| Citation: | Gaoxiang Yang, Xiaosong Tang. DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF THREE-SPECIES REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEM VIA THE MULTIPLE SCALE PERTURBATION METHOD[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(1): 206-229. doi: 10.11948/20210129 |
DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF THREE-SPECIES REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEM VIA THE MULTIPLE SCALE PERTURBATION METHOD
-
Abstract
In this paper, the general analysis of spatiotemporal dynamics of three-species reaction-diffusion system induced by Turing bifurcation is given. Firstly, by employing the Routh-Hurwitz criterion the conditions for Turing bifurcation in three-species reaction-diffusion equations are obtained. Secondly, through the tool of the multiple scale perturbation method the amplitude equations of Turing patterns are also given. Finally, we take a three-species predator-prey model as an example to illustrate the application of these general theoretical results, and meanwhile carry out many numerical simulations to depict spots pattern, stripes pattern and labyrinthine pattern and demonstrate the validity of these theories.
-

-
References
[1] N. F. Britton, Spatial stuctures and periodic Traveling waves in an integro-differential reaction-diffusion population model, SIAM journal on Applied Mathematics, 1990, 50, 1663-1688. doi: 10.1137/0150099 [2] M. Baurmann, T. Gross and U. Feudel, Instabilities in spatially extended predator-prey systems: Spatio-temporal patterns in the neighborhood of Turing-Hopf bifurcations, Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2007, 245 220-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.09.036 [3] X. Cao and W. Jiang, Interactions of Turing and Hopf bifurcations in an additional food provided diffusive predator-prey model, Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2019, 9, 1277-1304. doi: 10.11948/2156-907X.20180224 [4] M. R. Garvie, Finite-Difference Schemes for Reaction-Diffusion Equations Modeling PredatorPrey Interactions in MATLAB, Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2007, 69, 931-956. doi: 10.1007/s11538-006-9062-3 [5] E. Giricheva, Spatiotemporal dynamics of an NPZ model with prey-taxis and intratrophic predation, Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 95, 875-892. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4601-7 [6] S. B. Hsu, T. W. Hwang and Y. Kuang, A ratio-dependent food chain model and its applications to biological control, Mathematical Biosciences, 2003, 18, 55-83. [7] O. Jensen, V. O. Pannbacker, G. Dewel and P. Borckmans, Subcritical transitions to Turing structures, Physics Letters A, 1993, 179, 91-96. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(93)90655-J [8] Y. Kuramoto, Chenmical Oscillation, Waves, and Turbulence, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1984. [9] J. D. Murray, Mathematical Biology: Spatial Models and Biomedical Applications, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003. [10] P. Mishra, S. N. Raw and B. Tiwari, Study of a Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with prey defense and mutual interference of predators, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2019, 120, 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2019.01.012 [11] N. Mukherjee, S. Ghorai and M. Banerjee, Detection of turing patterns in a three species food chain model via amplitude equation, Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2019, 69, 219-236. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2018.09.023 [12] E. Meron, Nonlinear physics of ecosystems, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2015. [13] A. B. Medvinsky, S. V. Petrovskii, I. A. Tikhonova, H. Malchow and B. Li, Spatiotemporal complexity of plankton and fish dynamics, SIAM review, 2002, 44, 311-370. doi: 10.1137/S0036144502404442 [14] M. G. Neubert, H. Caswell and J. D. Murray, Transient dynamics and pattern formation: reactivity is necessary for Turing instabilities, Mathematical Biosciences, 2002, 175, 1-11. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(01)00087-6 [15] Q. Ouyang, Nonlinear Science and Dynamics of Pattern, Beijing Unversity Publication, Beijing, 2010. [16] R. D. Parshad, E. Quansah, K. Black, R. K. Upadhyay and S. K. Tiwari, Long time dynamics of a three-species food chain model with Allee effect in the top predator, Computers Mathematics with Applications, 2016, 71, 503-528. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2015.12.015 [17] H. Qian and J. D. Murray, A simple method of parameter space determination for diffusion-driven instability with three species, Applied Mathematics Letters, 2001, 14, 405-411. doi: 10.1016/S0893-9659(00)00169-5 [18] Y. Su and X. Zou, Rich spatial-temporal dynamics in a diffusive population model for pioneer-climax species, Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 95, 1731-1745. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4656-5 [19] R. A. Satnoianu, M. Menzinger and P. K. Maini, Turing instabilities in general systems, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2000, 41, 493-512. doi: 10.1007/s002850000056 [20] Y. Song, H. Jiang, Q. Liu and Y. Yuan, Spatiotemporal dynamics of the diffusive Mussel-Algae model near Turing-Hopf bifurcation, SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, 2017, 16, 2030-2062. doi: 10.1137/16M1097560 [21] G. Santu and P. Swarup, Pattern formation and control of spatiotemporal chaos in a reaction diffusion prey-predator system supplying additional food, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2016, 85, 57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2016.01.013 [22] Y. Song, T. Zhang and Y. Peng, Turing-Hopf bifurcation in the reaction-diffusion equations and its applications, Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2016, 33, 229-258. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.10.002 [23] Y. Song, H. Jiang and Y. Yuan, Turing-Hopf bifurcation in the reaction-diffusion system with delay and application to a diffusive predator-prey model, Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2019, 9, 1132-1164. doi: 10.11948/2156-907X.20190015 [24] A. M. Turing, The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 1952, 237, 37-72. [25] J. Wu, Theory and Applications of Partial Functional Differential Equations, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1996. [26] K. A. J. White and C. A. Gilligan, Spatial heterogeneity in three species, plant-parasite-hyperparasite systems, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 1998, 353, 543-557. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1998.0226 [27] S. Xu, M. Qu and C. Zhang, Investigating the Turing conditions for diffusion-driven instability in predator-prey system with hunting, Journal of Nonlinear Modeling and Analysis, 2021, 3(4), 663-676. [28] X. Zhang, G. Sun and Z. Jin, Spatial dynamics in a predator-prey model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response, Physical Review E, 2012, 85, Article ID: 021924. -
-
-
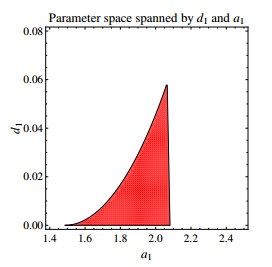
Figure 1. The red domain denotes the parameter space of Turing bifurcation spanned by
$ d_1 $ and$ a_1 $ according to Theorem 1. -
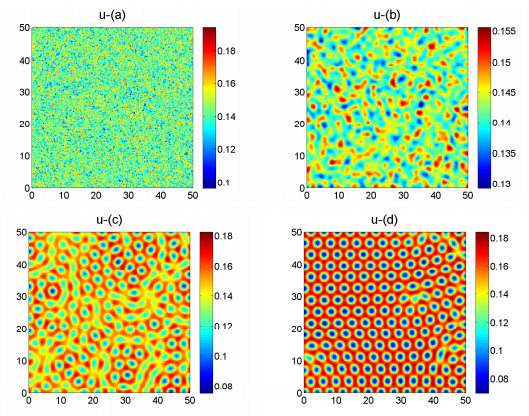
Figure 2. The time evolution plots of the density of the prey
$ u $ at the different$ t = 0 $ ,$ t = 10, t = 1000, t = 100000 $ respectively when the diffusion coefficient$ d_1 = 0.045 $ . -
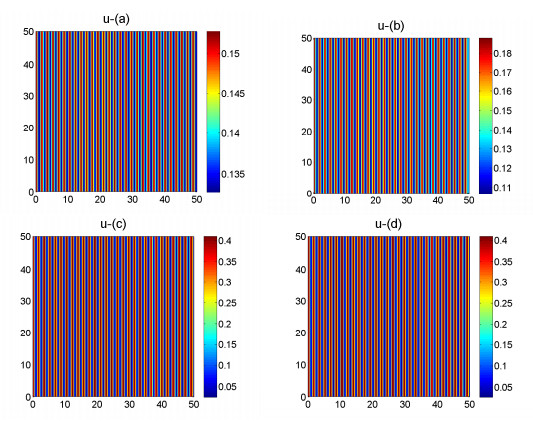
Figure 3. The time evolution plots of the density of the prey
$ u $ at the different$ t = 0 $ ,$ t = 10, t = 1000, t = 100000 $ respectively when the diffusion coefficient$ d_1 = 0.01 $ . -
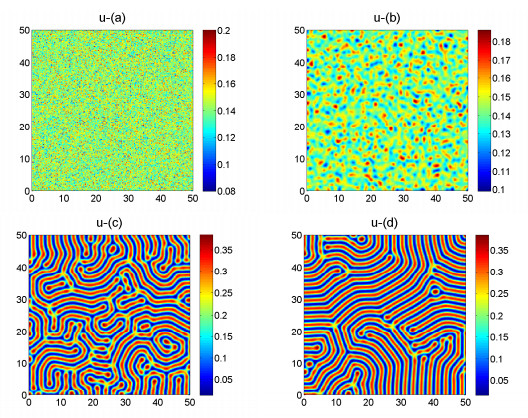
Figure 4. The time evolution plots of the density of the prey
$ u $ at the different$ t = 0 $ ,$ t = 10, t = 1000, t = 100000 $ respectively when the diffusion coefficient$ d_1 = 0.02 $ . -
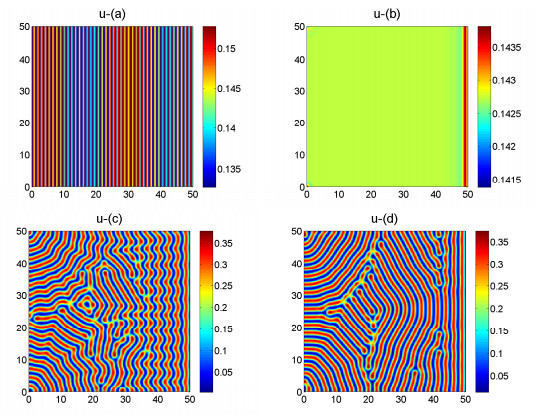
Figure 5. The time evolution plots of the density of the prey
$ u $ at the different$ t = 0 $ ,$ t = 10, t = 1000, t = 100000 $ respectively when the diffusion coefficient$ d_1 = 0.02 $ .




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: