| Citation: | Yifan Xing, Hong-Xu Li. GLOBAL DYNAMICS OF A REACTION-DIFFUSION SEIVQR EPIDEMIC MODEL IN ALMOST PERIODIC ENVIRONMENTS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(2): 762-785. doi: 10.11948/20240121 |
GLOBAL DYNAMICS OF A REACTION-DIFFUSION SEIVQR EPIDEMIC MODEL IN ALMOST PERIODIC ENVIRONMENTS
-
Abstract
We have formulated an almost periodic reaction-diffusion SEIVQR epidemic model that incorporates quarantine, vaccination, and a latent period. In contrast to prior methods that analyze stability by using Lyapunov functions, we establish the global threshold dynamics of this model by using the upper Lyapunov exponent $\lambda^*$. Our results demonstrate that the disease-free almost periodic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable if $\lambda^*<0$, whereas the disease uniformly persists if $\lambda^*>0$. To further validate our conclusions, we conducted numerical simulations of the model.
-

-
References
[1] N. Alikakos, An application of the invariance principle to reaction-diffusion equations, J. Differ. Equ., 1979, 33(2), 201–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-0396(79)90088-3 [2] C. Angstmann, B. Henry and A. Mcgann, A fractional order recovery SIR model from a stochastic process, Bull. Math. Biol., 2016, 78(3), 468–499. doi: 10.1007/s11538-016-0151-7 [3] M. Baniyaghoub, R. Gautam, Z. Shuai, et al., Reproduction numbers for infections with free-living pathogens growing in the environment, Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc., 2012, 6(2), 923–940. [4] D. Bentaleb and S. Amine, Lyapunov function and global stability for a two-strain SEIR model with bilinear and non-monotone incidence, Int. J. Biomath., 2019, 12(2), 1950021. doi: 10.1142/S1793524519500219 [5] D. Bichara, Y. Kang, C. Castillo-Chavez, et al., SIS and SIR epidemic models under virtual dispersal, Bull. Math. Biol., 2015, 77, 2004–2034. doi: 10.1007/s11538-015-0113-5 [6] V. Borkar and D. Manjunath, Revisiting SIR in the age of COVID-19: Explicit solutions and control problems, SIAM J. Control Optim., 2022, 60(2), S370–S395. doi: 10.1137/20M1372913 [7] T. Caraco and I. N. Wang, Free-living pathogens: Life-history constraints and strain competition, J. Theoret. Biol., 2008, 250(3), 569–579. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.10.029 [8] K. Cooke and P. Van Den Driessche, Analysis of an seirs epidemic model with two delays, J. Math. Biol., 1996, 35(2), 240–260. doi: 10.1007/s002850050051 [9] H. El-Saka, The fractional-order SIS epidemic model with variable population size, Egyptian Math. Soc., 2014, 22(1), 50–54. doi: 10.1016/j.joems.2013.06.006 [10] A. Fink, Almost Periodic Differential Equations, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1974. [11] A. Friedman, Partial Differential Equations of Parabolic Type, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1964. [12] K. Fushimi, Y. Enatsu and E. Ishiwata, Global stability of an SIS epidemicmodel with delays, Math. Appl. Sci., 2018, 41, 5345–5354. [13] A. Gabbuti, L. Romanò, P. Blanc, et al., Long-term immunogenicity of hepatitis B vaccination in a cohort of italian healthy adolescents, Vaccine, 2007, 25(16), 3129–3132. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.01.045 [14] J. Hale, Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems, American Mathematical Society, Providence RI, 1988. [15] S. Han and C. Lei, Global stability of equilibria of a diffusive SEIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence, Appl. Math. Lett., 2019, 98, 114–120. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2019.05.045 [16] C. He, Almost Periodic Differential Equations, Higher Education Publishing House, Beijing, (Chinese), 1992. [17] H. Huo and L. Feng, Global stability of an epidemic model with incomplete treatment and vaccination, Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc., 2012, 2012, 87–88. [18] H. Huo, Q. Yang and H. Xiang, Dynamics of an edge-based SEIR model for sexually transmitted diseases, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2019, 17(1), 669–699. [19] H. Kang, Asymptotic behavior of the basic reproduction number in an age-structured SIS epidemic patch model, J. Math. Biol., 2023, 87(46). [20] W. Kermack and A. McKendrick, A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A., 1927, 115, 700–721. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1927.0118 [21] T. Kuniya and J. Wang, Global dynamics of an SIR epidemic model with nonlocal diffusion, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2018, 43, 262–282. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2018.03.001 [22] J. Li, Y. Yang and Y. Zhou, Global stability of an epidemic model with latent stage and vaccination, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2011, 12(4), 2163–2173. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2010.12.030 [23] X. Lin and Q. Wang, Threshold dynamics of a time-periodic nonlocal dispersal SIS epidemic model with neumann boundary conditions, J. Differ. Equ., 2023, 373, 108–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2023.07.008 [24] J. Liu, Z. Bai and T. Zhang, A periodic two-patch SIS model with time delay and transport-related infection, J. Theoret. Biol., 2018, 437, 36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.10.011 [25] P. Liu and H. Li, Global stability of autononmous and nonautonomous hepatitis B virus models in patchy environment, J. Appl. Anal. Appl. Comput., 2020, 10(5), 1771–1799. [26] S. Liu, L. Zhang and Y. Xing, Dynamics of a stochastic heroin epidemic model, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2019, 351, 260–269. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2018.11.005 [27] Z. Ma, Spatiotemporal dynamics of a diffusive Leslie-Gower prey-predator model with strong Allee affect, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2019, 50, 651–674. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2019.06.008 [28] P. Magal and X. Zhao, Global attractors and steady states for uniformly persistent dynamical systems, SIAM J. Math. Anal., 2005, 37(1), 251–275. doi: 10.1137/S0036141003439173 [29] R. Martin and H. Smith, Abstract functional differential equations and reaction-diffusion systems, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc, 1990, 321(1), 1–44. [30] O. Melikechi, A. Young, T. Tang, et al., Limits of epidemic prediction using SIR models, J. Math. Biol., 2022, 85(4), 36. doi: 10.1007/s00285-022-01804-5 [31] J. Metz and O. Diekmann, The Dynamics of Physiologically Structured Populations, Springer, New York, 1986. [32] L. Qiang, B. Wang and Z. Wang, A reaction-diffusion epidemic model with incubation period in almost periodic environments, Euro. J. Appl. Math., 2021, 32(6), 1153–1176. doi: 10.1017/S0956792520000303 [33] A. Ricardo, Analysis of a fractional SEIR model with treatment, Appl. Math. Lett., 2018, 84, 56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2018.04.015 [34] G. Sell, Topological Dynamics and Ordinary Differential Equations, Van Nostrand Reinhold, London, 1971. [35] Y. Takeguchi and K. Yagasaki, Optimal control of the seir epidemic model using a dynamical systems approach, Jpn. J. Ind. Appl. Math., 2024, 41(1), 297–316. doi: 10.1007/s13160-023-00605-7 [36] B. Wang, W. Li and Z. Wang, A reaction-diffusion sis epidemic model in an almost periodic environment, Z. Angew. Math. Phys., 2015, 66(6), 3085–3108. doi: 10.1007/s00033-015-0585-z [37] B. Wang and X. Zhao, Basic reproduction ratios for almost periodic compartmental epidemic models, J. Dyn. Differ. Equ., 2013, 25(2), 535–562. doi: 10.1007/s10884-013-9304-7 [38] J. Wu, Theory and Applications of Partial Functional Differential Equations, Springer, New York, 1996. [39] Y. Xing and H. Li, Almost periodic solutions for a SVIR epidemic model with relapse, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2021, 18(6), 7191–7217. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021356 [40] Y. Xing and H. Li, Pseudo almost periodic solutions and global exponential stability of a generalized population model with delays and harvesting term, Comput. Appl. Math., 2022, 41(8), 350. doi: 10.1007/s40314-022-02049-0 [41] K. Yagasaki, Nonintegrability of the seir epidemic model, Phys. D., 2023, 453, 133820. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2023.133820 [42] N. Yoshida, Existence of exact solution of the Susceptible-Exposed-Infectious-Recovered (SEIR) epidemic model, J. Differ. Equ., 2023, 355, 103–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2023.01.017 [43] L. Zhang, S. Liu and X. Zhang, Asymptotic behavior of a stochastic virus dynamics model with intracellular delay and humoral immunity, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2019, 9(4), 1425–1442. [44] L. Zhang, Z. Wang and X. Zhao, Threshold dynamics of a time periodic reaction-diffusion epidemic model with latent period, J. Differ. Equ., 2015, 258(9), 3011–3036. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.12.032 [45] L. Zhang and Y. Xing, Extremal solutions for nonlinear first-order impulsive integro-differential dynamic equations, Math. Notes., 2019, 105, 124–132. [46] X. Zhang, Q. Shi, S. Ma, et al., Dynamic behavior of a stochastic SIQS epidemic model with levy jumps, Nonlinear Dyn., 2018, 93, 1481–1493. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4272-4 [47] X. Zhao, Dynamical Systems in Population Biology, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2017. [48] F. Zheng and H. Li, Pseudo almost automorphic mild solutions to non-autonomous differential equations in the "strong topology", Banach J. Math. Anal., 2022, 16(1), 1–32. doi: 10.1007/s43037-021-00152-8 [49] C. Zhu, J. Zhu and X. Liu, Influence of spatial heterogeneous environment on long-term dynamics of a reaction-diffusion SVIR epidemic model with relapse, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2019, 16(5), 5897–5922. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019295 -
-
-
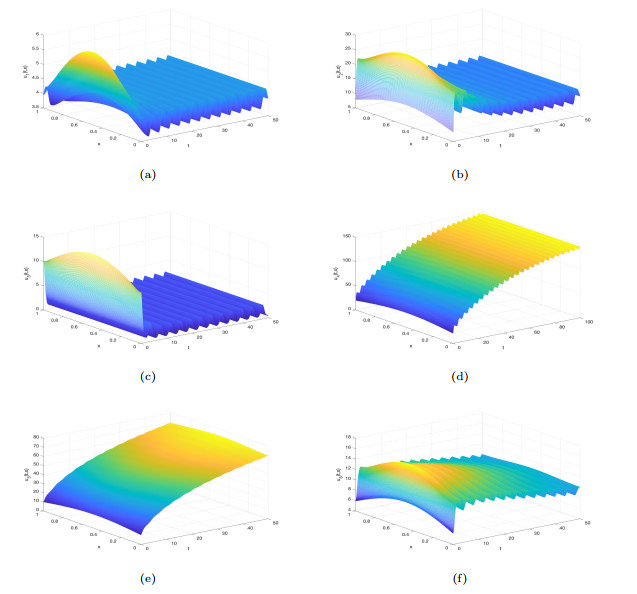
Figure 1.
Almost periodic solution curves for the model (2.6) with initial values as
$ u^1(0, x) $ $ \lambda^*<0 $ -
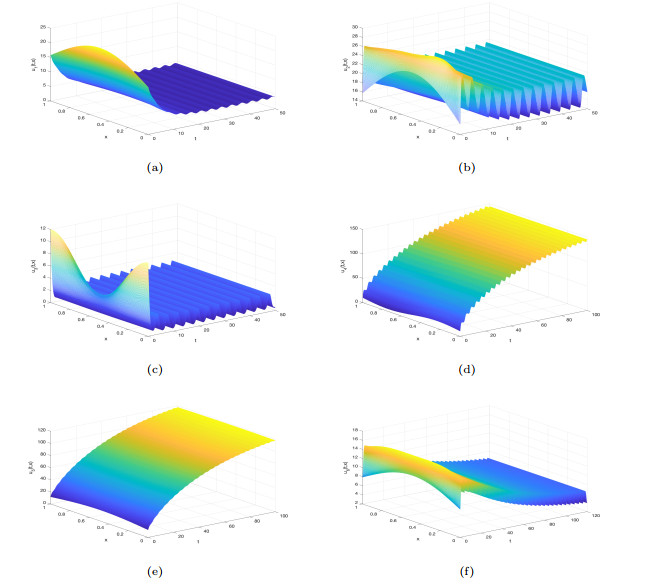
Figure 2.
Almost periodic solution curves for the model (2.6) with initial values as
$ u^1(0, x) $ $ \lambda^*>0 $ -
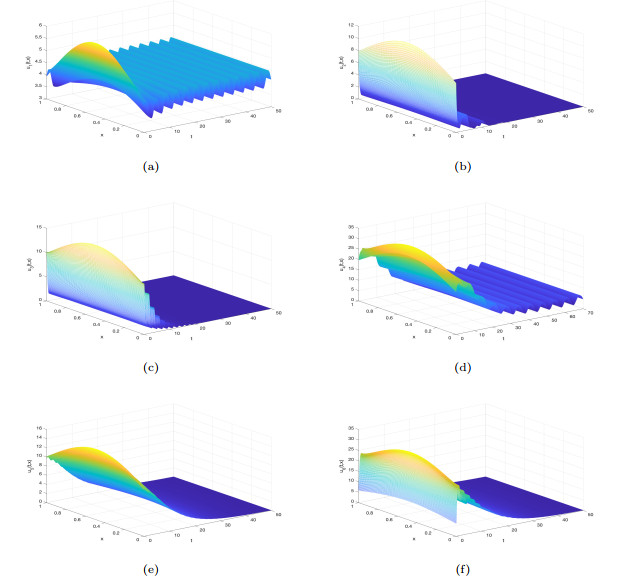
Figure 3.
Almost periodic solution curves for the model (2.6) with initial values as
$ u^2(0, x) $ $ \lambda^*>0 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: