] H. L. Smith and R. T. Trevino, Bacteriophage infection dynamics: multiple host binding sites, Math. Model. Nat. Phenom., 2009, 4(6), 109-134. doi: 10.1051/mmnp/20094604 [25] J. Tian and J. Wang, Global stability for cholera epidemic models, Math. Biosci., 2011, 232(1), 31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2011.04.001 [26] J. H. Tien and D. J. D. Earn, Multiple transmission pathways and disease dynamics in a waterborne pathogen model, Bull. Math. Biol., 2010, 72(6), 1506-1533. doi: 10.1007/s11538-010-9507-6 [27] A. R. Tuite, J. H. Tien, M. C. Eisenberg et al., Cholera epidemic in Haiti, 2010: Using a transmission model to explain spatial spread of disease and identify optimal control interventions, Ann. Intern. Med., 2011, 154(9), 593-601. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-9-201105030-00334 [28] P. van den Driessche and J. Watmough, Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission, Math. Biosci., 2002, 180, 29-48. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00108-6 [29] M. K. Waldor and J. J. Mekalanos, Lysogenic conversion by a filamentous phage encoding cholera toxin, Science, 1996, 272(5270), 1910-1914. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5270.1910 [30] J. Wang and S. Liao, A generalized cholera model and epidemic-endemic analysis, J. Biol. Dyn., 2012, 6(2), 568-589. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2012.658089 [31] X. Wang and J. Wang, Analysis of cholera epidemics with bacterial growth and spatial movement, J. Biol. Dyn., 2015, 9(1), 233-261. [32] X. Wang, D. Gao and J. Wang, Influence of human behavior on cholera dynamics, Math. Biosci., 2015, 267, 41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2015.06.009 [33] X. Wang and J. Wang, Disease dynamics in a coupled cholera model linking within-host and between-host interactions, J. Biol. Dyn., 2017, 11(S1), 238-262. [34] X. Wang and J. Wang, Modeling the within-host dynamics of cholera: bacterial-viral interaction, J. Biol. Dyn., 2017, 11(S2), 484-501. [35] C. Yang, D. Posny, F. Bao, and J. Wang, A multi-scale cholera model linking between-host and within-host dynamics, Int. J. Biomath., 2018, 11(3), 1850034. doi: 10.1142/S1793524518500341 -
-
-
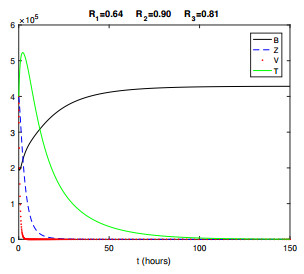
Figure 1. A typical scenario showing that solutions of system (2.1) converge to the trivial equilibrium
$ x_0 $ when$ \mathcal{R}_0 < 1 $ . In this particular case$ \mathcal{R}_0 = 0.9 $ and$ x_0 = (428571, 0, 0, 0) $ . -
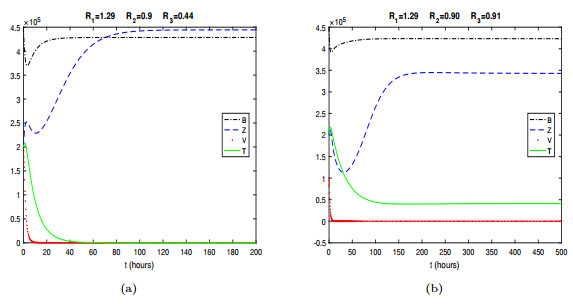
Figure 2. Two typical scenarios for the solutions of system (2.1) when
$ \mathcal{R}_0 = R_1 > 1 $ : (a) Solutions converge to the virus-free, immunity-free equilibrium$ x_{01} $ , where$ x_{01} = (428571, 444444, 0, 0) $ in this particular case; (b) Solutions converge to the virus-free equilibrium$ x_1 $ , where$ x_1 = (423353, 342820, 0, 40939) $ in this particular case. -
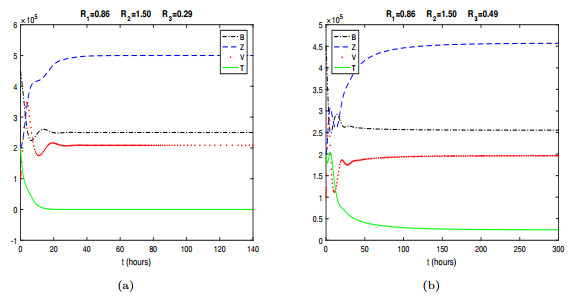
Figure 3. Two typical scenarios for the solutions of system (2.1) when
$ \mathcal{R}_0 = R_2 > 1 $ : (a) Solutions converge to the immunity-free equilibrium$ x_2 $ , where$ x_2 = (250000, 500000, 208333, 0) $ in this particular case; (b) Solutions converge to the positive interior equilibrium$ x_* $ , where$ x_* = (255392, 457221, 196223, 24052) $ in this particular case. -
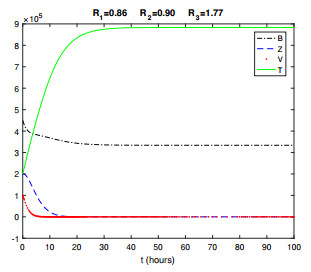
Figure 4. A typical scenario showing that solutions of system (2.1) converge to the equilibrium
$ x_3 $ free of human vibrios and viruses, when$ \mathcal{R}_0 = R_3 > 1 $ . In this particular case$ x_3 = (333819, 0, 0, 883388) $ .




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: