| Citation: | Guoqiao You, Changfeng Xue. FAST IDENTIFICATION OF THE HYPERBOLIC LAGRANGIAN COHERENT STRUCTURES IN TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOWS BASED ON THE EULERIAN-TYPE ALGORITHMS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2022, 12(2): 568-590. doi: 10.11948/20210229 |
FAST IDENTIFICATION OF THE HYPERBOLIC LAGRANGIAN COHERENT STRUCTURES IN TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOWS BASED ON THE EULERIAN-TYPE ALGORITHMS
-
Abstract
Based on the so-called mixing-based partition, we propose an efficient Eulerian algorithm to identify the hyperbolic Lagrangian coherent structure (LCS) of any given two-dimensional (2D) flow fields, which is framework independent. To extract the required LCS, the proposed algorithm only needs to solve one single partial differential equation. Moreover, data is only required at mesh points in the implementation of the proposed algorithm. In contrast, traditional Lagrangian ray tracing approach needs to solve a system consisting of two ordinary differential equations together with a line integral along the particular particle trajectory. Furthermore, if the velocity data is only available at mesh points, the Lagrangian approach needs to implement interpolation to obtain the velocity and also the velocity gradient at non-mesh points along the particle trajectory taking off from each mesh point, which could be quite time-consuming. Based on the doubling technique, we also propose an efficient iterative Eulerian-type algorithm to identify the longtime LCS for 2D periodic flows. Numerical examples are provided to confirm the accuracy, efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed Eulerian algorithms.
-

-
References
[1] M. Badas, F. Domenichini and G. Querzoli, Quantification of the blood mixing in the left ventricle using finite time Lyapunov exponents, Meccania, 2017, 52, 529-544. doi: 10.1007/s11012-016-0364-8 [2] B. Cardwell and K. Mohseni, Vortex shedding over two-dimensional airfoil: Where do the particles come from?, AIAA J., 2008, 46, 545-547. doi: 10.2514/1.35223 [3] A. Carusone, C. Sicot, J. Bonnet and J. Borée, Transient dynamical effects induced by single-pulse fluidic actuation over an airfoil, Exp. Fluids, 2021, 62, 25. doi: 10.1007/s00348-020-03108-0 [4] M. Dawoodian and A. Sau, Kinetics and prey capture by a paddling jellyfish: three-dimensional simulation and Lagrangian coherent structure analysis, J. Fluid Mech., 2021, DOI: 10.1017/jfm.2020.1069. [5] S. Gottlieb and C. Shu, Total variation diminishing Runge-Kutta schemes, Mathematics of Computation, 1998, 67, 73-85. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-98-00913-2 [6] M. Green, C. Rowley and A. Smiths, Using hyperbolic Lagrangian coherent structures to investigate vortices in biospired fluid flows, Chaos, 2010, 20, 017510. doi: 10.1063/1.3270045 [7] G. Haller, Distinguished material surfaces and coherent structures in three-dimensional fluid flows, Physica D, 2001, 149, 248-277. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(00)00199-8 [8] G. Haller, Lagrangian structures and the rate of strain in a partition of two-dimensional turbulence, Phys. Fluids A, 2001, 13, 3368-3385. [9] G. Haller, Lagrangian coherent structures from approximate velocity data, Physics of Fluid, 2002, 14, 1851-1861. doi: 10.1063/1.1477449 [10] G. Haller, A variational theory of hyperbolic Lagrangian coherent structure, Physica D, 2011, 240, 574-598. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2010.11.010 [11] G. Haller and T. Sapsis, Lagrangian coherent structures and the smallest finite-time Lyapunov exponent, Chaos, 2011, 21(2), 017510. [12] G. Haller and G. Yuan, Lagrangian coherent structures and mixing in two-dimensional turbulence, Physica D, 2000, 147, 352-370. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(00)00142-1 [13] D. Lasagna, A. Sharma and J. Meyers, Periodic shadowing sensitivity analysis of chaotic systems, J. Comput. Phys., 2019, 391, 119-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.04.021 [14] F. Lekien and N. Leonard, Dynamically consistent Lagrangian coherent structures, Experimental Chaos: 8-th Experimental Chaos Conference, 2004, 132-139. [15] F. Lekien and S. Ross, The computation of finite-time Lyapunov exponents on unstructured meshes and for non-Euclidean manifolds, Chaos, 2010, 20, 017505. doi: 10.1063/1.3278516 [16] F. Lekien, S. Shadden and J. Marsden, Lagrangian coherent structures in $ n$-dimensional systems, Journal of Mathematical Physics, 2007, 48, 065404. doi: 10.1063/1.2740025 CrossRef $ n$-dimensional systems" target="_blank">Google Scholar
[17] S. Leung, An Eulerian approach for computing the finite time Lyapunov exponent, J. Comput. Phys., 2011, 230, 3500-3524. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.01.046 [18] S. Leung, The backward phase flow method for the Eulerian finite time Lyapunov exponent computations, Chaos, 2013, 23, 043132. doi: 10.1063/1.4847175 [19] S. Leung, G. You, T. Wong and Y. K. Ng, Recent developments in Eulerian approaches for visualizing continuous dynamical systems, Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress of Chinese Mathematicians, 2019, 2, 579-622. [20] D. Lipinski and K. Mohseni, Flow structures and fluid transport for the hydromedusae Sarsia tubulosa and Aequorea victoria, J. Exp. Biology, 2009, 212, 2436-2447. doi: 10.1242/jeb.026740 [21] X. Liu, S. Osher and T. Chan, Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes, J. Comput. Phys., 1994, 115, 200-212. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1994.1187 [22] X. Liu, S. J. Osher and T. Chan, Weighted Essentially NonOscillatory schemes, J. Comput. Phys., 1994, 115, 200-212. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1994.1187 [23] S. Lukens, X. Yang and L. Fauci, Using Lagrangian coherent structures to analyze fluid mixing by cillia, Chaos, 2010, 20, 017511. doi: 10.1063/1.3271340 [24] B. Manda, B. Senyange and C. Skokos, Chaotic wave-packet spreading in two-dimensional disordered nonlinear lattices, Phys. Rev. E, 2020, 101, 032206. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.101.032206 [25] S. J. Osher and R. P. Fedkiw, Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003. [26] S. J. Osher and J. A. Sethian, Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations, J. Comput. Phys., 1988, 79, 12-49. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(88)90002-2 [27] T. Sagristè, S. Jordan and S. F., Visual analysis of the finite-time Lyapunov exponent, Comput. Graph. Forum, 2020, 39(3), 331-342. doi: 10.1111/cgf.13984 [28] T. Sapsis and G. Haller, Inertial particle dynamics in a hurricane, Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2009, 66, 2481-2492. doi: 10.1175/2009JAS2865.1 [29] S. Shadden, F. Lekien and J. Marsden, Definition and properties of Lagrangian coherent structures from finite-time Lyapunov exponents in two-dimensional aperiodic flows, Physica D, 2005, 212, 271-304. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2005.10.007 [30] C. Shu, Essentially non-oscillatory and weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws, in Advanced Numerical Approximation of Nonlinear Hyperbolic Equations, 1697 (Edited by B. Cockburn, C. Johnson, C. Shu and E. Tadmor), Springer, 1998, 325-432. Lecture Notes in Mathematics. [31] T. Solomon and J. Gollub, Chaotic particle-transport in timedependent rayleigh-b¡äenard convection, Phys. Rev. A, 1988, 38, 6280-6286. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.38.6280 [32] W. Tang, P. Chan and G. Haller, Accurate extraction of Lagrangian coherent structures over finite domains with application to flight data analysis over Hong Kong international airport, Chaos, 2010, 20, 017502. doi: 10.1063/1.3276061 [33] W. Tang and T. Peacock, Lagrangian coherent structures and internal wave attractors, Chaos, 2010, 20, 017508. doi: 10.1063/1.3273054 [34] G. You and S. Leung, An Eulerian method for computing the coherent ergodic partition of continuous dynamical systems, J. Comp. Phys., 2014, 264, 112-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.01.034 [35] G. You and S. Leung, Eulerian based interpolation schemes for flow map construction and line integral computation with applications to Lagrangian coherent structures extraction, Journal of Scientific Computing, 2018, 74, 70-96. doi: 10.1007/s10915-017-0424-9 [36] G. You and S. Leung, An improved Eulerian approach for the finite time Lyapunov exponent, Journal of Scientific Computing, 2018, 76, 1407-1435. doi: 10.1007/s10915-018-0669-y [37] G. You and S. Leung, Fast construction of forward flow maps using Eulerian based interpolation schemes, Journal of Scientific Computing, 2020, 82, 32. doi: 10.1007/s10915-020-01141-z [38] G. You and S. Leung, Computing the finite time Lyapunov exponent for flows with uncertainties, J. Comp. Phys., 2021, 405, 109905. [39] G. You, Y. Shan and Y. Xu, Fast computations for the Lagrangian-averaged vorticity deviation based on the Eulerian formulations, International Journal of Computational Methods, 2020, 17, 1950078. doi: 10.1142/S0219876219500786 [40] G. You, T. Wong and S. Leung, Eulerian methods for visualizing continuous dynamical systems using Lyapunov exponents, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2017, 39(2), A415-A437. doi: 10.1137/16M1066890 -
-
-
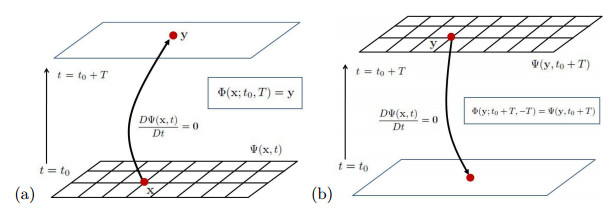
Figure 1. Lagrangian and Eulerian interpretations of the function
$ \Psi $ [17]. (a) Lagrangian ray tracing from a given grid location$ {\bf x} $ at$ t = 0 $ . Note that$ {\bf y} $ might be a non-grid point. (b) Eulerian values of$ \Psi $ at a given grid location$ {\bf y} $ at$ t = T $ gives the corresponding take-off location at$ t = 0 $ . Note the take-off location might not be a mesh point. -
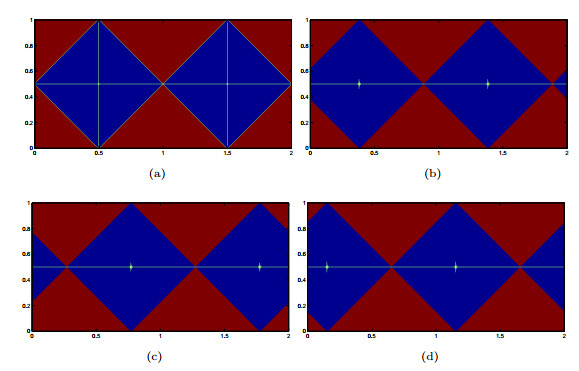
Figure 2. (Section 5.1) The mixing-based partition with
$ \epsilon = 0.1 $ at the time level (a)$ t = 1 $ , (b)$ t = 5 $ , (c)$ t = 7 $ and (d)$ t = 10 $ . -
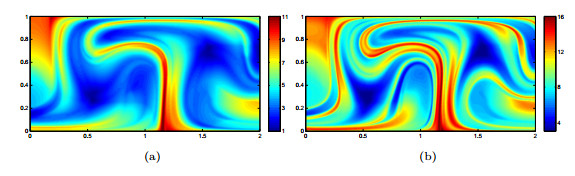
Figure 3. (Section 5.1) (a) The
$ \sigma_0^5( {\bf x}) $ field and (b) the$ \sigma_0^{10}( {\bf x}) $ field with$ \epsilon = 0.1 $ , computed using the proposed$\textsf{Algorithm 1}$ . -
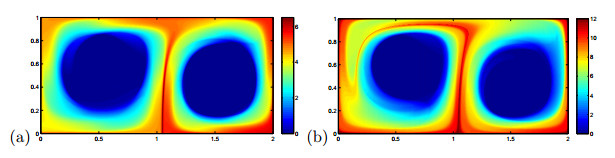
Figure 4. (Section 5.1) (a) The
$ \sigma_0^5( {\bf x}) $ field and (b) the$ \sigma_0^{10}( {\bf x}) $ field with$ \epsilon = 0.1 $ , computed using the Lagrangian approach. -
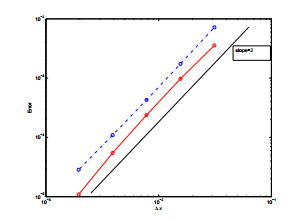
Figure 5. (Section 5.1) The
$ L_1 $ errors of the solutions$ \sigma_0^{10}( {\bf x}) $ computed using the proposed Eulerian approach (red solid line) and the Lagrangian approach (blue dot dashed line). We also plot a solid black line with slope 2 as a reference. -
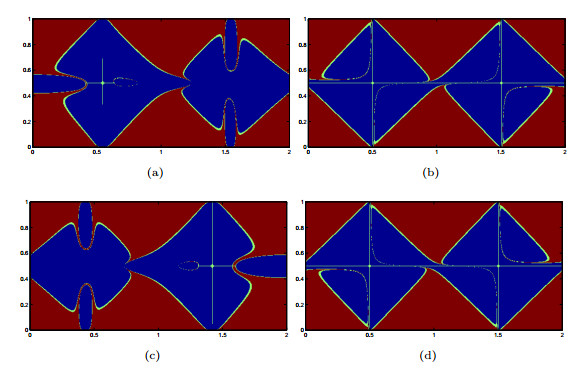
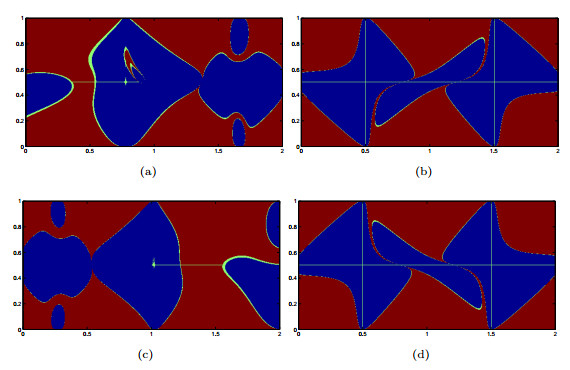
Figure 6. (Section 5.1) The mixing-based partition with
$ \epsilon = 0.5 $ at the time level (a)$ t = 1 $ , (b)$ t = 5 $ , (c)$ t = 7 $ and (d)$ t = 10 $ . The white triangles are the locations of the particle taking off from$ (0.5, 0.25) $ at$ t = 0 $ . -
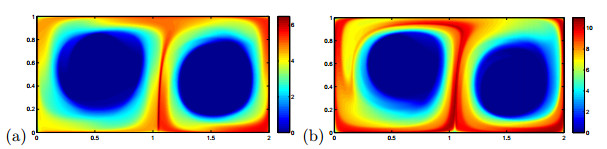
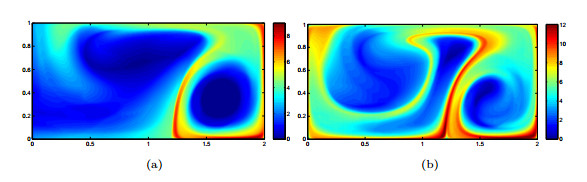
Figure 7. (Section 5.1) (a) The
$ \sigma_0^5( {\bf x}) $ field and (b) the$ \sigma_0^{10}( {\bf x}) $ field with$ \epsilon = 0.5 $ , computed using the proposed$\textsf{Algorithm 1}$ . -
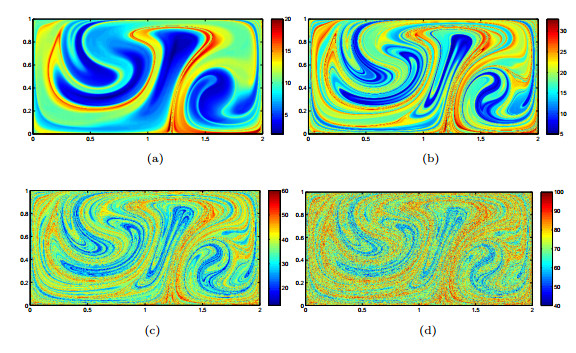
Figure 8. (Section 5.1) The
$ \sigma_0^T( {\bf x}) $ field computed using the$\textsf{Algorithm 2}$ , for (a)$ T = 20 $ , (b)$ T = 40 $ , (c)$ T = 80 $ and (d)$ T = 160 $ , respectively. -
Figure 9. (Section 5.1) The
$ L_1 $ errors of the solution$ \sigma_0^{160}( {\bf x}) $ computed using the proposed Eulerian approach (red solid line). We also plot a solid black line with slope 2 as a reference. -
Figure 10. (Section 5.2) The mixing-based partition at the time level (a)
$ t = 0 $ , (b)$ t = 0.3 $ , (c)$ t = 0.7 $ and (d)$ t = 1.9 $ . -
Figure 11. (Section 5.2) (a) The
$ \sigma_0^1( {\bf x}) $ field and (b) the$ \sigma_0^2( {\bf x}) $ field computed using the proposed Eulerian approach. -
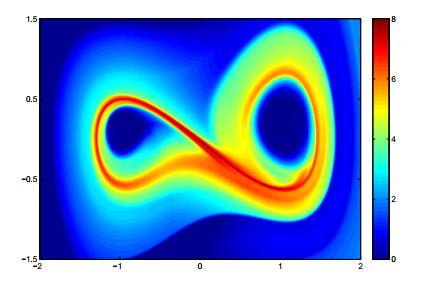
Figure 12. (Section 5.3) (a) The
$ \sigma_0^{10} $ field computed using the proposed Eulerian approach. -
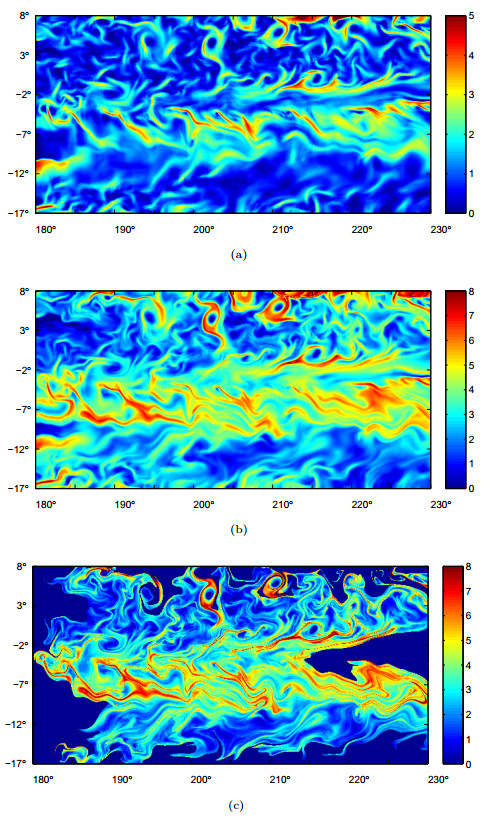
Figure 13. (Section 5.4) (a) The
$ \sigma_0^{20} $ field and (b) the$ \sigma_0^{50} $ field computed using the proposed Eulerian approach. (c) The$ \sigma_0^{50} $ field computed using the Lagrangian approach.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: