| Citation: | Xiaoqing Lin, Yue Yang, Yancong Xu, Mu He. BIFURCATIONS AND HYDRA EFFECTS IN ROSENZWEIG-MACARTHUR MODEL[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(2): 606-622. doi: 10.11948/20220241 |
BIFURCATIONS AND HYDRA EFFECTS IN ROSENZWEIG-MACARTHUR MODEL
-
Abstract
In this paper, a Rosenzweig-MacArthur predator-prey model with intraspecific competition of predators and Holling type Ⅱ functional response with a prey refuge is investigated by using dynamical approach. We study the number of positive equilibria, the local and global dynamics including Hopf bifurcation, saddle-node bifurcation, Bautin bifurcation. We provide the coexistence of stable and unstable limit cycles. In particular, we show the hydra effect that describes the positive effect of the predator's mortality, as well as the positive effects of prey refuge and intraspecific competition among predators, on the predator's population density. Furthermore, numerical simulations demonstrate the theoretical results including the hydra effect region and trophic cascade.
-

-
References
[1] P. D. Adhikary, S. Mukherjee and B. Ghosh, Bifurcations and hydra effects in Bazykin's predator-prey model, Theore. Populat. Biol., 2021, 140, 44–53. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2021.05.002 [2] V. Anna, W. Sebastian and F. Ulrike, When very slow is too fast-collapse of a predator-prey system?, J. Theor. Biol., 2019, 479, 64–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2019.07.008 [3] L. K. Boast, E. V. Chelysheva and V. V. D. Merwe, Cheetah translocation and reintroduction programs: Past, present, and future, Cheetahs: Biology and Conservation, 2018, 275–289. [4] D. I. Bolnick, Intraspecific competition favours niche width expansion in Drosophila melanogaster, Nature, 2012, 410(6827), 463–466. [5] L. Chen, F. Chen and L. Chen, Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response incorporating a constant prey refuge, Nonlinear Anal., 2010, 11, 246–252. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.10.056 [6] P. Driessche and J. Watmough, Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission, Math. Biosci., 2002, 180, 29–48. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00108-6 [7] L. Eigentler, Intraspecific competition in models for vegetation patterns: Decrease in resilience to aridity and facilitation of species coexistence, Ecol. Complex., 2020, 42, 100835. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2020.100835 [8] S. Funk, S. Bansal, C. T. Bauch, K. T. D. Eames, W. J. Edmunds, A. P. Galvani and P. Klepac, Nine challenges in incorporating the dynamics of behaviour in infectious diseases models, Epidemics, 2015, 10, 21–25. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2014.09.005 [9] J. Guckenheimer and P. J. Holmes, Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcations of Vector Fields, Springer, 1983. [10] M. Haque, M. S. Rahman, E. Venturino and B. L. Li, Effect of a functional response-dependent prey refuge in a predator-prey model, Ecol. Complex., 2014, 20, 248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2014.04.001 [11] S. B. Hsu and J. P. Shi, Relaxation oscillation profile of limit cycle in predator-prey system, Discrete & Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2009, 11(4), 893–911. [12] Y. Huang, F. Chen and L. Zhong, Stability analysis of a prey-predator model with Holling type Ⅲ response function incorporating a prey refuge, Appl. Math. Comput., 2016, 182, 672–683. [13] T. K. Kar, Stability analysis of a prey-predator model incorporating a prey refuge, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2005, 10, 681–691. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2003.08.006 [14] P. Lenka, Regime shifts caused by adaptive dynamics in prey-predator models and their relationship with intraspecific competition, Ecol. Complex., 2018, 36, 48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2018.06.003 [15] H. L. Li, L. Zhang, C. Hu, Y. L. Jiang and Z. D. Teng, Dynamical analysis of a fractional-order predator-prey model incorporating a prey refuge, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2016, 54, 435–449. [16] H. M. Manarul and S. Sahabuddin, Dynamics of a harvested prey-predator model with prey refuge dependent on both species, Inter. J. Bifur. & Chaos, 2018, 28(12), 1830040. [17] H. C. Michael and Y. Masato, How (co)evolution alters predator responses to increased mortality: Extinction thresholds and hydra effects, Ecology, 2019, 100, e02789. doi: 10.1002/ecy.2789 [18] H. C. Michael and A. Peter, Hydra effects in stable communities and their implications for system dynamics, Ecology, 2016, 97(5), 1135–1145. doi: 10.1890/15-0648.1 [19] I. S. C. Michel and A. Lucas, Multiple hydra effect in a predator-prey model with Allee effect and mutual interference in the predator, Ecol. Model., 2018, 373, 22–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2018.02.005 [20] D. Mukherjee, Role of fear in predator-prey system with intraspecific competition, Math. Comput. Simulat., 2020, 177, 263–275. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2020.04.025 [21] C. E. Parent, D. Agashe and D. I. Bolnick, Intraspecific competition reduces niche width in experimental populations, Ecology and Evolution, 2015, 4(20), 1–13. [22] J. P. Park, Y. Do and B. Jang, Multistability in the cyclic competition system, Chaos, 2018, 28, 113110. doi: 10.1063/1.5045366 [23] S. Samanta, R. Dhar, I. M. Elmojtaba and J. Chattopadhyay, The role of additional food in a predator-prey model with a prey refuge, J. Biol. Syst., 2016, 24, 345–365. doi: 10.1142/S0218339016500182 [24] S. Sarwardi, S. Ray and P. K. Mandal, Analysis of a competitive prey-predator system with a prey refuge, Biosystems, 2012, 110(3), 133–148. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2012.08.002 [25] G. Seo and D. L. DeAngelis, A predator-prey model with a Holling type Ⅰ functional response including a predator mutual interference, J. Nonlinear Sci., 2011, 21, 811–833. doi: 10.1007/s00332-011-9101-6 [26] M. Sieber and F. M. Hilker, The hydra effect in predator-prey models, J. Math. Biol., 2011, 64, 341–360. [27] C. S. B. D. Silva, K. R. Park and R. A. Blood, Intraspecific competition affects the pupation behavior of spotted-wing drosophila, Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1), 7775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44248-6 [28] A. Singh, H. Wang, W. Morrison and H. Weiss, Modeling fish biomass structure at near pristine coral reefs and degradation by fishing, J. Biol. Syst., 2012, 20, 21–36. doi: 10.1142/S0218339011500318 [29] J. P. Tripathi, S. Abbas and M. Thakur, Dynamical analysis of a prey-predator model with Beddington-DeAngelis type function response incorporating a prey refuge, Nonlinear Dyn., 2015, 80, 177–196. doi: 10.1007/s11071-014-1859-2 [30] H. Wang, W. Morrison, A. Singh and H. Weiss, Modeling inverted biomass pyramids and refuges in ecosystems, Ecol. Model., 2009, 220, 1376–1382. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.03.005 [31] H. Wang and S. Thanarajah, Refuge-mediated predator-prey dynamics and biomass pyramids, Math. Biosci., 2018, 298, 29–45. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2017.12.007 [32] H. S. Zhang, Y. L. Cai, M. S. Fu and W. M. Wang, Impact of the fear effect in a prey-predator model incorporating a prey refuge, Appl. Math. Comput., 2019, 356, 328–337. -
-
-
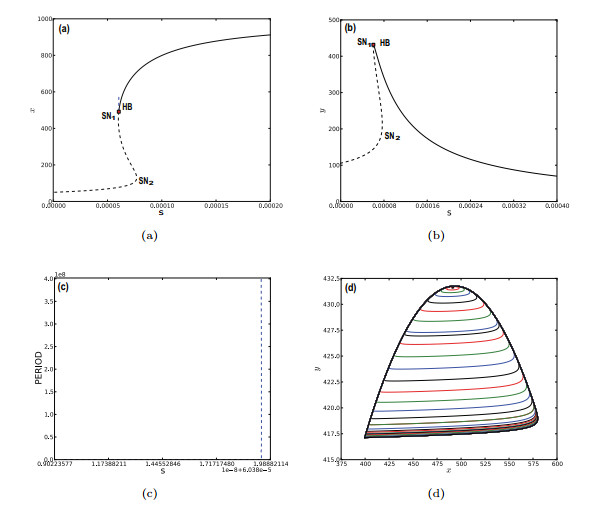
Figure 1.
Bifurcation diagram and phase portrait of model (2.1). HB,
$ SN_1 $ $ SN_2 $ $ s $ $ x $ $ s $ $ y $ $ s $ -
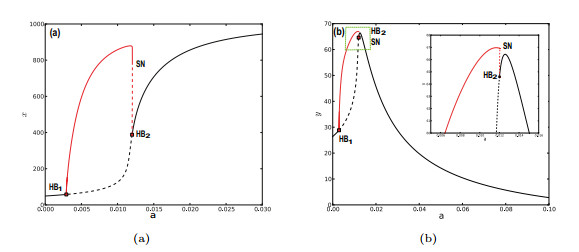
Figure 2.
One-parameter bifurcation diagram of model (2.1). (a) One-parameter bifurcation diagram with
$ a $ $ x $ $ a $ $ y $ $ HB_1 $ $ HB_2 $ $ SN $ -
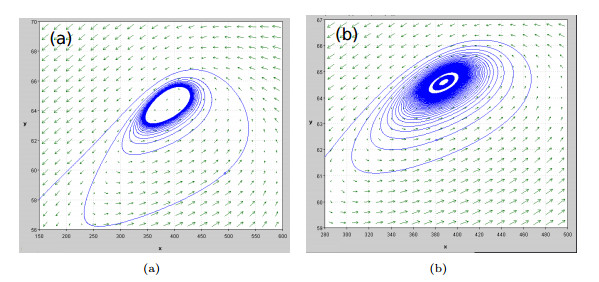
Figure 3.
Phase portrait of limit cycles in model (2.1). (a) One limit cycle at
$ a=0.01201. $ $ a=0.0120058, $ -
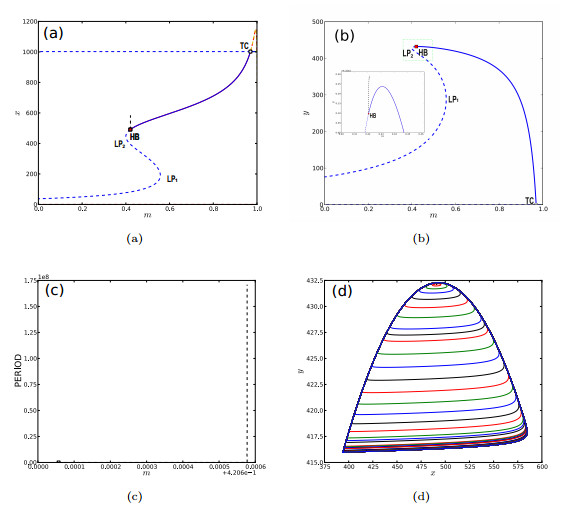
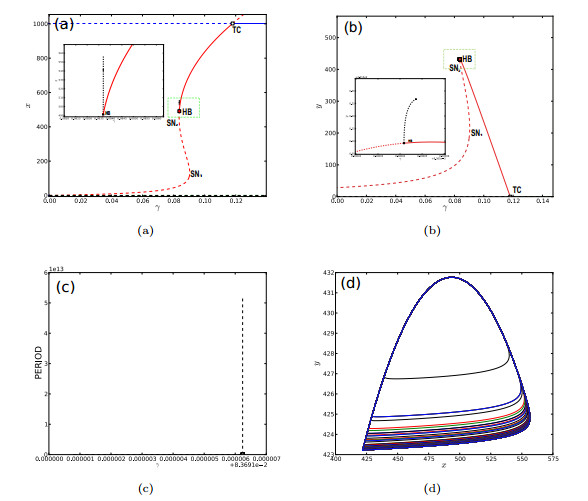
Figure 4.
Bifurcation diagrams of model (2.1).
$ HB $ $ TC $ $ LP $ $ m $ $ x $ $ m $ $ y $ $ m $ -
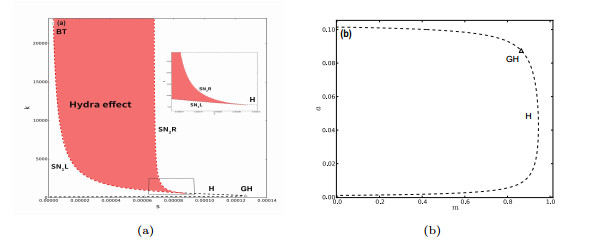
Figure 5.
Two-parameter bifurcation diagrams of model (2.1). (a) Bifurcation diagram in
$ s $ $ k $ $ m $ $ a $ $ SN_1L, $ $ SN_2R, $ $ H, $ $ BT $ $ GH $ -
Figure 6.
Bifurcation diagrams of model (2.1).
$ HB $ $ TC $ $ SN_i(i=1, 2) $ $ m $ $ x $ $ m $ $ y $ $ m $ -
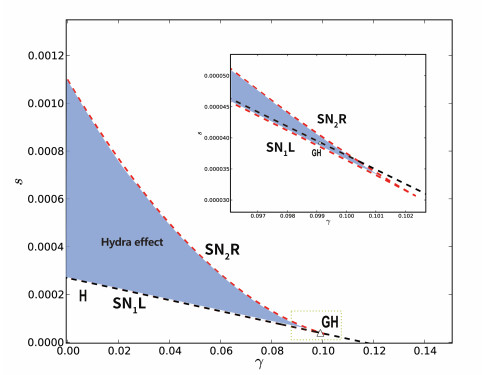
Figure 7.
Two-parameter bifurcation diagram with
$ s $ $ \gamma $ $ SN_1L, $ $ SN_2R, $ $ H $ $ GH $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: