| Citation: | Hong-Yu Li, Xin-Hui Shao. ON WEIGHTED AVERAGE FAST BLOCK KACZMARZ METHODS FOR SOLVING LARGE CONSISTENT LINEAR SYSTEMS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(2): 915-933. doi: 10.11948/20240208 |
ON WEIGHTED AVERAGE FAST BLOCK KACZMARZ METHODS FOR SOLVING LARGE CONSISTENT LINEAR SYSTEMS
-
Abstract
To solve large consistent linear systems, a weighted average fast block Kaczmarz (WAFBK) method is proposed, which is based on the ideas of greedy distance and weighted average. This method does not require the calculation of pseudoinverse of submatrices. Furthermore, we provide a detailed analysis of the convergence properties of various methods, corresponding to four different weights used in the selection probability criterion. And it has been proven that WAFBK-type methods converge to the unique least-norm solutions of linear systems. Numerical results confirm the effectiveness of the WAFBK-type methods and demonstrate their ability to accelerate the convergence rate of the fast deterministic block Kaczmarz method.
-
Keywords:
- Block Kaczmarz method /
- greedy distance /
- weighted average /
- consistent systems
-

-
References
[1] Z. Bai and L. Wang, On convergence rates of Kaczmarz-type methods with different selection rules of working rows, Appl. Numer. Math., 2023, 186, 289-319. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2023.01.013 [2] Z. Bai and W. Wu, On greedy randomized Kaczmarz method for solving large sparse linear systems, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 2018, 40(1), A592-A606. doi: 10.1137/17M1137747 [3] Z. Bai and W. Wu, On relaxed greedy randomized Kaczmarz methods for solving large sparse linear systems, Appl. Math. Lett., 2018, 83, 21-26. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2018.03.008 [4] Z. Bai and W. Wu, On greedy randomized augmented Kaczmarz method for solving large sparse inconsistent linear systems, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 2021, 43(6), A3892-A3911. doi: 10.1137/20M1352235 [5] J. Chen and Z. Huang, On a fast deterministic block Kaczmarz method for solving large-scale linear systems, Numer. Algorithms, 2022, 89(3), 1007-1029. doi: 10.1007/s11075-021-01143-4 [6] T. A. Davis and Y. Hu, The university of Florida sparse matrix collection, ACM Trans. Math. Softw., 2011, 38(1), 1-25. [7] K. Du, W. Si and X. Sun, Randomized extended average block Kaczmarz for solving least squares, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 2020, 42(6), A3541-A3559. doi: 10.1137/20M1312629 [8] J. M. Elble, N. V. Sahinidis and P. Vouzis, GPU computing with Kaczmarz’s and other iterative algorithms for linear systems, Parallel Comput., 2010, 36(5), 215-231. [9] T. Elfving, Block-iterative methods for consistent and inconsistent linear equations, Numer. Math., 1980, 35(1), 1-12. doi: 10.1007/BF01396365 [10] R. M. Gower and P. Richtárik, Randomized iterative methods for linear systems, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 2015, 36(4), 1660-1690. doi: 10.1137/15M1025487 [11] G. T. Herman and R. Davidi, Image reconstruction from a small number of projections, Inverse Probl., 2008, 24(4), 045011. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/24/4/045011 [12] S. Kaczmarz, Angenäherte Auflösung von systemen linearer Gleichungen, Bull. Int. Acad. Pol. Sci. Lett. A, 1937, 35, 355-357. [13] S. Lee and H. J. Kim, Noise properties of reconstructed images in a kilo-voltage on-board imaging system with iterative reconstruction techniques: A phantom study, Phys. Med., 2014, 30(3), 365-373. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2013.11.003 [14] F. Natterer, The Mathematics of Computerized Tomography, SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, 2001. [15] I. Necoara, Faster randomized block Kaczmarz algorithms, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 2019, 40(4), 1425-1452. doi: 10.1137/19M1251643 [16] D. Needell and J. A. Tropp, Paved with good intentions: Analysis of a randomized block Kaczmarz method, Linear Algebra Appl., 2014, 441, 199-221. doi: 10.1016/j.laa.2012.12.022 [17] D. Needell, R. Zhao and A. Zouzias, Randomized block Kaczmarz method with projection for solving least squares, Linear Algebra Appl., 2015, 484, 322-343. doi: 10.1016/j.laa.2015.06.027 [18] Y. Niu and B. Zheng, A greedy block Kaczmarz algorithm for solving large-scale linear systems, Appl. Math. Lett., 2020, 104, 106294. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2020.106294 [19] F. Pasqualetti, R. Carli and F. Bullo, Distributed estimation via iterative projections with application to power network monitoring, Automatica J. IFAC, 2012, 48(5), 747-758. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.02.025 [20] C. Popa and R. Zdunek, Kaczmarz extended algorithm for tomographic image reconstruction from limited data, Math. Comput. Simulation, 2004, 65(6), 579-598. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2004.01.021 [21] T. Strohmer and R. Vershynin, A randomized Kaczmarz algorithm with exponential convergence, J. Fourier Anal. Appl., 2009, 15(2), 262-278. doi: 10.1007/s00041-008-9030-4 [22] L. Tondji and D. A. Lorenz, Faster randomized block sparse Kaczmarz by averaging, Numer. Algorithms, 2023, 93(4), 1417-1451. doi: 10.1007/s11075-022-01473-x [23] Q. Wang, W. Li and W. Bao, Nonlinear Kaczmarz algorithms and their convergence, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 2022, 399, 113720. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2021.113720 [24] A. Xiao, J. Yin and N. Zheng, On fast greedy block Kaczmarz methods for solving large consistent linear systems, Comput. Appl. Math., 2023, 42(3), 119. doi: 10.1007/s40314-023-02232-x [25] J. Zhang, A new greedy Kaczmarz algorithm for the solution of very large linear systems, Appl. Math. Lett., 2019, 91, 207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2018.12.022 [26] A. Zouzias and N. M. Freris, Randomized extended Kaczmarz for solving least squares, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 2013, 34(2), 773-793. doi: 10.1137/120889897 -
-
-
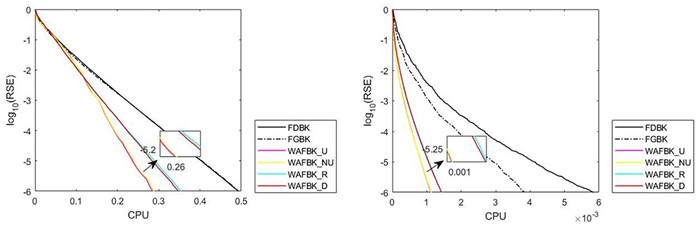
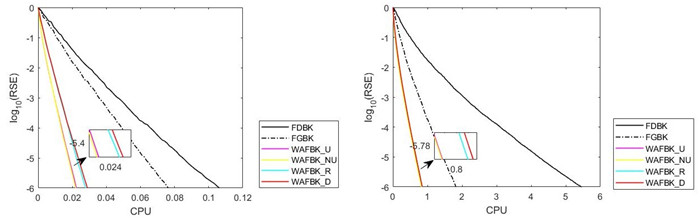
Figure 1.
Pictures of six methods for random matrices with
$ m=500,n=3000 $ $ m=3000,n=10000 $ $ {{\log }_{10}}(\text{RSE}) $ -
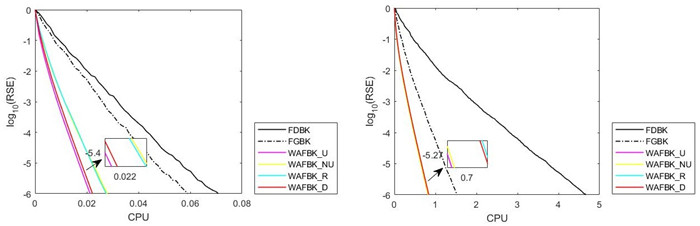
Figure 2.
Pictures of six methods for sparse matrices with bibd_17_8 (left) and lp_grow15 (right):
$ {{\log }_{10}}(\text{RSE}) $ -
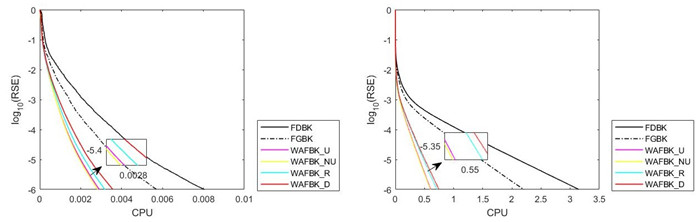
Figure 3.
Pictures of six methods for random matrices with
$ m=3000,n=500 $ $ m=10000,n=3000 $ $ {{\log }_{10}}(\text{RSE}) $ -
Figure 4.
Pictures of six methods for sparse matrices with flower_5_1 (left) and well1850 (right):
$ {{\log }_{10}}(\text{RSE}) $ -
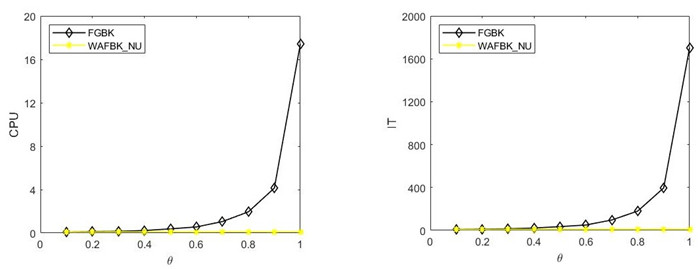
Figure 5.
CPU (left) and IT (right) versus
$ \theta $ $ 10000\times 1000 $ -
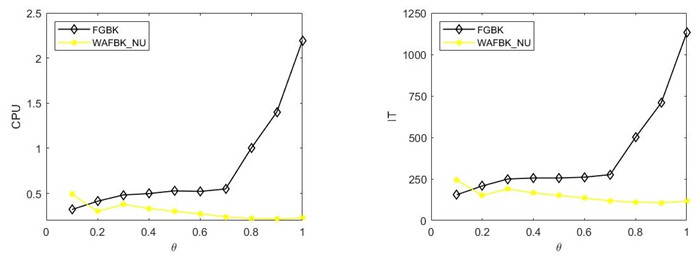
Figure 6.
CPU (left) and IT (right) versus
$ \theta $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: