| Citation: | Xiaoping Chen, Chengdai Huang, Jinde Cao, Xueying Shi, An Luo. HOPF BIFURCATION IN THE DELAYED FRACTIONAL LESLIE-GOWER MODEL WITH HOLLING TYPE II FUNCTIONAL RESPONSE[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2023, 13(5): 2555-2571. doi: 10.11948/20220451 |
HOPF BIFURCATION IN THE DELAYED FRACTIONAL LESLIE-GOWER MODEL WITH HOLLING TYPE II FUNCTIONAL RESPONSE
-
Abstract
In this paper the fractional-order Leslie-Gower model with Holling type II functional response and a single time delay is firstly considered. The stability interval and bifurcation points of developed model are derived via analytic extrapolation by regarding time delay as a bifurcation parameter. Besides, a delayed feedback control is successfully designed to put off the onset of Hopf bifurcation, extend the stability domain, and then the system possesses the stability in a larger parameter range. Some numerical simulations are shown in order to check the availability of the theoretical results.
-
Keywords:
- Stability /
- Hopf bifurcation /
- fractional order /
- Leslie-Gower model /
- time delay
-

-
References
[1] J. F. Andrews, A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1968, 10, 707–723. doi: 10.1002/bit.260100602 [2] M. A. Aziz-Alaoui and M. Daher Okiye, Boundedness and global stability for a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-Type Ⅱ schemes, Appl. Math. Lett., 2003, 16, 1069–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0893-9659(03)90096-6 [3] E. H. Abed and J. Fu, Local feedback stabilization and bifurcation control: Ⅱ. Stationary bifurcation, Syst. Control Lett., 1987, 8, 467–473. doi: 10.1016/0167-6911(87)90089-2 [4] J. Cao and R. Yuan, Bifurcation analysis in a modified Lesile-Gower model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response and delay, Nonlinear Dyn., 2016, 84, 1341–1352. doi: 10.1007/s11071-015-2572-5 [5] G. Chen, J.L. Moiola and H. Wang, Bifurcation control: theories, methods and applications, Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos, 2000, 10, 511–548. doi: 10.1142/S0218127400000360 [6] W. Deng, C. Li and J. Lü, Stability analysis of linear fractional differential system with multiple time delays, Nonlinear Dyn., 2007, 48, 409–416. doi: 10.1007/s11071-006-9094-0 [7] Y. Fan, X. Huang, Z. Wang and Y. Li, Improved quasi-synchronization criteria for delayed fractional-order memristor-based neural networks via linear feedback control, Neurocomputing, 2018, 306, 68–79. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.03.060 [8] Y. Fan, X. Huang, Z. Wang and Y. Li, Global dissipativity and quasi-synchronization of asynchronous updating fractional-order memristor-based neural networks via interval matrix method, J. Franklin Inst., 2018, 355, 5998–6025. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.05.058 [9] Y. Fan, X. Huang, Z. Wang and Y. Li, Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in a simplified memristor-based fractional-order neural network with discontinuous memductance function, Nonlinear Dynam., 2018, 93, 611–627. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4213-2 [10] X. Huang, Y. Fan, J. Jia, Z. Wang and Y. Li, Quasi-synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks with parameter mismatches, IET Control Theory Appl., 2017, 11, 2317–2327. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2017.0196 [11] C. Huang, J. Cao and M. Xiao, Hybrid control on bifurcation for a delayed fractional gene regulatory network, Chaos Solitons Fract., 2016, 87, 19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2016.02.036 [12] J. Jia, X. Huang, Y. Li, J. Cao and A. Alsaedi, Global stabilization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks with time delay, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2020, 31, 997–1009. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2915353 [13] A. Korobeinikov, A Lyapunov function for Leslie-Gower predator-prey models, Appl. Math. Lett., 2001, 14, 697–699. doi: 10.1016/S0893-9659(01)80029-X [14] P. H. Leslie, Some further notes on the use of matrices in population mathematics, Biometrika, 1948, 35, 213–245. doi: 10.1093/biomet/35.3-4.213 [15] P. H. Leslie, A stochastic model for studying the properties of certain biological systems by numerical methods, Biometrika, 1958, 45, 16–31. doi: 10.1093/biomet/45.1-2.16 [16] P. H. Leslie and J.C. Gower, The properties of a stochastic model for the predator-prey type of interaction between two species, Biometrika, 1960, 47, 219–234. doi: 10.1093/biomet/47.3-4.219 [17] Y. Li and D. Xiao, Bifurcations of a predator-prey system of Holling and Leslie types, Chaos Soliton. Fract., 2007, 34, 606–620. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2006.03.068 [18] A. F. Nindjin, et al., Analysis of a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-type Ⅱ schemes with time delay, Nonlinear Anal. RWA., 2006, 7, 1104–1118. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2005.10.003 [19] I. Petras, Fractional-order nonlinear systems: modeling, analysis and simulation, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2011. [20] F. Padula, S. Alcantara, R. Vilanova and A. Visioli, $H_{\infty}$ control of fractional linear systems, Automatica, 2013, 49, 2276–2280. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.04.012 CrossRef $H_{\infty}$ control of fractional linear systems" target="_blank">Google Scholar
[21] Y. Pan, H. Yu and M. Er, Adaptive neural pd control with semiglobal asymptotic stabilization guarantee, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst., 2014, 25, 2264–2274. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2308571 [22] Y. Pan, Y. Liu, B. Xu and H. Yu, Hybrid feedback feedforward: an efficient design of adaptive neural network control, Neural Networks, 2016, 76, 122–134. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2015.12.009 [23] Y. Pan and H. Yu, Composite learning from adaptive dynamic surface control, IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2016, 61, 2603–2609. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2495232 [24] Y. Song, S. Yuan and J. Zhang, Bifurcation analysis in the delayed Leslie-Gower predator-prey system, Appl. Math. Model., 2009, 33, 4049–4061. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2009.02.008 [25] M. Shi and Z. Wang, Stability and Hopf bifurcation control of a fractional-order small world network model, Sci. China Phys. Mech., 2013, 43, 467–477. [26] P. Sopasakis and H. Sarimveis, Stabilising model predictive control for discrete-time fractional-order systems, Automatica, 2017, 75, 24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.09.014 [27] R. Yafia, F. Adnani and H. Alaoui, Limit cycle and numerical simulations for small and large delays in a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-type Ⅱ schemes, Nonlinear Anal. RWA., 2008, 9, 2055–2067. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2006.12.017 [28] S. Yuan and Y. Song, Stability and Hopf bifurcations in a delayed Leslie-Gower predator-prey system, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2009, 355, 82–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2009.01.052 [29] P. Yu and G. Chen, Hopf bifurcation control using nonlinear feedback with polynomial functions, Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos, 2004, 14, 1683–1704. doi: 10.1142/S0218127404010291 [30] L. Zhang and Y. Yang, Finite time impulsive synchronization of fractional order memristive BAM neural networks, Neurocomputing, 2020, 384, 213–224. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.056 [31] L. Zhang and Y. Yang, Optimal quasi-synchronization of fractional-order memristive neural networks with PSOA, Neural Comput. Appl., 2020, 32, 9667–9682. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04488-z [32] A. A. Zamani, S. Tavakoli and S. Etedali, Fractional order PID control design for semi-active control of smart base-isolated structures: A multi-objective cuckoo search approach, ISA Trans., 2017, 67, 222–232. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2017.01.012 -
-
-
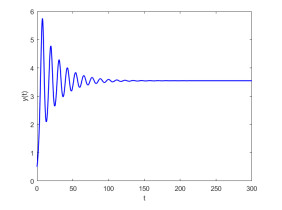
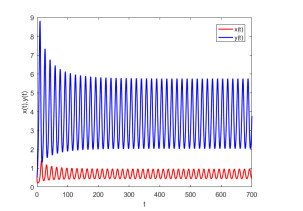
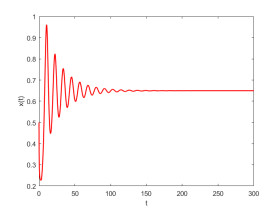
Figure 1.
The positive equilibrium point
$E^* $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=3<\tau_{0}=3.4387 $ -
Figure 2.
The positive equilibrium point
$ E^* $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=3<\tau_{0}=3.4387 $ -
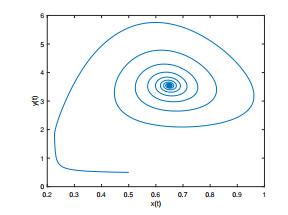
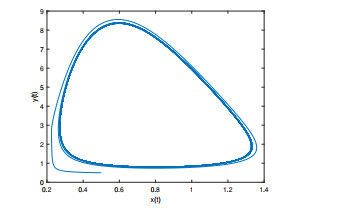
Figure 3.
The positive equilibrium point
$ E^* $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=3<\tau_{0}=3.4387 $ -
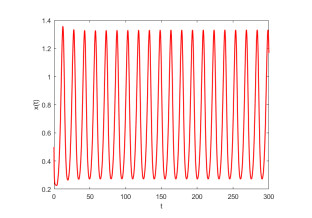
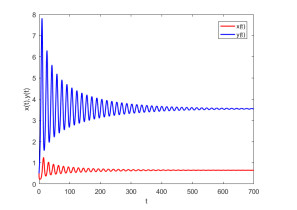
Figure 4.
The positive equilibrium point
$ E^* $ $ E^* $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=4>\tau_{0}=3.4387 $ -
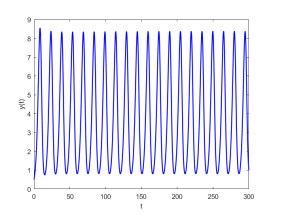
Figure 5.
The positive equilibrium point
$ E^* $ $ E^* $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=4>\tau_{0}=3.4387 $ -
Figure 6.
The positive equilibrium point
$ E^* $ $ E^* $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=4>\tau_{0}=3.4387 $ -
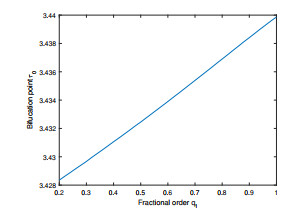
Figure 7.
Illustration of bifurcation point
$ \tau_0 $ $ q_1 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ -
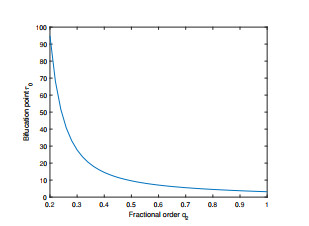
Figure 8.
Illustration of bifurcation point
$ \tau_0 $ $ q_2 $ $ q_1=0.92 $ -
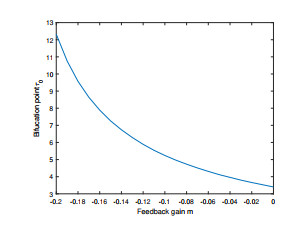
Figure 9.
Illustration of bifurcation point
$ \tau_0^* $ $ m $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ -
Figure 10.
The positive equilibrium point of controlled system (5.2) is unstable with initial value (0.5, 0.5),
$ m=-0.1 $ $ \tau=5.24 $ $ q_1=1 $ $ q_2=1 $ -
Figure 11.
Controlled system (5.2) converges to the positive equilibrium point with initial value (0.5, 0.5),
$ m=-0.1 $ $ \tau=5.24 $ $ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ -
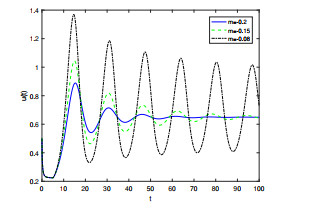
Figure 12.
The effect of bifurcation control for system (5.2) becomes better as feedback gain decreases with initial value (0.5, 0.5),
$ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=5.24 $ $ m=-0.2 $ $ m=-0.15 $ $ m=-0.08 $ -
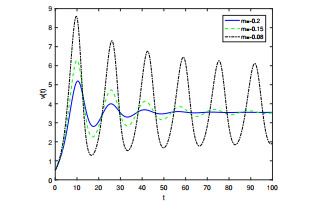
Figure 13.
The effect of bifurcation control for system (5.2) becomes better as feedback gain decreases with initial value (0.5, 0.5),
$ q_1=0.92 $ $ q_2=0.95 $ $ \tau=5.24 $ $ m=-0.2 $ $ m=-0.15 $ $ m=-0.08 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: