| Citation: | Ying Zhang, Ziqiong Chen, Pengzhan Huang. A FINITE ELEMENT ITERATIVE ALGORITHM OF THE STEADY-STATE FLUID-FLUID INTERACTION PROBLEM[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2024, 14(6): 3214-3226. doi: 10.11948/20230495 |
A FINITE ELEMENT ITERATIVE ALGORITHM OF THE STEADY-STATE FLUID-FLUID INTERACTION PROBLEM
-
Abstract
In this work, we propose a finite element iterative algorithm to solve the stationary fluid-fluid interaction model. First, we give the finite element discretization for the considered equations. Due that the finite element discretization system is nonlinear, then we design an iterative algorithm for solving the nonlinear equations, where error correction strategy is used to control iterative error at each iteration. Finally, some numerical tests are carried out to demonstrate theoretical results of the proposed algorithm.
-

-
References
[1] M. Aggul, A grad-div stabilized penalty projection algorithm for fluid-fluid interaction, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2022, 414, 126670. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2021.126670 [2] M. Aggul, J. M. Connors, D. Erkmen and A. E. Labovsky, A defect-deferred correction method for fluid-fluid interaction, SIAM J., 2018, 56(4), 2484–2512. [3] M. Aggul, F. G. Eroglu, S. Kaya and A. E. Labovsky, A projection based variational multiscale method for a fluid-fluid interaction problem, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 2020, 365, 112957. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.112957 [4] M. Aggul and S. Kaya, Defect-deferred correction method based on a subgrid artificial viscosity model for fluid-fluid interaction, Appl. Numer. Math., 2021, 160, 178–191. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2020.10.004 [5] C. Bernardi, T. C. Rebollo, R. Lewandowski and F. Murat, A model for two coupled turbulent fluids part Ⅱ: Numerical analysis of a spectral discretization, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 2003, 40(6), 2368–2394. [6] C. Bernardi, T. C. Rebollo, M. G. Mármol, R. Lewandowski and F. Murat, A model for two coupled turbulent fluids part Ⅲ: Numerical approximation by finite elements, Numer. Math., 2004, 98(1), 33–66. doi: 10.1007/s00211-003-0490-9 [7] D. Bresch and J. Koko, Operator-splitting and Lagrange multiplier domain decomposition methods for numerical simulation of two coupled Navier-Stokes fluids, Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci., 2006, 16(4), 419–429. [8] Z. Chen, Finite Element Methods and their Applications, Springer, New York, 2005. [9] J. M. Connors and J. S. Howell, A fluid-fluid interaction method using decoupled subproblems and differing time steps, Numer. Meth. Part. Differ. Equs., 2012, 28(4), 1283–1308. doi: 10.1002/num.20681 [10] J. M. Connors, J. S. Howell and W. J. Layton, Decoupled time stepping methods for fluid-fluid interaction, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 2012, 50(3), 1297–1319. doi: 10.1137/090773362 [11] Y. N. He and A. W. Wang, A simplified two-level method for the steady Navier-Stokes equations, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 2008, 197(17–18), 1568–1576. [12] P. Z. Huang, Y. N. He and X. L. Feng, Second order time-space iterative method for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations, Appl. Math. Lett., 2016, 59, 79–86. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2016.02.018 [13] P. Z. Huang, W. Q. Li and Z. Y. Si, Several iterative schemes for the stationary natural convection equations at different Rayleigh numbers, Numer. Meth. Part. Differ. Equs., 2015, 31(3), 761–776. doi: 10.1002/num.21915 [14] P. Z. Huang, T. Zhang and Z. Y. Si, A stabilized Oseen iterative finite element method for stationary conduction-convection equations, Math. Meth. Appl. Sci., 2012, 35(1), 103–118. doi: 10.1002/mma.1541 [15] S. Hussain, M. A. A. Mahbub and F. Shi, A stabilized finite element method for the Stokes-Stokes coupling interface problem, J. Math. Fluid Mech., 2022, 24(3), 63. doi: 10.1007/s00021-022-00694-3 [16] J. Koko, Uzawa conjugate gradient domain decomposition methods for coupled Stokes flows, J. Sci. Comput., 2006, 26(2), 195–216. doi: 10.1007/s10915-005-4933-6 [17] J. Li, P. Z. Huang, J. Su and Z. X. Chen, A linear, stabilized, non-spatial iterative, partitioned time stepping method for the nonlinear Navier-Stokes/Navier-Stokes interaction model, Bound. Value Probl., 2019, 2019(1), 1–19. doi: 10.1186/s13661-018-1115-7 [18] J. Li, P. Z. Huang, C. Zhang and G. H. Guo, A linear, decoupled fractional time-stepping method for the nonlinear fluid-fluid interaction, Numer. Methods Part. Differ. Equs., 2019, 35(5), 1873–1889. doi: 10.1002/num.22382 [19] W. Li and P. Z. Huang, A two-step decoupled finite element algorithm for a nonlinear fluid-fluid interaction problem, Univ. Politeh. Buchar. Sci. Bull. Ser. A Appl. Math. Phys., 2019, 81(4), 107–118. [20] W. Li and P. Z. Huang, A decoupled algorithm for fluid-fluid interaction at small viscosity, Filomat, 2023, 37(19), 6365–6372. doi: 10.2298/FIL2319365L [21] W. Li and P. Z. Huang, On a two-order temporal scheme for Navier-Stokes/Navier-Stokes equations, Appl. Numer. Math., 2023, 194, 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2023.08.004 [22] W. Li, P. Z. Huang, and Y. N. He, Grad-div stabilized finite element schemes for the fluid-fluid interaction model, Commun. Comput. Phys., 2021, 30(2), 536–566. doi: 10.4208/cicp.OA-2020-0123 [23] W. Li, P. Z. Huang and Y. N. He, An unconditionally energy stable finite element scheme for a nonlinear fluid-fluid interaction model, IMA J. Numer. Anal., 2024, 44(1), 157–191. doi: 10.1093/imanum/drac086 [24] W. Li, P. Z. Huang and Y. N. He, Second order unconditionally stable and convergent linearized scheme for a fluid-fluid interaction model, J. Comput. Math., 2023, 41(1), 72–93. [25] W. Y. Li and Y. X. Xu, Schwarz domain decomposition methods for the fluid-fluid system with friction-type interface conditions, Appl. Numer. Math., 2021, 166, 114–126. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2021.04.005 [26] J. L. Lions, R. Temam and S. Wang, Numerical analysis of the coupled atmosphere-ocean models (CAO Ⅱ), Comput. Mech. Adv., 1993, 1(1), 55–119. [27] L. Z. Qian, J. R. Chen and X. L. Feng, Local projection stabilized and characteristic decoupled scheme for the fluid-fluid interaction problems, Numer. Meth. Part. Differ. Equs., 2017, 33(3), 704–723. doi: 10.1002/num.22116 [28] L. Z. Qian, X. L. Feng and Y. N. He, Crank-Nicolson leap-frog time stepping decoupled scheme for the fluid-fluid iteraction problems, J. Sci. Comput., 2020, 84(1), 4. doi: 10.1007/s10915-020-01254-5 [29] T. C. Rebollo, S. D. Pino and D. Yakoubi, An iterative procedure to solve a coupled two-fluids turbulence model, ESAIM: Math. Model. Numer. Anal., 2010, 44(4), 693–713. doi: 10.1051/m2an/2010015 [30] R. Temam, Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1984. [31] K. Wang and Y. S. Wong, Error correction method for Navier-Stokes equations at high Reynolds numbers, J. Comput. Phys., 2013, 255, 245–265. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2013.07.042 [32] L. Wang, J. Li and P. Z. Huang, An efficient iterative algorithm for the natural convection equations based on finite element method, Int. J. Numer. Meth. Heat Fluid Flow, 2018, 28(3), 584–605. doi: 10.1108/HFF-03-2017-0101 [33] Y. H. Zhang, Y. R. Hou and L. Shan, Stability and convergence analysis of a decoupled algorithm for a fluid-fluid interaction problem, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 2016, 54(5), 2833–2867. doi: 10.1137/15M1047891 [34] Y. H. Zhang, Y. R. Hou and L. Shan, Error estimates of a decoupled algorithm for a fluid-fluid interaction problem, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2018, 333, 266–291. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2017.10.039 [35] Y. H. Zhang, L. Shan and Y. R. Hou, New approach to prove the stability of a decoupled algorithm for a fluid-fluid interaction problem, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2020, 371, 112695. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2019.112695 [36] Y. H. Zhang, H. B. Zheng, Y. R. Hou and L. Shan, Optimal error estimates of both coupled and two-grid decoupled methods for a mixed Stokes-Stokes model, Appl. Numer. Math., 2018, 133, 116–129. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2018.01.022 -
-
-
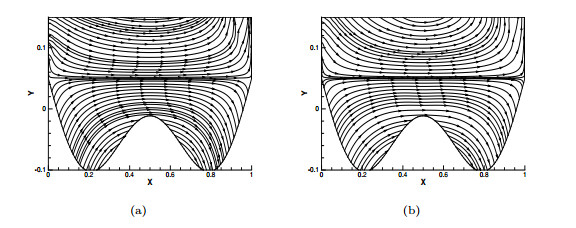
Figure 1.
The numerical velocity streamlines with
$ \nu_1=5.0E-4, \nu_2=5.0E-3, \kappa=2.45E-3 $ -
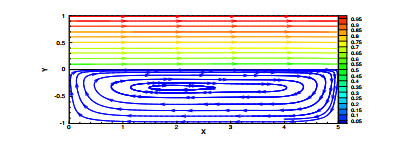
Figure 2.
Velocity streamlines: Exact solution(a), numerical solution(b).




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: