| Citation: | Songnan Liu, Xiaojie Xu, Zhangyi Dong. LONG-TIME BEHAVIOR OF STOCHASTIC STAGED PROGRESSION EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH HYBRID SWITCHING FOR THE TRANSMISSION OF HIV[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(1): 125-152. doi: 10.11948/20210085 |
LONG-TIME BEHAVIOR OF STOCHASTIC STAGED PROGRESSION EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH HYBRID SWITCHING FOR THE TRANSMISSION OF HIV
-
Abstract
In this paper, one stochastic hybrid switching SP (staged progression) model for the transmission of HIV is proposed and investigated. The system disturbed by both white and telegraph noises, sufficient conditions for positive recurrence and the existence of an ergodic stationary distribution to the solutions are established. The existence of stationary distribution implies stochastic weak stability to some extent. Furthermore, sufficient conditions for extinction of disease are established. At last, some examples and simulations are provided to illustrate our results.
-

-
References
[1] T. Caraballo, M. E. Fatini and M. E. Khalifi, Analysis of a stochastic distributed delay epidemic model with relapse and gamma distribution kernel, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2020, 133, 109-643. [2] Y. Cao, L. Qin, L. Zhang, J. Safrit and D. D. Ho, Virologic and immunologic characterization of long-term survivors of HIV type 1 infection, N. Engl. J. Med., 1995, 332, 201. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199501263320401 [3] R. Durrett, Stochastic spatial models, SIAM Rev., 1999, 41, 677-718. doi: 10.1137/S0036144599354707 [4] N. Du, R. Kon, K. Sato and Y. Takeuchi, Dynamical behavior of Lotka-Volterra competition systems: Non-autonomous bistable case and the effect of telegraph noise, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2004, 170, 399-422. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2004.02.001 [5] A. Gray, D. Greenhalgh, L. Hu, X. Mao and J. Pan, A stochastic differential equation SIS epidemic model, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2011, 71, 876-902. doi: 10.1137/10081856X [6] J. Hyman, J. Li and E. Stanley, Modeling the impact of random screening and contact tracing in reducing the spread of HIV, Mathematical Biosciences, 2003, 181, 17-54. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00128-1 [7] R. Z. Has'minskii, Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations, Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 1980. [8] D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43, 525-546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 [9] J. Hyman and J. Li, An intuitive formulation for the reproductive number for the spread of diseases in heterogeneous populations, Math. Biosci., 2000, 167, 65-86. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(00)00025-0 [10] J. M. Hyman, J. Li and E. A. Stanley, The differential infectivity and staged progression models for the transmission of HIV, Math. Biosci., 1999, 155, 77. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(98)10057-3 [11] J. M. Hyman, J. Li and E. A. Stanley, The initialization and sensitivity of multigroup models for the transmission of HIV, J. Theor. Biol., 2001, 208, 227. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2000.2214 [12] A. Ida, S. Oharu and Y. Oharu, A mathematical approach to HIV infection dynamics, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2007, 204, 172-186. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2006.04.057 [13] J. A. Jacquez, J. S. Koopman, C. P. Simon and I. M. Longini, Role of the primary infection in epidemics of HIV infection in gay cohorts, J. AIDS., 1994, 7, 1169. [14] J. A. Jacquez, C. P. Simon and J. Koopman, Core groups and the R0s for subgroups in heterogeneous SIS and SI models, in: Mollison (Ed. ), Epidemic Models: Their Structure and Relation to Data, Cambridge University, Cambridge, 1995, 279. [15] J. Y. Kim, J. H. Ko, Y. Kim, Y. J. Kim and B. S. Chin, Viral load kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 infection in first two patients in Korea, J. Korean Med. Sci., 2020, 35, e86. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e86 [16] S. Liu, X. Xu, D. Jiang, T. Hayatb and B. Ahmadb, Stationary distribution and extinction of the DS-I-A model disease with periodic parameter function and Markovian switching, Appl. Math. Comput., 2017, 311, 66-84. [17] S. Liu, D. Jiang, X. Xu, T. Hayatb and B. Ahmadb, Dynamics of hybrid switching DS-I-A epidemic model, Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1). [18] Q. Liu, D. Jiang, N. Shi, T. Hayat and A. Alsaedi, Nontrivial periodic solution of a stochastic non-autonomous SISV epidemic model, Physica A, 2016, 462, 837-845. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.06.041 [19] Q. Liu and D. Jiang, Stationary distribution of a stochastic staged progression HIV model with imperfect vaccination, Phys. A, 2019, 527, 121-271. [20] A. Lahrouz and L. Omari, Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with non-linear incidence, Stat. Prob. Lett., 2013, 83, 960-968. doi: 10.1016/j.spl.2012.12.021 [21] F. Li, S. Zhang and X. Meng, Dynamics analysis and numerical simulations of a delayed stochastic epidemic model subject to a general response function, Comput. Appl. Math., 2019, 38, 95. doi: 10.1007/s40314-019-0857-x [22] Z. Liu, Dynamics of positive solutions to SIR and SEIR epidemic models with saturated incidence rates, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2013, 14, 1286-1299. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2012.09.016 [23] Q. Luo and X. Mao, Stochastic population dynamics under regime switching, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2007, 334, 69-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.12.032 [24] X. Mao, Stochastic Differential Equations and Their Applications, Horwood, Chichester, 1997. [25] S. E. Park, Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features ofsevere acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19), Clin. Exp. Pediatr., 2020, 63, 119-124. doi: 10.3345/cep.2020.00493 [26] S. Spencer, Stochastic epidemic models for emerging diseases, PhD. thesis, University of Nottingham, 2008. [27] A. Singh, B. Razooky, C. D. Cox, et al., Transcriptional bursting from the HIV-1 promoter is a significant source of stochastic noise in HIV-1 gene expression, Biophys, 2010, 98(8), L32-L34. [28] M. Slatkin, The dynamics of a population in a Markovian environment, Ecology, 1978, 59, 249-256. doi: 10.2307/1936370 [29] A. Settati and A. Lahrouz, Stationary distribution of stochastic population systems under regime switching, Appl. Math. Comput., 2014, 244, 235-243. [30] Y. Takeuchi, N. Du, N. T. Hieu and K. Sato, Evolution of predator-prey systems described by a Lotka-Volterra equation under random environment, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2006, 323, 938-957. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.11.009 [31] G. Zeluf-Andersson and L. Eriksson, Beyond viral suppression: The quality of life of people living with HIV in Sweden, AIDS Care, 2019, 31(4), 403-412. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2018.1545990 [32] L. Zu, D. Jiang and D. ORegan, Conditions for persistence and ergodicity of a stochastic lotkacvolterra predatorcprey model with regime switching, Commun. Nonlin. Sci. Numer. Simul., 2015, 29, 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.04.008 [33] X. Zhang, D. Jiang, A. Alsaedi and T. Hayat, Stationary distribution of stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination under regime switching, Appl. Math. Lett., 2016, 59, 87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2016.03.010 [34] C. Zhu and G. Yin, Asymptotic properties of hybrid diffusion systems, SIAM J. Control Optim., 2007, 46, 1155-1179. doi: 10.1137/060649343 [35] B. Zhou, X. Zhang and D. Jiang, Dynamics and density function analysis of a stochastic SVI epidemic model with half saturated incidence rate. Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2020, 137, 109-865. -
-
-
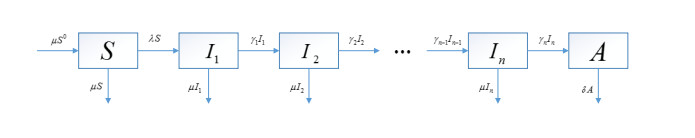
Figure 1. In the SP model every infected individual goes through the same series of stages. This model can account for a short early highly infectious stage equivalent to the acute phase of infection, a middle period of low infectiousness, and a late chronic stage with higher infectiousness, where
$ \lambda = r\sum_{i = 1}^n\beta_iI_i(t)S(t) $ . -
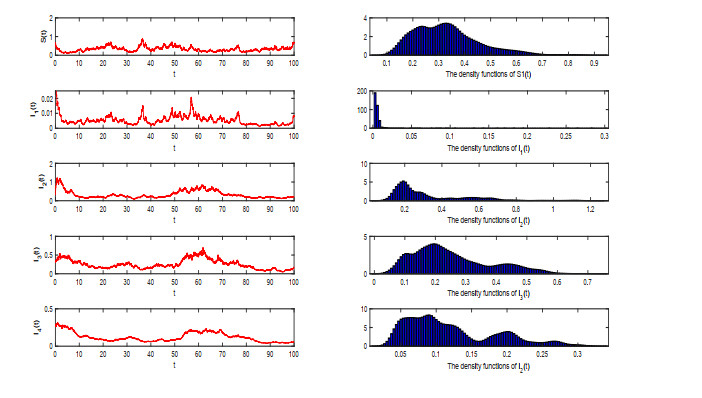
Figure 2.
$ ( S(t) , I_1(t), I_2(t), I_3(t), I_4(t)) $ has ergodic property. The pictures on the right are the density functions of system (1.1) for$ \sigma_1 = 0.3 $ ,$ \sigma_2 = 0.2 $ ,$ \sigma_3 = 0.1 $ ,$ \sigma_4 = 0.2 $ and$ \sigma_5 = 0.2 $ . We employ the Milstein's Higher Order Method with initial value$ ( S(0) , I_1(0), I_2(0), I_3(0), I_4(0)) = (0.3, 0.7, 0.3) $ . -
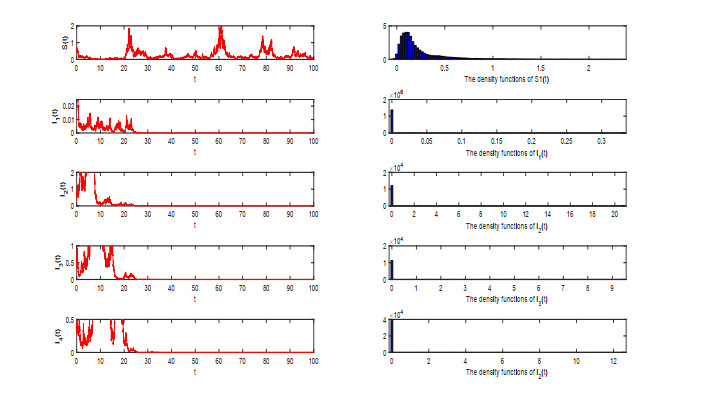
Figure 3.
$ I_1(t)) $ $ I_2(t) $ ,$ I_3(t) $ and$ I_4(t) $ will tends to zero exponentially with probability one. The pictures on the right are the density functions of system (1.1) for$ \sigma_1 = 0.8 $ ,$ \sigma_2 = 0.9 $ ,$ \sigma_3 = 0.9 $ ,$ \sigma_4 = 0.9 $ and$ \sigma_5 = 0.9 $ . We use the Milstein's Higher Order Method with initial value$ ( S(0) , I_1(0), I_2(0), I_3(0), I_4(0)) = (0.7, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3) $ . -
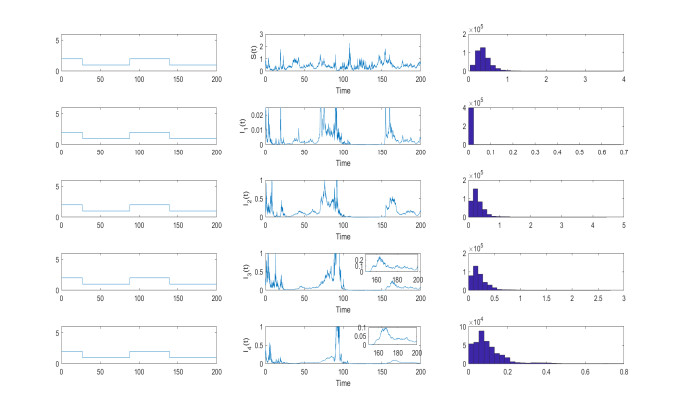
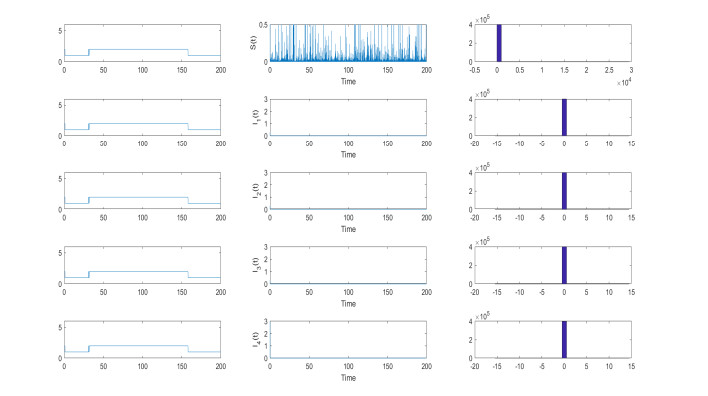
Figure 4.
$ ( S(t) , I_1(t), I_2(t), I_3(t), I_4(t)) $ is positive recurrence. The pictures on the left are Markovian chain. The pictures on the right are the density functions of system (1.4) for$ l\in\mathcal{M} = \{1, 2\} $ . We employ the Milstein's Higher Order Method with initial value$ ( S(0) , I_1(0), I_2(0), I_3(0), I_4(0)) = (0.7, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3) $ . -
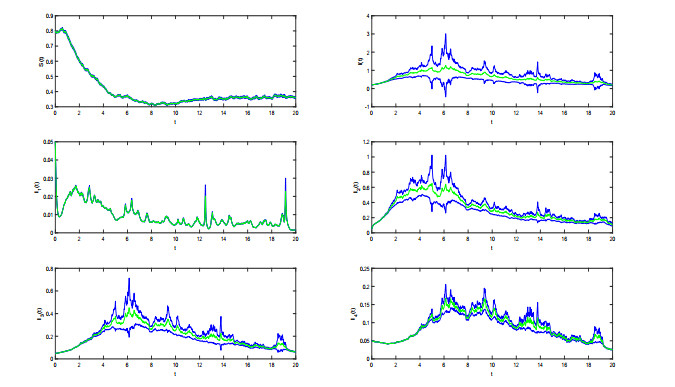
Figure 5. Computer simulation of a single path of
$ ( S(t) , I_1(t), I_2(t), I_3(t), I_4(t)) $ for the SDE model (1.4) with intial condition$ (0.7, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3) $ . -
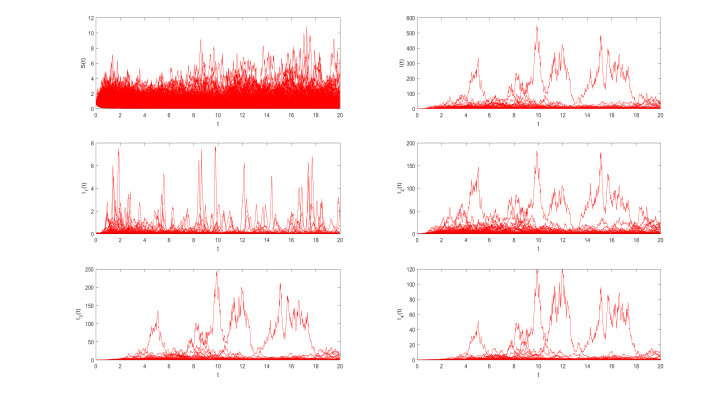
Figure 6. Computer simulation of 1000 pathes of
$ ( S(t) , I_1(t), I_2(t), I_3(t), I_4(t)) $ for the SDE model (1.4). - Figure 7. This picture is the 95% confidence intervals from 1000 stochastic simulations.
-
Figure 8.
$ I_1(t) $ ,$ I_2(t) $ ,$ I_3(t) $ and$ I_4(t) $ will tends to zero exponentially with probability one. The pictures on the left are Markovian chain. The pictures on the right are the density functions of system (1.4) for$ l\in\mathcal{M} = \{1, 2\} $ . We employ the Milstein's Higher Order Method with initial value$ ( S(0) , I_1(0), I_2(0), I_3(0), I_4(0)) = (0.7, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3) $ .




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: