| Citation: | Yiwei Wang, Lijun Zhang, Mingji Zhang. STUDIES ON INDIVIDUAL FLUXES VIA POISSON-NERNST-PLANCK MODELS WITH SMALL PERMANENT CHARGES AND PARTIAL ELECTRONEUTRALITY CONDITIONS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(1): 87-105. doi: 10.11948/20210045 |
STUDIES ON INDIVIDUAL FLUXES VIA POISSON-NERNST-PLANCK MODELS WITH SMALL PERMANENT CHARGES AND PARTIAL ELECTRONEUTRALITY CONDITIONS
-
Abstract
We study a one-dimensional Poisson-Nernst-Planck system for ionic flows through membrane channels with two ion species, one positively charged and one negatively charged. Nonzero but small permanent charges are included. The cross-section area of the channel is included in the system, which provides certain information of the geometry of the three-dimensional channel. This is crucial for our analysis. Of particular interest is to analyze the qualitative properties of the individual fluxes with partial neutral boundary conditions, which provides complementary insights and better understanding of the ionic flow properties. Our study shows that the individual fluxes depend sensitively on multiple system parameters such as permanent charges, channel geometry, boundary conditions (concentrations and potentials) and boundary layers caused by the violation of electroneutrality conditions. Numerical simulations are further performed to provide a more intuitive illustration of our analytical results, and it turns out that numerical results are consistent with our analytical ones.
-
Keywords:
- PNP, permanent charges /
- channel geometry /
- individual fluxes /
- boundary layers
-

-
References
[1] N. Abaid, R. S. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Asymptotic expansions of I-V relations via a Poisson-Nernst-Planck system, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2008, 7, 1507-1526. doi: 10.1137/070691322 [2] R. Aitbayev, P. W. Bates, H. Lu, L. Zhang and M. Zhang, Mathematical studies of Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: dynamics of ionic flows without electroneutrality conditions, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2019, 362, 510-527. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2018.10.037 [3] V. Barcilon, Ion flow through narrow membrane channels: Part I, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1992, 52, 1391-14041. doi: 10.1137/0152080 [4] V. Barcilon, D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Ion flow through narrow membrane channels: Part Ⅱ, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1992, 52, 1405-1425. doi: 10.1137/0152081 [5] V. Barcilon, D. Chen, R. S. Eisenberg and J. W. Jerome, Qualitative properties of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: Perturbation and simulation study, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1997, 57, 631-648. doi: 10.1137/S0036139995312149 [6] P. W. Bates, J. Chen and M. Zhang, Dynamics of ionic flows via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with local hard-sphere potentials: Competition between cations, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2020, 17, 3736-3766. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020210 [7] P. W. Bates, Y. Jia, G. Lin, H. Lu and M. Zhang, Individual flux study via steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: Effects from boundary conditions, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2017, 16, 410-430. doi: 10.1137/16M1071523 [8] P. W. Bates, W. Liu, H. Lu and M. Zhang, Ion size and valence effects on ionic flows via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems, Commun. Math. Sci., 2017, 15, 881-901. doi: 10.4310/CMS.2017.v15.n4.a1 [9] P. W. Bates, Z. Wen and M. Zhang, Small permanent charge effects on individual fluxes via Poisson-Nernst-Planck models with multiple cations, J. Nonlinear Sci., 2021, 31, 1-62. doi: 10.1007/s00332-020-09667-0 [10] D. Boda, D. Busath, B. Eisenberg, D. Henderson and W. Nonner, Monte Carlo simulations of ion selectivity in a biological Na+ channel: Charge-space competition, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2002, 4, 5154-5160. doi: 10.1039/B203686J [11] J. Cartailler, Z. Schuss and D. Holcman, Analysis of the Poisson-Nernst-Planck equation in a ball for modeling the voltage-current relation in neurobiological microdomains, Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 2017, 339, 39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2016.09.001 [12] D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Charges, currents and potentials in ionic channels of one conformation, Biophys. J., 1993, 64, 1405-1421. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81507-8 [13] J. Chen, Y. Wan, L. Zhang and M. Zhang, Mathematical analysis of Poisson-Nernst-Planck models with permanent charges and boundary layers: Studies on individual fluxes, Nonlinearity, 2021, 34, 3879-3906. doi: 10.1088/1361-6544/abf33a [14] J. Ding, Z. Wang and S. Zhou, Positivity preserving finite difference methods for Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations with steric interaction: application to slit-shaped nanopore conductance, J. Comput. Phys., 2019, 397, Article ID: 108864. [15] B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion channels with permanent charges, SIAM J. Math. Anal., 2007, 38, 1932-1966. doi: 10.1137/060657480 [16] B. Eisenberg, W. Liu and H. Xu, Reversal charge and reversal potential: case studies via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck models, Nonlinearity, 2015, 28, 103-128. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/28/1/103 [17] N. Gavish, Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations with steric effects- non-convexity and multiple stationary solutions, Phys. D: nonlinear Phenomena, 2018, 368, 50-65. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2017.12.008 [18] N. Gavish, Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations with high-order steric effects, Phys. D: nonlinear Phenomena, 2020, 411, Article ID: 132536. [19] D. Gillespie, A singular perturbation analysis of the Poisson-Nernst-Planck system: Applications to Ionic Channels, Ph. D Dissertation, Rush University at Chicago, 1999. [20] D. Gillespie and R. S. Eisenberg, Modified Donnan potentials for ion transport through biological ion channels, Phys. Rev. E, 2001, 63, Article ID: 061902. [21] D. Gillespie, W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Coupling Poisson–Nernst–Planck and density functional theory to calculate ion flux, J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 2002, 14, 12129-12145. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/14/46/317 [22] D. Gillespie, W. Nonner and R. S. Eisenberg, Density functional theory of charged, hard-sphere fluids, Phys. Rev. E, 2003, 68, Article ID: 0313503. [23] A. L. Hodgkin and R. D. Keynes, The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre, J. Physiol., 1955, 128, 61-88. [24] U. Hollerbach, D. Chen and R. S. Eisenberg, Two- and three-dimensional Poisson-Nernst-Planck simulations of current flow through Gramicidian-A, J. Comput. Sci., 2002, 16, 373-409. [25] Y. Hyon, B. Eisenberg and C. Liu, A mathematical model for the hard sphere repulsion in ionic solutions, Commun. Math. Sci., 2010, 9, 459-475. [26] Y. Hyon, J. Fonseca, B. Eisenberg and C. Liu, Energy variational approach to study charge inversion (layering) near charged walls, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2012, 17, 2725-2743. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2012.17.2725 [27] Y. Hyon, C. Liu and B. Eisenberg, PNP equations with steric effects: a model of ion flow through channels, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, 116, 11422-11441. doi: 10.1021/jp305273n [28] S. Ji, B. Eisenberg and W. Liu, Flux ratios and channel structures, J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2019, 31, 1141-1183. doi: 10.1007/s10884-017-9607-1 [29] S. Ji and W. Liu, Poisson-Nernst-Planck Systems for Ion Flow with Density Functional Theory for Hard-Sphere Potential: I-V relations and Critical Potentials. Part I: Analysis, J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2012, 24, 955-983. doi: 10.1007/s10884-012-9277-y [30] S. Ji, W. Liu and M. Zhang, Effects of (small) permanent charges and channel geometry on ionic flows via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck models, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2015, 75, 114-135. doi: 10.1137/140992527 [31] Y. Jia, W. Liu and M. Zhang, Qualitative properties of ionic flows via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with Bikerman's local hard-sphere potential: Ion size effects, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2016, 21, 1775-1802. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2016022 [32] J. Kierzenka and L. Shampine, A BVP Solver Based on Residual Control and the Matlab PSE. ACM Trans. Math. Software, 2001, 27, 299-316. doi: 10.1145/502800.502801 [33] M. S. Kilic, M. Z. Bazant and A. Ajdari, Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. Ⅱ. Modified Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations, Phys. Rev. E, 2007, 75, Article ID: 021503. [34] M. G. Kurnikova, R. D. Coalson, P. Graf and A. Nitzan, A Lattice Relaxation Algorithm for 3D Poisson-Nernst-Planck Theory with Application to Ion Transport Through the Gramicidin A Channel, Biophys. J., 1999, 76, 642-656. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77232-2 [35] G. Lin, W. Liu, Y. Yi and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with density functional theory for local hard-sphere potential, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2013, 12, 1613-1648. doi: 10.1137/120904056 [36] W. Liu, Geometric singular perturbation approach to steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2005, 65, 754-766. doi: 10.1137/S0036139903420931 [37] W. Liu, One-dimensional steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion channels with multiple ion species, J. Differ. Equations, 2009, 246, 428-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2008.09.010 [38] J. Liu and B. Eisenberg, Molecular Mean-Field Theory of Ionic Solutions: a Poisson-Nernst-Planck-Bikerman Model, Entropy, 2020, 22, 550. doi: 10.3390/e22050550 [39] W. Liu, X. Tu and M. Zhang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for ion flow with density functional theory for hard-sphere potential: I-V relations and critical potentials. Part Ⅱ: Numerics, J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2012, 24, 985-1004. doi: 10.1007/s10884-012-9278-x [40] W. Liu and B. Wang, Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems for narrow tubular-like membrane channels, J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2010, 22, 413-437. doi: 10.1007/s10884-010-9186-x [41] W. Liu and H. Xu, A complete analysis of a classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck model for ionic flow, J. Differ. Equations, 2015, 258, 1192-1228. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.10.015 [42] H. Lu, J. Li, J. Shackelford, J. Vorenberg and M. Zhang, Ion size effects on individual fluxes via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with Bikerman's local hard-sphere potential: Analysis without electroneutrality boundary conditions, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2018, 23, 1623-1643. [43] W. Nooner and R. S. Eisenberg, Ion permeation and glutamate residues linked by Poisson-Nernst-Planck theory in L-type Calcium channels, Biophys. J., 1998, 75, 1287-1305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)74048-2 [44] J. K. Park and J. W. Jerome, Qualitative properties of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems: Mathematical study, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1997, 57, 609-630. doi: 10.1137/S0036139995279809 [45] S. Sahu and M. Zwolak, Golden aspect ration for ion transport simulation in nanopores, Phys. Rev. E, 2018, 98, Article ID: 012404. [46] Z. Schuss, B. Nadler and R. S. Eisenberg, Derivation of Poisson and Nernst-Planck equations in a bath and channel from a molecular model, Phys. Rev. E, 2001, 64, 1-14. [47] A. Singer and J. Norbury, A Poisson-Nernst-Planck model for biological ion channels-an asymptotic analysis in a three-dimensional narrow funnel, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2009, 70, 949-968. doi: 10.1137/070687037 [48] A. Singer, D. Gillespie, J. Norbury and R. S. Eisenberg, Singular perturbation analysis of the steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck system: applications to ion channels, European J. Appl. Math., 2008, 19, 541-560. doi: 10.1017/S0956792508007596 [49] M. Valisk$\acute{o}$, B. Matejczyk, Z. Hat$\acute{o}$, T. Krist$\acute{o}$f, E. M$\acute{a}$dai, D. Fertig, D. Gillespie and D. Boda, Multiscale analysis of the effect of surface charge pattern on a nanopore's rectification and selectivity properties: From all-atom model to Poisson-Nernst-Planck, J. Chem. Phys., 2019, 150, Article ID: 144703. [50] X. Wang, D. He, J. Wylie and H. Huang, Singular perturbation solutions of steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems, Phys. Rev. E, 2014, 89, 1-14. [51] Z. Wen, P. W. Bates and M. Zhang, Effects on I-V relations from small permanent charge and channel geometry via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations with multiple cations, Nonlinearity, 2021, 34, 4464-4502. doi: 10.1088/1361-6544/abfae8 [52] Z. Wen, L. Zhang and M. Zhang, Dynamics of classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with multiple cations and boundary layers, J. Dyn. Diff. Equat., 2021, 33, 211-234. doi: 10.1007/s10884-020-09861-4 [53] M. Zhang, Asymptotic expansions and numerical simulations of I-V relations via a steady-state Poisson-Nernst-Planck system, Rocky MT. J. Math., 2015, 45, 1681-1708. [54] M. Zhang, Boundary layer effects on ionic flows via classical Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems, Comput. Math. Biophys., 2018, 6, 14-27. doi: 10.1515/cmb-2018-0002 [55] M. Zhang, Competition between cations via Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems with nonzero but small permanent charges, Membranes, 2021, 11, 236. doi: 10.3390/membranes11040236 -
-
-
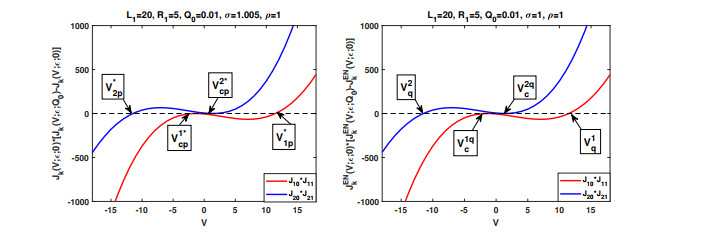
Figure 1. Identification of critical potentials
$ V_{kp}^* $ with boundary layers and$ V_q^k $ under electroneutrality boundary conditions for small$ \varepsilon = 0.01 $ . We also point out that$ V_{cp}^{k*} $ is a common zero with$ J_k(V;0) $ with boundary layers while$ V_{c}^{kq} $ is a common zero with$ J_k(V;0) $ under electroneutrality boundary conditions, see Figure 2. One can easily see that for$ (\sigma, \rho) = (1.005, 1.0), $ $ V_q^1-V_{1p}^* = 0.024618 $ and$ V_q^2-V_{2p}^* = -0.022409 $ . This shows clearly the important role played by the boundary layers in the study of ionic flows through membrane channels. -
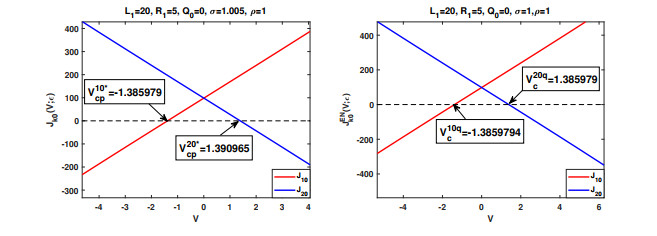
Figure 2. Numerical simulations to
$ J_{k0}(V) $ for both the case with boundary layers and the one under electroneutrality boundary conditions by$ J_k(V;0) $ with$ \varepsilon = 0.01 $ . Critical potentials$ V_{cp}^{k0*} $ and$ V_c^{k0q} $ are identified. From Figure 1, one can see that$ V_{cp}^{k0*} $ is close to$ V_{cp}^{k*} $ , and$ V_c^{k0q} $ is close to$ V_c^{kq} $ (see the discussion in (ⅲ) for more details). -
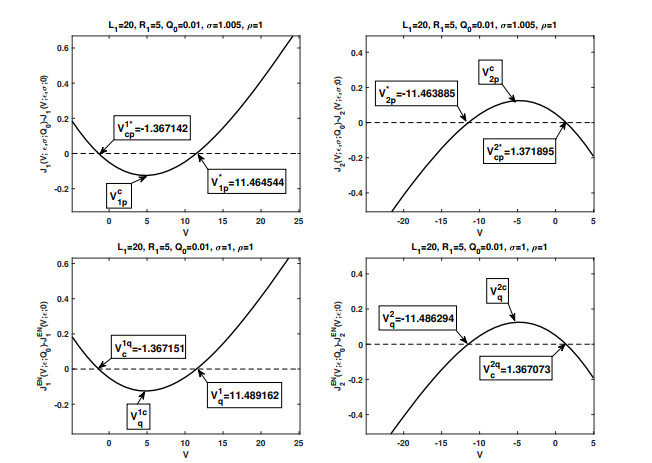
Figure 3. Orders of the critical potentials
$ V_{kp}^* $ with boundary layers and$ V_q^{k} $ under electroneutrality boundary conditions, respectively for$ k = 1, 2 $ with$ \varepsilon = 0.01 $ . Under our set-up, the result with boundary layers is consistent with statement (ⅱ) in Theorem 3.1, and the one under electroneutrality boundary conditions is also consistent with statement (ⅱ) in Theorem 4.8 of [30] with$ \beta_1 $ replaced by$ \beta_2 $ under current set-up.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: