| Citation: | Kangkang Chang, Qimin Zhang, Huaimin Yuan. STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION AND CONTROL STRATEGY OF A STOCHASTIC DENGUE MODEL WITH SPATIAL DIFFUSION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(1): 153-178. doi: 10.11948/20210094 |
STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION AND CONTROL STRATEGY OF A STOCHASTIC DENGUE MODEL WITH SPATIAL DIFFUSION
-
Abstract
In this paper, we establish a dengue model, which is described by the spatial diffusion and Brownian motion, and discuss the stationary distribution and optimal control of the stochastic dengue model. At first, we show the existence of the global positive solution by constructing Lyapunov function. The sufficient conditions are given for the existence and uniqueness of stationary distribution of the positive solution. Subsequently, we introduce the control strategy, namely, decrease the infected individual and spray mosquito insecticides. The first order necessary conditions are derived for the existence of optimal control by applying Pontryagins maximum principle. Finally, numerical simulations are introduced to confirm the analytical results. The simulation results verified the existence of stationary distribution, and there are certain differences in the solutions of the stationary distribution in different spaces. The influence of different noise intensity on the stationary distribution and the effect of different control strategy for stochastic dengue fever.
-

-
References
[1] S. Aniţa and V. Capasso, Regional Control for Spatially Structured Mosquito Borne Epidemics, Vietnam Journal of Mathematics, 2021, 49(1), 21-35. doi: 10.1007/s10013-020-00395-2 [2] A. Abdelrazec, J. BšŠlair, C. Shan and H. Zhu, Modeling the spread and control of dengue with limited public health resources, Mathematical Biosciences, 2016, 271, 136-145. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2015.11.004 [3] L. Esteva and C. Vargas, Analysis of a dengue disease transmission model, Mathematical Biosciences, 1998, 150, 131-151. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(98)10003-2 [4] W. H. Fleming, and R. W. Rishel, Deterministic and Stochastic Optimal Control, Springer, New York, NY, USA, 1975. [5] D. J. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM review, 2001, 43(3), 525-546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 [6] L. Hu, M. Tang, Z. Wu, Z. Xi and J. Yu, The threshold infection level for Wolbachia invasion in random environments, Journal of Differential Equations, 2019, 266(7), 4377-4393. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2018.09.035 [7] M. Iftikhar, A. Sohail and N. Ahmad, Detrministic and stochastic analysis of dengue spread model, Biomedical Engineering: Applications. Basis and Communications, 2019, 31(03), Article ID 1950008. [8] M. A. Khan, A. Khan, A. Elsonbaty and A. A. Elsadany, Modeling and simulation results of a fractional dengue model, The European Physical Journal Plus, 2019, 134(8), 379-393. doi: 10.1140/epjp/i2019-12765-0 [9] T. K. Kar and S. Jana, Application of three controls optimally in a vector-borne disease-a mathematical study, Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2013, 18(10), 2868-2884. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2013.01.022 [10] H. Kuo, Introduction to Stochastic Integration, Springer, 2006. [11] K. Liu, Stationary Distributions of Second Order Stochastic Evolution Equations with Memory in Hilbert Spaces. Stochastic Processes and their Applications, 2020, 130, 366-393. doi: 10.1016/j.spa.2019.03.015 [12] Q. Liu, D. Jiang and T. Hayat, Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic dengue epidemic model, Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355, 8891-8914. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.10.003 [13] E. Massaro, D. Kondor and C. Ratti, Assessing the interplay between human mobility and mosquito borne diseases in urban environments, Scientific reports, 2019, 9(1), 1-13. [14] R. C. Mittal, R. Goel and N. Ahlawat, An Efficient Numerical Simulation of a Reaction-Diffusion Malaria Infection Model using B-splines Collocation, Chaos Solitons and Fractals, 2021, 143, Article ID 110566. [15] X. Mao, Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications (Second Edition), Horwood Publishing, Chichester, Horwood, 2007. [16] E. A. Newton and P. Reiter, A model of the transmission of dengue fever with an evaluation of the impact of ultra-low volume (ULV) insecticide applications on dengue epidemics, The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene, 1992, 47(6), 709-720. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.709 [17] C. Paupy, B. Ollomo, B. Kamgang, S. Moutailler, D. Rousset, M. Demanou, J. Hervé, E. Leroy and F. Simard, Comparative role of Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti in the emergence of dengue and chikungunya in central Africa, Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 2010, 10(3), 259-266. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2009.0005 [18] L. S. Pontryagin, V. G. Boltyanskii, R. V. Gamkrelidze and E. F. Mishchenko, The Maximum Principle. The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes, New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1962. [19] H. S. Rodriguesa, M. Teresab, T. Monteirob and D. F. Torresc, Seasonality effects on dengue: basic reproduction number, sensitivity analysis and optimal control, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2016, 39(16), 4671-4679. doi: 10.1002/mma.3319 [20] H. S. Rodriguesa, M. Teresab, T. Monteirob and D. F. Torresc, Optimal Control of a Dengue Epidemic Model with Vaccination, American Institute of Physics, 2011, 1389(1), 1232-1235. [21] L. Sedda, B. M. Taylor, A. E. Eiras, J. T. Marques and R. J. Dillon, Using the intrinsic growth rate of the mosquito population improves spatio-temporal dengue risk estimation, Acta. Tropica, 2020, 208, Article ID 105519. [22] W. Sun, L. Xue and X. Yan, Stability of a dengue epidemic model with independent stochastic perturbations, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2018, 468, 998-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2018.08.033 [23] T. Sardar, S. Rana and J. Chattopadhyay, A mathematical model of dengue transmission with memory, Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat, 2015, 22, 511-525. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.08.009 [24] J. J. Tewa, J. L. Dimi and S. Bowong, Lyapunov functions for a dengue disease transmission model, Chaos Solitons and Fractals, 2009, 39, 936-941. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2007.01.069 [25] M. Umar, M. A. Z. Raja, Z. Sabir, A. S. Alwabli and M. Shoaib, A stochastic computational intelligent solver for numerical treatment of mosquito dispersal model in a heterogeneous environment, The European Physical Journal Plus, 2020, 135(7), 1-23. [26] P. J. Witbooi, G. J. Abiodun, G. J. V. Schalkwyk and I. H. I. Ahmed, Stochastic modeling of a mosquito-borne disease, Advances in Difference Equations, 2020, 1, 1-15. [27] Y. Xue, L. Hu and L. Nie, Modelling the Wolbachia Strains for Dengue Fever Virus Control in the Presence of Seasonal Fluctuation, Journal of Nonlinear Modeling and Analysis, 2021, 3(2), 209-224. [28] J. Yong and X. Zhou, Stochastic Control: Hamiltonian Systems and HJB Equations, Springer, 1999. [29] M. Zhu, Z. Lin and L. Zhang, Spatial-temporal risk index and transmission of a nonlocal dengue model, Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2020, 53, Article ID 103076. [30] L. Zhang and S. Wang, A time-periodic and reaction-diffusion Dengue fever model with extrinsic incubation period and crowding effects, Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2020, 51, Article ID 102988. [31] M. Zhang and Z. Lin, The diffusive model for aedes aegypti mosouito on a periodically evolving domain, Dynamical Systems Series B, 2019, 24(9), 4703-4720. -
-
-
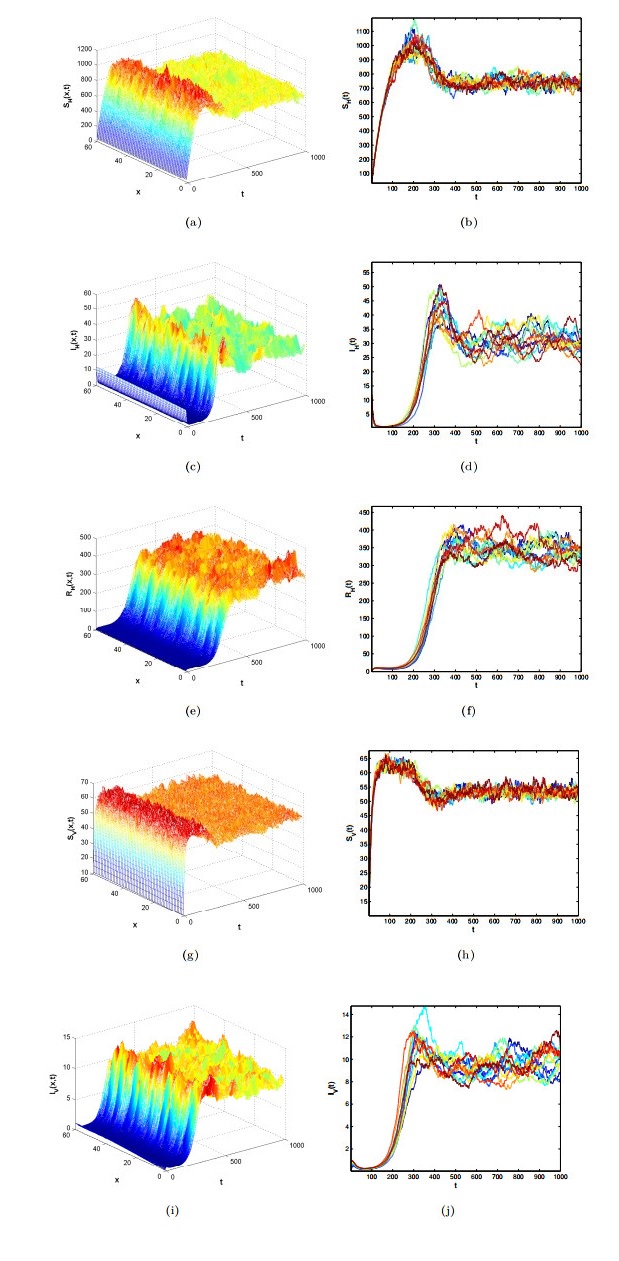
Figure 1. The solutions are observed in system (2.5) under initial conditions
$(S_{H, 0}(x), I_{H, 0}(x), R_{H, 0}(x), $ $S_{V, 0}(x), I_{V, 0}(x))=(33+\sin\frac{\pi x}{60}, 11+\sin\frac{\pi x}{60}, 0, 10+\sin\frac{\pi x}{60}, \sin\frac{\pi x}{60})$ -
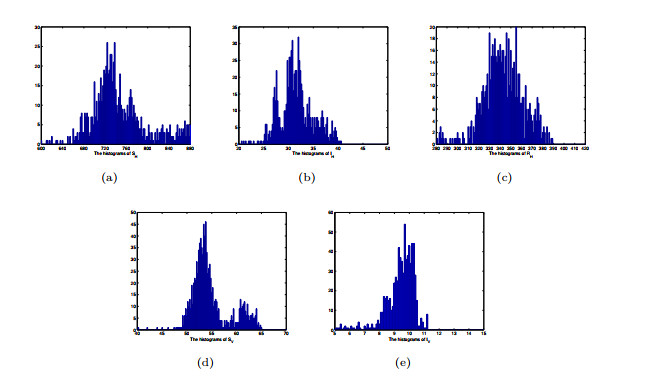
Figure 2. The histograms of
$S_{H}, I_{H}, R_{H}, S_{V}, I_{V}$ -
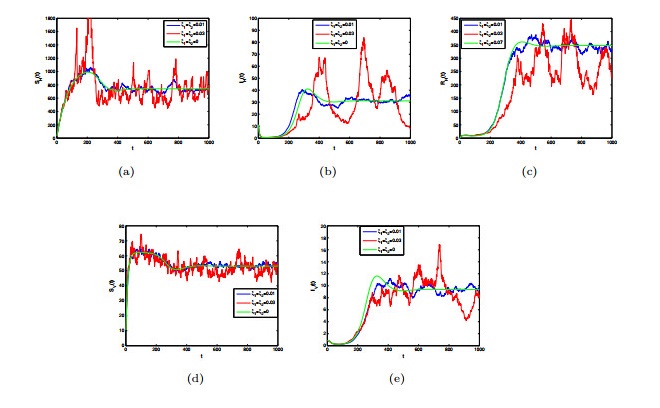
Figure 3. The evolution of a single path of
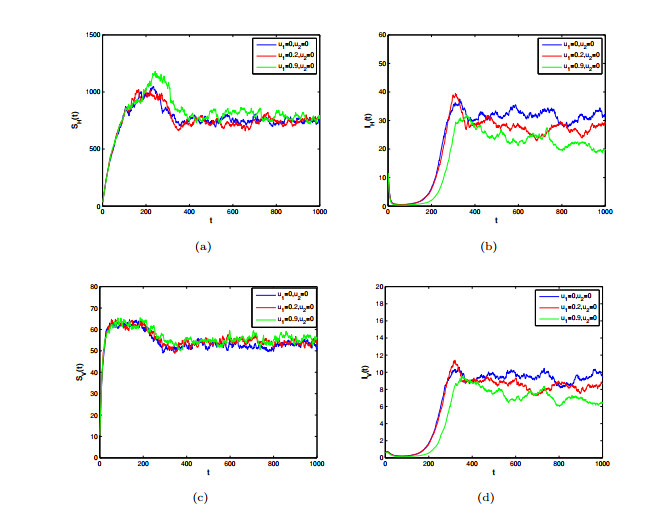
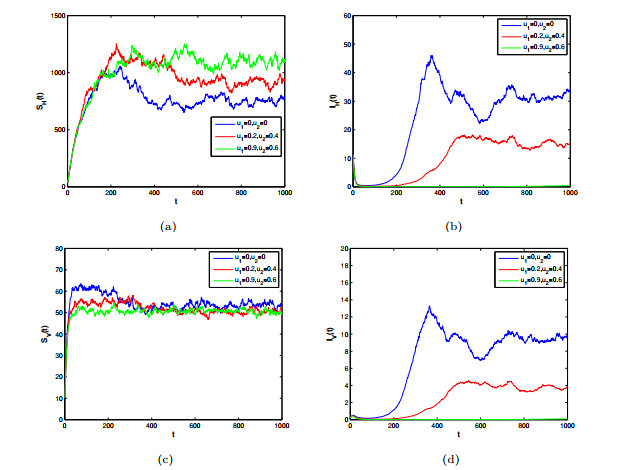
$S_{H}, I_{H}, R_{H}, S_{V}, I_{V}$ for different noise intensity - Figure 4. The effects of treating infected individuals
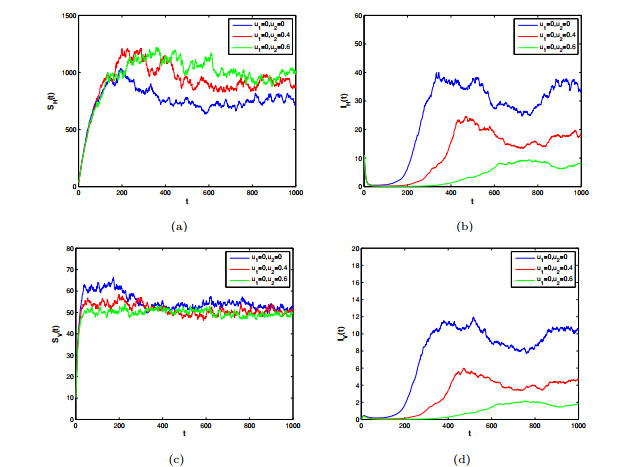
- Figure 5. The effects of mosquito control
- Figure 6. The effects of both control measures
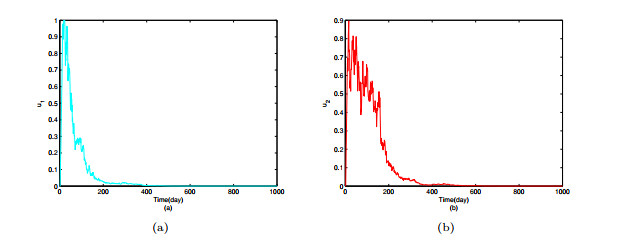
- Figure 7. The graph for the two controls




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: